Background and overview[1]
Catalytic hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds is an industrially important reaction, e.g. used in the preparation of intermediates for agricultural chemicals, dyes and optical brighteners. To prepare stilbene optical brighteners, for example, 4,4′-dinitrostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid must be reduced to 4,4′-diamino-stilbene-2, 2′-Disulfonic acid, by classical reduction methods or by catalytic hydrogenation. 3-Amino-4-chloroacetanilide can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate. The preparation of 3-amino-4-chloroacetanilide can be prepared from the corresponding nitro compounds. The analytical hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds to the corresponding aromatic amines Proceeding through several intermediate stages, an important one is the hydroxylamine intermediate formed, arylhydroxylamines also known as strong carcinogens and therefore posing a high hazard potential in the case of interrupted or incomplete hydrogenation. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a preparation method with less impurities and high yield. If 3-amino-4-chloroacetanilide is inhaled, move the patient to fresh air; if skin contact occurs, take off contaminated clothing, rinse the skin thoroughly with soap and water, and seek medical attention if you feel unwell; if the eye contact If exposed to sunlight, separate eyelids, rinse with running water or saline, and seek medical attention immediately; if ingested, rinse mouth immediately, do not induce vomiting, and seek medical attention immediately.
Preparation[1]
The preparation process of 3-amino-4-chloroacetanilide is as follows:
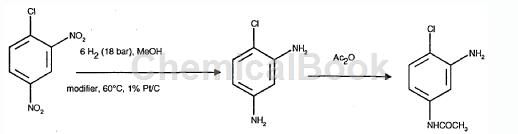
Add 15 parts of sodium acetate, 60 parts of NaHCO3, 1320 parts of MeOH and 1015 parts of 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene into the hydrogenation reactor at 50°C under nitrogen, then add 11 parts of 1% PtC , add 0.15 parts of NH4VO3 and 66 parts of water. The hydrogenation is carried out at 60°C and 18 bar. The isolated product was 3-amino-4-chloro-aniline (785 parts, 85% of theory). 3-Amino-4-chloroacetanilide is prepared by reacting 3-amino-4-chloroacetanilide with acetic acid.
Main reference materials
[1] WO1996036597 PROCESSFORTHECATALYTICHYDROGENATIONOFAROMATICNITROCOMPOUNDS

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

