Background and overview[1]
The benzoic acid compound 4-methylthiobenzoic acid is widely used in chemical industries such as food, medicine, and dyes. It is also an important type of organic synthesis intermediate. At present, there have been a large number of literature reports on the synthesis methods of benzoic acid, including: toluene liquid phase oxidation method, benzonitrile hydrolysis method, toluene chloride hydrolysis method, phthalic anhydride hydrolysis method, alcohol oxidation method, etc. Toluene liquid phase oxidation is currently the most important method for producing benzoic acid. It is usually produced by air oxidation of toluene using catalysts such as cobalt and manganese. However, this type of reaction has a low single conversion rate and requires multiple cycles of oxidation reactions, and the reaction time is Limited functional group tolerance. Toluene chlorination hydrolysis, benzonitrile, and phthalic anhydride hydrolysis require the use of inorganic alkali dehydrogenation. After the reaction is completed, acid neutralization produces a large amount of industrial salts. In addition, these methods usually have the disadvantage of limited tolerance of functional groups, so many benzoic acids containing sensitive functional groups (such as thiol groups, cyano groups, ester groups, etc.) cannot be distinguished by the above methods.
Preparation[1]
Preparation of 4-methylthiobenzoic acid:
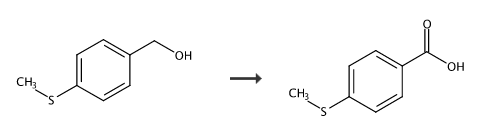
In a 10mL round-bottomed flask, add 0.77g of 4-methylthiobenzyl alcohol and 2g of diethylene glycol dimethyl ether in sequence. The resulting mixed solution is exposed to 40KHz/30W/70°C ultrasonic radiation in an ultrasonic reaction device. 30 minutes. Diethylene glycol dimethyl ether was removed under reduced pressure and recrystallized to obtain 0.79g of 4-methylthiobenzoic acid, with a yield of 95%. Directly using 4-methylthiobenzyl alcohol as the starting material, cheap green and safe air as the oxidant, and cheap diethylene glycol dimethyl ether as the accelerator, the benzoic acid compounds are synthesized under solvent-free conditions. environmentally friendly method.
References
[1]CN201810308573.9 A method for synthesizing benzoic acid compounds by ultrasonic-assisted oxidation of benzyl alcohol compounds

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

