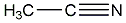
Structural formula
| Business number | 01HW |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H3N |
| Molecular weight | 41.05 |
| label |
Methyl cyanide, Cyanomethane, Methyl cyanide, Ethaneitrile, synthetic raw materials |
Numbering system
CAS number:75-05-8
MDL number:MFCD00001878
EINECS number:200-835-2
RTECS number:AL7700000
BRN number:741857
PubChem number:24856425
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -45[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 81.6[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.79 (15℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 1.42[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 13.33 (27℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1264.0[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 274.7[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.83[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -0.34[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 12.8 (CC); 6 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 524[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 16.0[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 3.0[14]
15. Solubility: miscible with water, soluble in most organic substances such as ethanol and ether Solvent. [15]
16. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4ºC): 0.7822
17. Relative density (g/mL, 25/ 4ºC): 0.7766
18. Relative density (g/mL, 30/4ºC): 0.77125
19. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.34411
20 .Refractive index (25ºC): 1.34163
21. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.375
22. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.325
23. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, 25ºC): 33.25
24. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, 80.5ºC): 29.84
25. Heat of fusion (KJ /mol): 8.17
26. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 51.50
27. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 1266.09
28. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 1.31
29. Electrical conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 6×10-10
30. Body expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC): 0.00137
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 2460mg/kg (rat oral); 1250mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
LC50: 7551ppm (rat inhalation, 8h)
2. Irritation [17] Rabbit transdermal : 500mg, mild stimulation (open stimulation test)
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity [18] Cats inhale its vapor 7mg/m 3, 4 hours a day for a total of 6 months. One month after exposure to the poison, the conditioned reflex began to be destroyed. Pathological examination showed pathological changes in liver, kidney and lung.
4. Mutagenicity [19] Sex chromosome deletion and non-disjunction: Saccharomyces cerevisiae 47600ppm. Sister chromatid exchange: hamster ovary 5g/L.
<stroMaterials are reacted under the action of aluminum oxide catalyst at a temperature of 360-420°C to synthesize acetonitrile in one step. The reaction liquid is subjected to water absorption and distillation to obtain the finished product. Raw material consumption quota: acetic acid (98%) 1763kg/t, liquid ammonia (99.5%) 691kg/t.
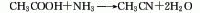
2. Acetylene amination method: Using acetylene and ammonia as raw materials and aluminum oxide catalyst, acetonitrile is synthesized in one step at a temperature of 500-600°C. Raw material consumption quota: acetylene 10231m3, liquid ammonia (99.4%) 1007kg/t.
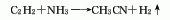
3. Propylene ammonia oxidation by-products Method: When propylene, ammonia and air are used as raw materials and acrylonitrile is synthesized through a catalyst, acetonitrile is also produced as a by-product. Each ton of acrylonitrile can produce 25-100kg acetonitrile by-product.
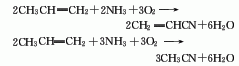
4. From acetamide and penta Obtained from dehydration of phosphorus oxide.
5. Obtained from the reaction of dimethyl sulfate and sodium cyanide.
Refining method: Industrial products often contain impurities such as water, hydrocarbons, acrylonitrile, acetic acid, and ammonia. During purification, the water in the crude acetonitrile is first removed by azeotropic distillation using an azeotropic mixture of acetonitrile and water, and then rectification is performed to remove high boiling point substances. For further refining, it can be dried with calcium chloride, filtered and then refluxed with 0.5% to 1% phosphorus pentoxide, and then distilled under normal pressure. Repeat this operation until phosphorus pentoxide is no longer colored (during reflux and distillation, a drying tube containing phosphorus pentoxide should be connected to prevent moisture in the air from entering), and then add newly melted potassium carbonate for distillation to remove trace amounts. of phosphorus pentoxide, and finally fractionated to obtain the pure product.
In addition to using azeotropic distillation and calcium chloride for dehydration, anhydrous sodium sulfate, potassium carbonate, type 4A molecular sieve or silica gel can also be used for dehydration. If there is a trace amount of unsaturated nitrile, it can be removed by refluxing with a small amount of potassium hydroxide aqueous solution (1 mL of 1% potassium hydroxide aqueous solution per 1000 mL of acetonitrile) at the beginning. If it contains isonitrile, it can be removed by treatment with concentrated hydrochloric acid, then dried with potassium carbonate and then distilled.
6. Place absolutely dry acetamide and phosphoric anhydride in a copper container, install a fractionating column and a water condenser, heat, control the temperature so that the reaction is not too violent, and react until no distillation occurs. So far, the crude product has been collected:
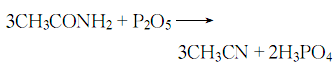
Add saturated potassium carbonate solution to the above crude product until no bubbles appear, then add a small amount of dry potassium carbonate, stir evenly, and let it stand. Pour out the crude nitrile in the upper layer and carry out fractionation together with phosphoric anhydride. The distillate at 80-82°C is collected as the finished product.
Purpose
1. Acetonitrile is the raw material for the preparation of orthoacetate, and is used to produce methyl dipermethrin and 2-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoro-1-propenyl-2,2-dimethylcyclo It is an intermediate of propane carboxylate (propane carboxylic acid ester) and can be used as a raw material for sulfonylurea herbicide intermediates and pyrimidine derivatives. It can be used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce vitamin B1 and in the synthetic rubber industry to extract the C4 fraction. agent. Used as chromatographic analysis standard material, solvent and gas chromatography stationary solution.
2. Mainly used as solvent. For example, it can be used as a solvent for extracting butadiene, a solvent for synthetic fibers and a solvent for some special coatings. Solvent used in the petroleum industry to remove tar, phenol and other substances from petroleum hydrocarbons. In the oil industry, it is used as a solvent for extracting fatty acids from animal and vegetable oils, and in medicine, it is used as a reaction medium for the recrystallization of steroid drugs. When a polar solvent with a high dielectric constant is required, a binary azeotropic mixture of acetonitrile and water is often used: containing 84% acetonitrile, boiling point 76°C. Acetonitrile is an intermediate for medicine (vitamin B1) and spices, and a raw material for manufacturing s-triazine nitrogen fertilizer synergist. Also used as a denaturant for alcohol. Used as fatty acid extraction agent, alcohol denaturant, butadiene extraction agent and solvent for acrylonitrile synthetic fiber. In addition, it can also be used to synthesize ethylamine, acetic acid, etc., and also has many uses in fabric dyeing and lighting industries.
3. Used in the preparation of vitamin B1 and other drugs and spices, and also used as fatty acid extraction agent. [30]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

