Background and overview[1-2]
Vinyl benzoate (vinylbenzoate) is an organic small molecule reactive diluent containing reactive functional groups and an important monomer in the photocuring system. Its structural feature is that the vinyl double bond is directly connected to an ester bond. Due to the influence of the adjacent oxygen atom, the double bond is an electron-rich double bond, thus showing higher activity, making it a new environmentally friendly activity. Thinner, used to replace the original acrylic reactive diluent. At present, the main methods for synthesizing vinyl benzoate include acetylene method, ethylene method and transesterification method.
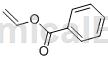
Structure
Apply[1]
With the continuous development of science and technology and the increasing emphasis on environmental protection, environmentally friendly light curing technology has also developed rapidly and has been widely used in coatings, inks, adhesives, microelectronics, dental restorations, biomaterials and other fields. Currently, the commonly used reactive diluents in photocurable materials are mainly acrylate monomers, but they are highly volatile, have low flash points, are highly toxic, and mostly have pungent odors; and many acrylate monomers are well-known carcinogens. Substances, the environmental pollution problems caused by their use are difficult to overcome. In some countries its use has been restricted, so the exploration of new reactive diluents is of great interest.
Preparation[2]
Step 1: Preparation method of catalyst
Put activated carbon with a certain specific surface area and 30% nitric acid solution into a three-necked flask and heat it to reflux in a 60℃ water bath for 4 hours. Then filter out the activated carbon in the solution and rinse the activated carbon repeatedly with distilled water. The carbon filter cake is neutralized and dried. Weigh 6.5g of the treated activated carbon, 60mL of deionized water and 0.5538g of palladium chloride solution into a three-necked flask, heat the reaction solution to 80℃, stir for 6 hours, and then cool to 40 ℃; add 15mL of 36% HCHO and stir for 1h; then add NaOH solution (4mol·L-1) dropwise until the reaction solution pH=8~9, maintain for 0.5h; the reaction solution Then raise the temperature to 80°C to promote the reduction reaction. At the same time, NaOH solution is continuously added to keep the pH constant until Pd is completely reduced. Filter out the supported activated carbon in the reducing solution, fully wash the filter cake with deionized water, and dry it to constant weight to obtain the supported Pd/C solid catalyst A.
Step 2: Preparation of vinyl benzoate
Add 5.5g benzoic acid, 35.0g vinyl acetate, and 1.2243g catalyst A into a 250mL four-necked flask, stir and heat to 80°C, reflux for 10 hours, and measure The selectivity to vinyl benzoate is 95.78%.
Main reference materials
[1]CN201810545842.3 A method for preparing vinyl benzoate
[2]CN201110362536.4 A method of synthesizing vinyl benzoate

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

