Background[1]
Chloroanilines containing substituents, such as monosubstituted 4-chloro-2-methylaniline, are widely used in medicine and pesticides. Since experiments on the para-position chlorination of substituted phenolic hydroxyl groups with copper chloride were carried out in the early 1970s, no one has systematically studied the chlorination of substituted anilines. However, the preparation of substituent-containing chloroanilines has always been relatively cumbersome in the industry. It is generally prepared by first protecting the amino group, then chlorination, separation, and finally deprotection; there are also methods by attaching amino groups or other functional groups to other substrates, but the preparation cost is high, the pollution is large, and the synthesis steps are long.
Preparation[1]
Preparation of 4-chloro-2-methylaniline:
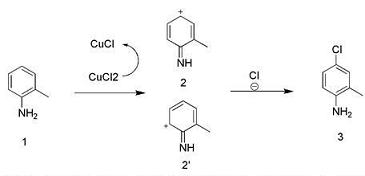
Dissolve 1.07 g (10 mmol) of 2-methylaniline in 20 ml of 36% hydrochloric acid solution, add 2.68 g (20 mmol) of CuCl2, and raise the reaction temperature to 60°C. Start to introduce oxygen and hydrogen chloride gas (oxygen is 0.02 mol/h mol/h, hydrogen chloride gas is 0.01 mol/h). After 6 hours of reaction, spotting showed that the spots on the raw material disappeared. After the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, 30 ml of ethyl acetate was added with stirring, the pH was adjusted to 7 with saturated sodium carbonate, and the mixture was extracted. The organic phase was washed twice with saturated brine and dried.
The crude reaction solution was analyzed by GC-MS. (The results showed that: the molecular weight of 107 at the retention time of 6.11 minutes was the raw material, and the relative peak area was 10%; the molecular weight of 141 at the retention time of 6.78 minutes was the monochlorinated product. The relative peak area is 5.8%; the product with a molecular weight of 141 at 7.25 minutes is another chlorinated product, with a relative peak area of 82%; the product with a molecular weight of 176 at 8.36 minutes is a dichlorinated product, with a relative peak area of 1.6%.). Further recover 5 ml of the solvent, add 2 ml of petroleum ether, cool, and precipitate a white crystalline solid, which is filtered to obtain 1.06 g of 4-chloro-2-methylaniline with a yield of 75% and a purity of 96% (HPLC).
Main reference materials
[1] CN201110272190.9 Preparation method of monosubstituted para-chloroaniline

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

