Background and overview[1][2]
Rimonabant is a new type of weight-loss drug. 2-Bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone is the key intermediate for the synthesis of rimonabant. Currently, there are very few reports on the synthesis of this intermediate abroad. There are no domestic reports. The existing synthesis method of 2-bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone is to use glacial acetic acid as the solvent, and react p-chloropropiophenone with liquid bromine at room temperature. The purity of the product is low, and it contains a large amount of difficult-to-separate by-products.
Physical and chemical properties and structure[1]
The molecular formula of 2-bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone: C9H8ClOBr, molecular weight: 247.5. Appearance: colorless crystalline solid, melting point: 76-77°C. According to the structure of 2-bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone, the synthesis method was improved and a synthetic process route for 2-bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone was designed. This method uses metal halide as the catalyst. The catalyst Liquid bromine and p-chloropropiophenone are used as raw materials to synthesize 2-bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone. It has good catalytic activity. This method has fast reaction speed, short reaction time, high reaction selectivity, and relatively high product yield and purity. high.
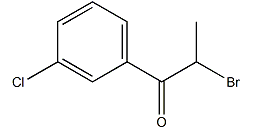
2-Bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone
Preparation[2]
Into a reactor equipped with a reflux condenser and a dropping funnel, add 48.0g (2.0mol) of magnesium powder and 400mL of tetrahydrofuran (THF) solution. Slowly add 218.0g (2.0mol) of ethyl bromide from the dropping funnel. Control the temperature of the reaction solution to 50-60°C to keep the solution in a slightly boiling state. After the dropwise addition is completed, heat and reflux for 1.0-1.5 hours to ensure that the magnesium reaction is complete and the Grignard reagent is obtained. Under stirring, slowly add 275.2g (2.0mol) of m-chlorobenzonitrile into the Grignard reagent prepared above. After the dropwise addition, react for 3.0-4.0h to generate an intermediate. The reaction is completed and no separation is required. Slowly add 3 mol/L hydrochloric acid to hydrolyze the intermediate, separate the inorganic phase, distill the organic phase under normal pressure to remove THF, and distill under reduced pressure to obtain 3-chloropropiophenone.
In a four-neck reaction bottle equipped with an electric stirrer, reflux condenser and thermometer, add 33.7g of 3-chloropropiophenone, 16.8g of liquid bromine, 50.0g of solvent, and 0.75g of catalyst in sequence. Put the reflux condenser tube and thermometer on, start the stirrer, and when the temperature is controlled to 15°C, start timing, and the reaction time is 2.5 hours. After the reaction is completed, the solvent is distilled off, the remaining solution is washed with water, and a refined solvent is added to dissolve, then cooled, crystallized, and filtered to obtain the refined 2-bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone product, and 2-bromo-3′-chloropropiophenone is collected. The rate reaches 97.13% and the melting point is 76-77℃.
Main reference materials
[1] Xiao Xinrong, Liu Chuanxiang, Gao Zhiping, Zhu Liangyong, & Chen Menghui. (2007). Synthesis of 3-methyl-5-phenyl-2-arylmorpholine hydrochloride and its anti-experimental depression activity. Applied Chemistry, 024(006), 648-651.
[2] Zhang Jing, Chen Shengzong, Wu Can, & Shi Bianfang. (2002). Research on the synthesis of 3-chloro-2′-bromopropiophenone. Chemical Reagents (06), 41-42.
[3] Ai Xi, Xiao Xinrong, Chen Ke, Cao Gao, & Guo Xiaohua. (2004). Synthesis of 2-aryl-2-morpholinol. Organic Chemistry, 24(8), 902-905.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

