Background and overview[1][2]
2-Amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid is used to make M-type reactive dyes and acid dyes, such as acid yellow 99#, red 184#, brown 145#, acid medium orange 4#, 29 #, green 26#, brown 19#, 21# and other dye intermediates. Its production wastewater contains a rich variety of organic species and high COD content, making wastewater treatment difficult. Compared with non-sulfonic acid type (K-type) and asymmetric type (S-type) metal complex dyes containing one sulfonic acid group, 1:2 (M-type) metal complex dyes containing two sulfonic acid groups , it has excellent water solubility, good level dyeing, high dye uptake rate, can produce medium and dark colors, and is suitable for dyeing a variety of protein fibers.
Especially in recent years, the demand for garment leather has grown rapidly, which has put forward higher requirements for dyes in terms of permeability, water resistance, light resistance, friction resistance and resistance to dry cleaning solvents. M-type dyes can adapt to these requirements and are of great significance to improving the quality of fur products. 2-Amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid is an important intermediate in the synthesis of M-type dyes, and it appears in a variety of dye structures. The synthesis of this intermediate generally uses 4-nitrochlorobenzene-2-sulfonic acid as raw material, and is prepared by nitrification, alkaline hydrolysis and selective reduction.
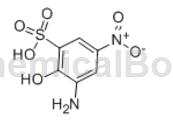
2-Amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid
Apply[3]
Modified high-efficiency water reducing agent:
A 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid dye intermediate waste liquid modified high-efficiency water reducing agent, including the following parts by weight of raw materials: 70 parts of sodium sulfanilate and 58 parts of phenol , 40 parts of water, 92 parts of formaldehyde, 16 parts of acrylic acid, 5 parts of sodium hydroxide, 160 parts of 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid dye intermediate waste liquid.
The preparation method includes the following steps:
(1) Dissolution and filtration: Add an appropriate amount of water to the reaction kettle, then add sodium sulfamate and phenol respectively, heat the reaction kettle to 85-92°C, and stir for 1 hour;
(2) Addition: Slowly add sodium hydroxide into the reaction kettle and adjust the pH of the solution to 7.6-8.2;
(3) Condensation polymerization: Heat the reaction kettle to 90-95°C, slowly add formaldehyde dropwise into it, so that the formaldehyde is dripped within 2 hours, and keep it warm for 2 hours;
(4) Copolymerization: Add 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid dye intermediate waste liquid and acrylic acid into the reaction kettle, keep the solution temperature between 82-86°C and react for 1 hour, naturally Cool to room temperature and adjust the solid content with remaining water to obtain the finished product. When used, the water-reducing agent is mixed into the cement at 1.6wt% of the weight of the cement.
Advantages:
(1) Using 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid dye intermediate waste liquid as reaction raw material helps save resources and reduce raw material costs, and effectively improves the sulfamic acid-based water reducing agent The cost is too high and practical application is difficult.
(2) Use 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid dye intermediate waste liquid to modify and graft onto the water-reducing agent polymer molecular chain, which helps to improve the water-reducing agent polymer molecules. steric hindrance between them, thereby improving its dispersion ability and water reduction rate, reducing the slump loss and water bleeding of concrete, and the product has good workability. The present invention utilizes 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6- Use sulfonic acid dye intermediate waste liquid to prepare high value-added water-reducing agent, which can not only realize waste utilization, but also obtain a convenient and economical 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid dye intermediate waste Liquid modified sulfamic acid is a high-efficiency water reducing agent and has broad application prospects.
(3) There is no emission of three wastes during the preparation process, which is safe and environmentally friendly; the reaction cycle is short, and the preparation method is simple and efficient.
Preparation[2]
1. Nitration of 4-nitrochlorobenzene-2-sulfonic acid
Add 28.4g 20% fuming sulfuric acid into the three-necked flask, add 29.7g (0.1 mol) 4-nitrochlorobenzene-2-sulfonic acid under stirring at 50-60°C, after dissolving, add 8.5 dropwise at 60°C g96% (1.13 mole) nitric acid, raise the temperature to 95°C and keep it for 10 hours. The reaction solution was poured into 40g of ice water and diluted to precipitate a white precipitate, which was filtered by suction. The filter cake was washed with salt water and dried to obtain 27.1g of 100% product, yield.
2.2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-6-sulfonic acid alkaline hydrolysis
Add 60 ml of water and 28.3 g (0.1 mol) of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-6-sulfonic acid into the three-necked flask. Stir and raise the temperature to 60°C, adjust pH=7~8, add dropwise 20% sodium hydroxide solution (containing 9.6g sodium hydroxide, 0.24 mole), raise the temperature to 95°C and react for 2 to 3 hours. The end point was detected by thin layer chromatography, and the developing solvent was ethyl acetate:methanol=5:1. The reaction solution is cooled to room temperature, neutralized with hydrochloric acid, and acidified to pH=1~2, white needle crystals are obtained. Suction filter, wash the filter cake with brine, and dry. The salt-containing product weighed 24.5g at 100%, and the yield was 92.8%.
3.2,4-Dinitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid selective reduction
Add 100ml water and 26.4g (0.1 mol) 2,4-dinitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid into the three-necked flask. Adjust pH ≥ 7 with 20% sodium hydroxide solution. Raise the temperature to 60°C, add dropwise 20% sodium sulfide solution (containing 14.1g of sodium sulfide, 0.18 mole), raise the temperature to 75°C and react for 3 to 4 hours. The end point was detected by thin layer chromatography, and the developing solvent was ethyl acetate:methanol=5:1. Cool to room temperature, neutralize with hydrochloric acid, and acidify to pH=1~2 to obtain light brown precipitate. Suction filter and dry the filter cake. 22g of brown-gray powder was obtained. The content was determined by diazotization titration to be 95.4%, and the yield was 89.7%.
Main reference materials
[1] Sun Guichun. (2014). Synthesis of metal complex dye acid black ace. Dyes and Dyeing (6), 19-22.
[2] Song Dongming, & Cao Chuanzhen. (1998). Synthesis of 2-amino-4-nitrophenol-6-sulfonic acid. Dyes and Dyeing (4), 17-19.
[3] Sun Guichun. (2014). Synthesis of metal complex dye acid black ace. Dyes and Dyeing (6), 19-22.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

