Background and overview[1]
2,4-Dichloroaniline is an important drug and dye intermediate. It is a white needle-shaped crystal that can be dissolved in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether as well as acids. It is slightly soluble in water and easily soluble in the air. Oxidative discoloration, its melting point is 59~63℃, and its boiling point is 242℃.
Due to process route restrictions and environmental pressure, the domestic production of 2,4-dichloroaniline industrial products is very small and cannot meet domestic demand, and most of them rely on imports. The synthesis routes of 2.4-dichloroaniline reported in the literature mainly include the following two categories: 1) Acetanilide method: using acetanilide as raw material, 2,4-dichloroaniline is obtained through chlorination and hydrolysis. The traditional method of preparing 2,4-dichloroaniline using nitrobenzene as raw material requires four steps of reduction, acylation, chlorination and deacylation. In addition to monochlorine and polychlorine by-products, there are also positional isomers of 2,4-dichloroaniline in the products of this process, which is relatively difficult to separate and affects product quality. At the same time, this process uses chlorine gas as the chlorinating agent. Considering the atomic utilization rate, the usage rate of chlorine is low (half of the chlorine is not utilized and generates hydrogen chloride). In addition, the reaction system in which chlorine is used as a chlorinating agent is a heterogeneous system. A large excess of chlorine is required to achieve a certain conversion rate during the reaction, thereby increasing the consumption of raw materials and the post-processing load. Regarding the chlorination step, most literature uses traditional kettle reaction chlorination, the reaction temperature is difficult to control, the product purity is low, and polychlorine substitution products are easily generated. 2) p-chloronitrobenzene method: using p-chloronitrobenzene as raw material, 2,4-dichloroaniline is obtained through hydrogenation and reduction in one step.
Apply[2-3]
2,4-Dichloroaniline is an important drug and dye intermediate. Examples of its applications are as follows:
1) Preparation of 3,5-dichloroaniline, which includes the following steps: (1) Dissolve 2,4-dichloroaniline in hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid to form 2,4-dichloroaniline hydrochloride or sulfuric acid salt, add bromine dropwise while stirring at room temperature to obtain the hydrochloride or sulfate of 2-bromo-4,6-dichloroaniline; (2) add the 2-bromo-4,6-dichloroaniline to the 2-bromo-4,6-dichloroaniline obtained in step (1) Add ethanol or isopropyl alcohol to the reaction solution of dichloroaniline hydrochloride or sulfate, cool to about 0°C, add sodium nitrite aqueous solution dropwise, continue stirring for 30 to 50 minutes after dripping, slowly heat up to boiling, and steam out 3,5-Dichlorobromobenzene is ready for use; (3) Add ammonia water and catalyst to the 3,5-dichlorobromobenzene obtained in step (2), and react at 130~180°C for 3~6 hours to obtain 3,5-dichlorobromobenzene. Chloroaniline. The method of the invention has the advantages of easily available raw materials, simple reaction, mild conditions, and high yield.
2) Preparation of 2,4-dichlorophenylhydrazine. This method uses 2,4-dichloroaniline, acetonazine and water as raw materials, and reacts at a certain temperature to prepare 2,4-dichlorophenylhydrazine. . During the reaction process, excess acetonazine and water are added to complete the reaction of 2,4-dichloroaniline in the reaction system. After the reaction is completed, water and acetonazine are removed by distillation under reduced pressure, and the solid material is obtained after washing and drying. 2,4-Dichlorophenylhydrazine. Compared with the traditional diazotization reaction process for preparing 2,4-dichlorophenylhydrazine, the method of the present invention has fewer reaction steps, simple process, low requirements on equipment, easy reaction control, high yield, low production cost and no waste. It has low material emissions and is a green and environmentally friendly production process.
Preparation[4]
The method for synthesizing 2,4-dichloroaniline includes the following steps. The following concentrations are all mass concentrations:
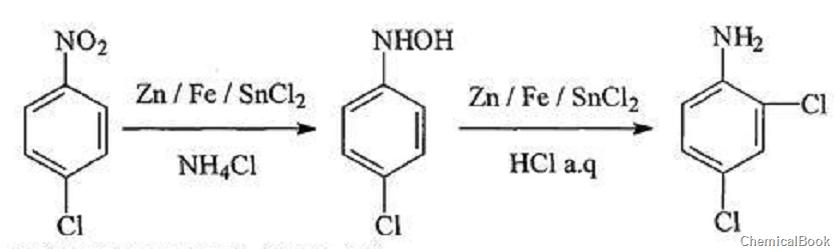
1) Add a methanol or ethanol solution of p-chloronitrobenzene with a concentration of 25 to 35% and an aqueous ammonium chloride solution with a concentration of 5 to 10% into the reactor. The weight ratio of p-chloronitrobenzene to ammonium chloride is 10:1, heat and stir under nitrogen protection. When the temperature reaches 75-80°C, add the reducing agent. The weight ratio of p-chloronitrobenzene to the reducing agent is 1:1~3. Control the adding speed of the reducing agent to maintain the reaction temperature. Maintain at 75-80°C. After the reducing agent is added, the reaction solution refluxes until it is colorless and transparent;
2) Stir and cool under nitrogen protection. When the temperature is lower than 60°C, slowly add concentrated hydrochloric acid, and keep the reaction temperature at 55-60°C during the addition of concentrated hydrochloric acid. The weight ratio of p-chloronitrobenzene to concentrated hydrochloric acid The ratio is 1:15~20. After adding concentrated hydrochloric acid, react at 60°C for 1~3 hours;
3) The above reaction solutionCool to room temperature, filter and discard the filter residue, adjust the pH value of the filtrate in an ice bath until solid precipitates, and the solid obtained is recrystallized in an alcohol aqueous solution with a concentration of 40 to 60% to obtain white needle-shaped crystals of 2,4-dichloroaniline. The above alcohol aqueous solution is an aqueous solution of ethanol or methanol.
Main reference materials
[1] CN110590564A-Method for synthesizing 2,4-dichloroaniline by continuous chlorination
[2] CN201310046616.83, preparation method of 5-dichloroaniline
[3] CN201710375740.7 A preparation method of 2,4-dichlorophenylhydrazine
[4] CN200810161608.7 A method of synthesizing 2,4-dichloroaniline

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

