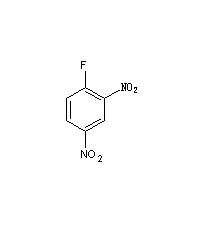
Structural formula
| Business number | 01G3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H3FN2O4 |
| Molecular weight | 186.1 |
| label |
2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene, Sanger reagent, 1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, dinitrofluorobenzene, 1-Fluoro-2-4-dinitrobenzene, 1,3-Dinitro-4-fluorobenzene, Senger’s Reagent, FNDP, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:70-34-8
MDL number:MFCD00007056
EINECS number:200-734-3
RTECS number:CZ7800000
BRN number:398632
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: Yellow needle-like crystals, which turn into orange-yellow liquid after liquefaction. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 27.5~30[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 178 (3.33kPa); 296[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.48[4]
5. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.32×10-3 (25℃)[5]
6. Octanol/ Water partition coefficient: 1.83[6]
7. Flash point (℃): >110 (CC)[7]
8. Solubility: Soluble in ether, benzene, hot ethanol, and propylene glycol. [8]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Oral LCLo in mice: 50 mg/kg; LCLo administered onto the skin in mice: 100 mg/kg; LCLo injected subcutaneously in mice: 100 mg/kg;
2. Mutagenicity:
Salmonella microbial changes testing system: 5 ug/plate; Salmonella microbial changes testing system: 33 ug/plate; Bacteria-Escherichia coli microbiological changes test system: 5 umol/L;
3. Acute toxicity[9] LD50 : 50mg/kg (rat oral)
4. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradable[10] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 420d (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects[11] This substance is harmful to the environment. Special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies. .
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 39.33
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 117.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 325.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 59.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 15.59
Scheduling��Chemical Data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 91.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 224
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[12] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[13] Strong oxidants, strong bases
3. Conditions to avoid contact[14] Heating
4. Polymerization hazard[15] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[16] Nitrogen oxidation substance, hydrogen fluoride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[17] Storage in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement the “two people to send and receive, two people to keep” system. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
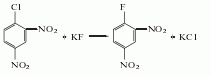
1. Obtained from nucleophilic substitution reaction using 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and anhydrous potassium fluoride as raw materials.
2.Mix anhydrous potassium fluoride, dimethyl sulfoxide and an appropriate amount of polymerization inhibitor, control the heating to 120°C, and then add 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene [reactants The ratio is 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene: anhydrous potassium fluoride: dimethyl sulfoxide: polymerization inhibitor = 1.0: 1.8: 3.4: 0.1 (molar ratio)]. Maintain the reaction temperature at 110~120℃ (strictly control the reaction temperature to prevent explosion), react for 3 hours:
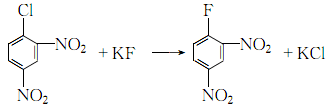
After the reaction, quickly cool to room temperature. Remove the potassium fluoride residue by suction filtration, add water to the filtrate and wash it, let it stand and separate the water layer (dimethyl sulfoxide can be recovered), wash the oil layer twice with water, distill under reduced pressure at 2.73kPa, collect 176~180℃ The distillate is the finished product 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene.
Purpose
1. Used as a chromogenic reagent for the photometric determination of organic amines and neomycin. It is also used for the preparation of fluoride ion selective electrodes and the automatic flow injection dynamic potential method for the determination of paracetamol, isoniazid and phenoxypropylamine. Used as a chromatographic derivatization reagent for the determination of primary amines, secondary amines, alcohols, phenols, thiols, imidazole and carbonyl compounds.
2. Used as a reagent for protein analysis and a reducing agent for the determination of phenol, morphine, amino acids, aldehydes, and oximes. [18]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

