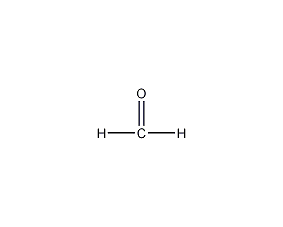
Structural formula
| Business number | 0131 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH2O |
| Molecular weight | 30.03 |
| label |
formalin, Formic aldehyde, methylene oxide, Methyl aldehyd, Methylene oxide, Formalin, Formallydehyde, Methanal solution, Oxymethylene, Dormol, pesticide intermediates, Aliphatic aldehydes, ketones and their derivatives, organic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:50-00-0
MDL number:MFCD00003274
EINECS number:200-001-8
RTECS number:LP8925000
BRN number:1209228
PubChem number:24894976
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: A colorless gas with a strong irritating and suffocating odor.
2. Relative density of steam (g/mL, air=1): 1.081-1.085
3. Relative density (g/mL, water=1): 0.82
4.Refractive index (nD20): 1.3755-1.3775
5. Flash point (℃): 56 (gas); 83 (37% aqueous solution, closed cup)
6. Boiling point (℃): -19.5 (gas); 98 (37% aqueous solution)
7. Melting point (℃): -92
8. Auto-ignition temperature (℃): 430
9. Vapor pressure (KPa,-57.3℃): 13.33
10. Explosion limit (V/V): 7%~73% in air
11. Log value (logP) of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: 0.35
12. Critical temperature (ºC): 137.2~141.2
13. Critical pressure (MPa): 6.784~6.637
14. Viscosity (mPa·s,-20ºC): 0.242
15. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): 7.0
16. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): 73
17. Solubility: Easily soluble in water and ether. The aqueous solution concentration can reach up to 55%. It can be freely miscible with water, ethanol and acetone. It can be gradually oxidized into formic acid in the air and is a strong reducing agent. Its vapor forms an explosive mixture with air, which can cause combustion and explosion when exposed to open flames or high heat. In general products, 10% to 12% methanol is added as an inhibitor, otherwise polymerization will occur.
18. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -570.77
19. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -108.57
20. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 218.76
21. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -102.5
22. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 35.39
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: LD50800mg/kg (rat oral), 2700mg/kg (rabbit transdermal); LC50590mg/m3 (rat inhalation);
 alt=”” src=”http://images.basechem.org/internal/day_100928/201009281001152446.gif” />
After the reaction is completed, the reactants are quenched to 80-85°C, absorbed with water, and then distilled to evaporate the unreacted methanol. The kettle liquid is treated with anion exchange resin, and an appropriate amount of polymerization inhibitor is added to the resulting formaldehyde solution, and stirred to mix. The finished product is obtained.
7. Gaseous formaldehyde automatically polymerizes into cyclic trimerformaldehyde at room temperature.
8. Formaldehyde can easily react with ammonia or ammonium salts to condense into hexamethylenetetramine, which is called methenamine.
Purpose
1. Formaldehyde is an important organic raw material, mainly used in the plastic industry (such as phenolic resin, urea-formaldehyde plastic-electric jade), synthetic fibers (such as synthetic vinylon-polyvinyl formal), leather industry, medicine, and dyes wait. Formalin has bactericidal and antiseptic capabilities and can be used to soak biological specimens. Its dilute solution (0.1-0.5%) can be used to soak seeds and disinfect them in agriculture. Catalytic oxidation is commonly used in industry to produce formaldehyde from methanol. Formaldehyde can produce a silver mirror reaction with the silver ammonia solution, causing a thin layer of metallic silver as bright as a mirror to adhere to the inner wall of the test tube (the combined silver is reduced and formaldehyde is oxidized); it reacts with the newly prepared copper hydroxide suspension to form a red precipitate Cuprous oxide.
2. Formaldehyde is widely used in synthetic resins, surfactants, plastics, rubber, leather, papermaking, dyes, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, photographic films, explosives, building materials, and in disinfection, fumigation and antisepsis processes. When it comes to formaldehyde, it can be said that formaldehyde is a generalist in the chemical industry, but the use of anything must have a limit and a standard. Once the use exceeds the standards and limits, it will bring disadvantages.
1) In the wood industry, it is used to produce urea-formaldehyde resin and phenolic resin. It is produced by mixing formaldehyde and urea in a certain molar ratio.
2) Textile industry The use of formaldehyde is involved in the resin finishing process of clothing. In the production of clothing fabrics, in order to achieve anti-wrinkle, anti-shrinkage, flame retardant and other functions, or to maintain the durability of printing and dyeing, or to improve the feel, formaldehyde needs to be added to the additives. At present, formaldehyde printing and dyeing auxiliaries are mostly used in pure cotton textiles, because pure cotton textiles are prone to wrinkles, and the use of formaldehyde-containing auxiliaries can improve the stiffness of cotton fabrics. Textiles containing formaldehyde will gradually release free formaldehyde when people wear and use it, causing respiratory inflammation and skin inflammation through human respiratory tract and skin contact, and can also cause eye irritation. Formaldehyde can cause allergies and can also induce cancer. Manufacturers use dyeing auxiliaries containing formaldehyde. In particular, some manufacturers use cheap auxiliaries with extremely high formaldehyde content in order to reduce costs, which is very harmful to the human body.
3) Preservative solution Formaldehyde is a substance released by the decomposition of formaldehyde and sodium bisulfite above 60°C. It is colorless, has a pungent smell, and is easily soluble in water. 35% to 40% formaldehyde aqueous solution, commonly known as formalin, has antiseptic and sterilizing properties and can be used to soak biological specimens, sterilize seeds, etc.
The main reason why formaldehyde has antiseptic and bactericidal properties is that the amino groups on the proteins that make up organisms (including bacteria) can react with formaldehyde.
4) The food industry utilizes the antiseptic properties of formaldehyde and adds it to foods that are difficult to store, such as aquatic products.
3. Used as analytical reagent, such as determination of ammonium salt. Used as thin layer chromatography analysis reagent. Also used as a bactericidal disinfectant. Used in phenolic resin production. Preparation of biological specimens.
4. Formaldehyde is the first generation preservative. It has good killing effect on Staphylococcus aureus, Galmonospora, mold, yeast and other Gram bacteria. However, the economic cost of using formaldehyde as a preservative in liquid detergents is too high, and the smell is irritating and toxic to operators.
5. Used as a reducing agent for electroless copper plating, for analysis of electroplating solutions and preparation of zinc electroplating additives.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

