Background and overview[1][2]
P-Trifluoromethylthioaniline is a compound useful as an intermediate for the production of pesticides such as insecticides and acaricides.
P-Trifluoromethylthioaniline can be produced by reacting 4-aminothiophenol and trifluoroiodomethane while subjecting them to UV irradiation in the presence of ammonia. However, the manufacturing method using a UV irradiation device requires complicated manufacturing equipment, and therefore it is not necessarily a method that is advantageous in terms of industrial production. In addition, trifluoroiodomethane has a very low boiling point (-22.5°C), so complex manufacturing equipment is required to ensure safety.
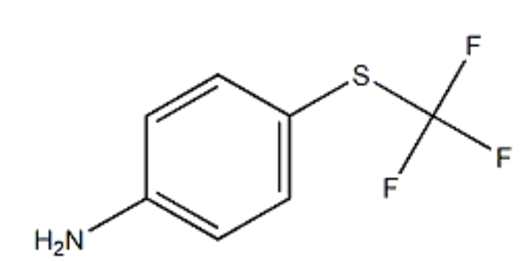
p-Trifluoromethylthioaniline
Apply[3]
Preparation of p-trifluoromethylthiobenzene bromide:
Add trifluoromethylthioaniline, hydrobromic acid and water into the container, add sodium nitrite aqueous solution dropwise; add hydrobromic acid and copper powder into another container to form a copper salt solution, and then add the copper salt solution Add to the previous container, and extract p-trifluoromethylthiobromobenzene after reaction.
Preparation[2]
A. Preparation of p-methylthionitrobenzene
In a 250ml three-neck flask equipped with a reflux condenser, a thermometer and a magnetic stirring device, add p-bromonitrobenzene (20.2g, 0.1mol), acetonitrile (150ml) and sodium methylmercaptide (8.4g, 0.12mol ) stir to dissolve, then raise the temperature to reflux, keep stirring the reaction at reflux until TLC shows that the raw materials disappear, about 14 hours. After the reaction is completed, most of the acetonitrile (about 120ml) is recovered by distillation, and then naturally cooled to room temperature, and the remaining liquid is poured into water ( 200 ml), a solid precipitated, collected the solid by filtration, washed with water and dried to obtain p-methylthionitrobenzene (15.1g), with a yield of 89.3% and a melting point of 71-73°C.
B. Preparation of p-trichloromethylthionitrobenzene
In a 500ml three-neck flask equipped with a reflux condenser, a thermometer and a magnetic stirring device, add p-methylthionitrobenzene (16.9g, 0.1mol), carbon tetrachloride (240ml) and the catalyst azobisiso Butyronitrile (0.2g), stir evenly and then heat it up to 60°C, then introduce chlorine gas (the introduction rate should not be too fast, so that the chlorine gas does not overflow), react for about 10 hours, GC shows that the raw materials disappear, the reaction is over, the reaction is over After distillation, most of the carbon tetrachloride (about 220ml) is recovered, and then naturally cooled to room temperature. The residual liquid is poured into water (300ml) to separate out the solid. The solid is collected by filtration, washed with water and dried to obtain p-trichloromethylthionitro. Benzene (22.7g), yield 83.3%, melting point 90-92°C.
C. Preparation of p-trifluoromethylthionitrobenzene
In a 1L high-pressure reaction kettle, add p-trichloromethylthionitrobenzene (54.6g, 0.2mol) and 1,2-dichloroethane (500ml), stir evenly and then add anhydrous hydrogen fluoride ( About 30g), then heated to 80°C, stirred for about 6 hours, GC showed that the raw materials disappeared, the reaction was over, after the reaction, most of the 1,2-dichloroethane (about 420ml) was recovered by distillation, and then distilled under reduced pressure and collected 11 For the fraction at 125°C/2660Pa, p-trifluoromethylthionitrobenzene (37.4g) was obtained, with a yield of 83.9%.
D. Preparation of p-trifluoromethylthioaniline
In a 1L high-pressure reaction kettle, add p-trifluoromethylthionitrobenzene (44.6g, 0.2mol), methanol (450ml) and Raney nickel (5g), stir evenly, add hydrogen, and heat to 60°C, keep the pressure in the kettle at about 4MPa until hydrogen is no longer absorbed, and react for about 6 hours. After the reaction is completed, cool to room temperature naturally, filter to remove the catalyst, remove the solvent under reduced pressure, and distill the residual liquid under reduced pressure to collect 101- The 105°C/8mmHg fraction is p-trifluoromethylthioaniline (35.3g), with a yield of 91.5%. 1H NMR (CDCl3, 500MHz) δ: 3.93 (2H, s), 6.33-6.48 (2H, m), 6.93-7.08 (2H, m). m/z: 193.290(M+H)+.
Main reference materials
[1] Ling Qingyun, & Jiang Zhongliang. A method for preparing 4-trifluoromethylthioaniline.
[2] Xu Jiabin, Chen Pinhong, Ye Jinxing, & Liu Guosheng. (2015). Palladium-catalyzed trifluoromethylthiolation of aryl c—h bonds. Acta Chemica Sinica, 73(12), 1294-1297.
[3] Lv Changwu, Gu Zhifeng, Liu Yi, Gao Liang, & Liu Jinbiao. (2017). Metal-free catalytic trifluoromethylthiolation reaction of sodium arylsulfinates. Synthetic Chemistry (10).

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

