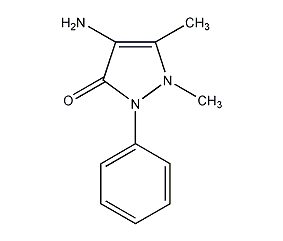
Structural formula
| Business number | 01TB |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C11H13N3O |
| Molecular weight | 203.24 |
| label |
1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-amino-3-pyrazolone, 4-Amino-1,2-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-2-phenyl-3H-pyrazol-3-one, 4-amino-2,3-dimethyl-1-phenylpyrazolone-[5], 4-Aminoantipyrine crystal, 4-Aminoantipyraline, 4-Aminoantipyrine, 1,5-Dimethyl-2-phenyl-4-aminopyrazoline, 4-Amino-2,3-dimethyl-1-phenyl-3-pyrazolin-5-one, Ampyrone |
Numbering system
CAS number:83-07-8
MDL number:MFCD00003145
EINECS number:201-452-3
RTECS number:CD2480000
BRN number:181635
PubChem number:24890855
Physical property data
1. Character: light yellow crystal
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 0.8
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air =1): Uncertain
4. Melting point (ºC): 109
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Uncertain
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Uncertain
7. Refractive index: Uncertain
8. Flash point (ºC): Uncertain
9. Ratio Optical rotation (º): Uncertain
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Uncertain
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Uncertain
p>
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Uncertain
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14. Critical temperature (ºC ): Uncertain
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19. Solubility: soluble Soluble in water, benzene and ethanol, slightly soluble in ether
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Rat caliber LD50: 1700 mg/kg; rat abdominal LD50: 1200 mg/kg
Mouse caliber LC50: 800 mg/kg ; Mouse abdominal LC50: 270 mg/kg
2. Teratogenicity
E. coli: 312 ug/well; Salmonella: 5 umol/plate
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 58.10
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 168.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 442.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 47.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 23.03
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 49.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 15
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 305
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 0
14, Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15, Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. In the presence of alkaline conditions and oxidants, it reacts with phenolic compounds to produce red dye.
2. It is harmful if taken orally and is irritating to the eyes, respiratory system and skin.
Storage method
Argon-filled sealed and stored in a cool, dry and dark place.
Synthesis method
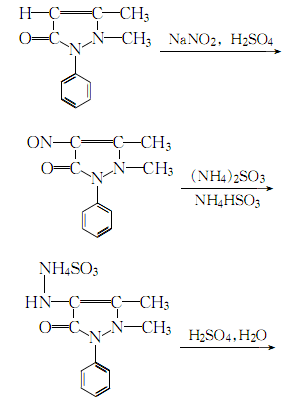
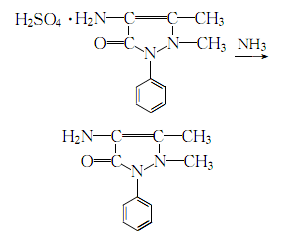
1. Antipyrine is nitrosated with sodium nitrite, reduced with ammonium bisulfite and ammonium sulfite, hydrolyzed with sulfuric acid, and finally neutralized with liquid ammonia to obtain 4-aminoantipyrine. The process is as follows: Antipyrine and 50% sulfuric acid are mixed into a solution, which contains 38%-40% antipyrine and 11%-12% sulfuric acid. Flow this solution and the sodium nitrite solution into the nitrosation reactor at the same time, control the flow rates of both, control the reaction temperature to 45-50°C, react under stirring, and use iodine powder starch test paper to measure the reaction end point to adjust the water flow rate. The nitrosantipyrine generated by nitrosation immediately flows into the reduction tank and reacts with the aqueous solution of the reducing agents ammonium bisulfite and ammonium sulfite prepared in the tank. Take a sample to measure the pH value and degree of reduction. The pH value is between 5.4-5.8 and the degree of reduction is about 15 (that is, the number of milliliters of 0.1N iodine solution consumed by 1ml of reducing solution). After the reduction is completed, the pH value is adjusted to 5.8-6.0, and the reduction degree is about 5. Raise the temperature to 100°C and hydrolyze for 3 hours. Lower the temperature to 80°C, neutralize with liquid ammonia to pH 7-7.5, and let stand for layering. Separate the waste water to obtain 4-aminoantipyrine oil (content above 80%). Press it into a crystallization tank, stir, cool and crystallize, and filter to obtain 4-aminoantipyrine.
2. Antipyrine is nitrosated, reduced by ammonium bisulfite and ammonium sulfite, hydrolyzed with sulfuric acid, and finally neutralized with liquid ammonia And 4-aminoantipyroline can be obtained.
Purpose
1. Used to determine alcohol, phenol, amines and their homologues. Chromatographic determination of alkylphenols.
2.Used as a chromogenic reagent for the photometric determination of phenols, alcohols, and amine organic compounds. And used as a reagent for the polarographic determination of phenolic compounds.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

