Background and overview[1-2]
Methyl p-toluenesulfonate is also known as 4-methyl toluenesulfonate. White crystals. Easily soluble in ethanol, ether and benzene, but insoluble in water. Irritating. Hygroscopic. Used as a selective methylating reagent in organic synthesis. Derived from the reaction of p-toluenesulfonyl chloride and methanol. Industrial synthesis of methyl p-toluenesulfonate usually uses concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst for direct esterification reaction. However, using concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst produces many by-products, and the dilute sulfuric acid produced causes serious corrosion to the equipment. Product separation is complicated and the yield is low. , serious pollution and other shortcomings. The reaction conditions are harsh, the process is complex, and the product yield is low. Therefore, finding a method for preparing methyl p-toluenesulfonate with simple process conditions, environmental friendliness, and high yield is still a hot topic in this field.
Apply[3-4]
Methyl p-toluenesulfonate is used as a selective methylating reagent in organic synthesis. It is used in the manufacture of dyes and organic synthesis. It is used as a raw material for preparing methylation. It is also used as a selective methylating reagent and catalyst in organic synthesis. Applications For example:
1) Prepare high-yield, high-purity DAST source powder.
The synthesis process is divided into two steps: 1. Use absolute ethanol as the solvent to react 4-methylpyridine and methyl p-toluenesulfonate to prepare 4-methyl-N-methylpyridine-p-toluenesulfonate Anhydrous ethanol solution of acid salt; 2. Using absolute ethanol as the solvent, under the catalysis of di-n-butylamine or piperidine, 4-methyl-N-methylpyridine p-toluenesulfonate and p-dimethyl Through the reaction of aminobenzaldehyde, DAST source powder can be obtained with a high yield of 85-95% and a high purity of 90-95%.
Using absolute ethanol as the reaction solvent avoids the harm to the operator’s body caused by toxic and harmful solvents such as toluene and methanol, and also reduces the pollution of the waste liquid to the environment; the successful research and development of this invention is conducive to the cultivation of high-quality, large-scale The large-sized DAST crystals have laid a good material and theoretical foundation for the research on DAST crystals and related products.
2) Preparation of 4-(4-dimethylaminostyryl)methylpyridine p-toluenesulfonate,
Mix 4-methylpyridine and methyl p-toluenesulfonate, place it in anhydrous methanol and pour it into a three-hole flask for ion exchange reaction; then dissolve p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde in anhydrous methanol Place it in a three-hole flask and perform a condensation reflux reaction to obtain a crystallized product; rinse the obtained crystallized product with chloroform and quickly filter it to obtain a solid with green metallic luster, and then heat the solid with green metallic luster to completely dissolve it. in anhydrous methanol, cooled and air-dried and recrystallized to prepare 4-(4-dimethylaminostyryl)methylpyridine-p-toluenesulfonate; the preparation method is simple, the reaction steps are simple, the reaction time is short, and the cost is low. High yield.
Preparation[2,5]
Method 1: Synthesis method of selective methylation reagent methyl p-toluenesulfonate, including the following steps:
(i) In a reaction vessel equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, and dropping funnel, add 0.271 mol of p-toluenesulfonyl bromide (2) and 1.57-1.59 of 2,2,2-trifluoroethyl methyl ether. mol, control the stirring speed at 160-190rpm, the solution temperature at 35–40°C, dropwise add 300ml of potassium carbonate solution, control the dropping time at 2-3h, maintain the stirring state for 5-6h after the addition, and separate the oil layer. Wash with salt solution, sodium sulfite solution, dimethylamine solution in sequence, dehydrate with dehydrating agent, and distill under reduced pressure. Collect fractions at 140–145°C to obtain methyl p-toluenesulfonate (1).
Wherein, the mass fraction of the potassium carbonate solution described in step (i) is 45-50%, the salt solution described in step (i) is any one of potassium bromide and sodium chloride, and step (i) ), the mass fraction of the sodium sulfite solution is 30-35%, the mass fraction of the dimethylamine solution described in step (i) is 75-80%, and the dehydrating agent described in step (i) is calcium sulfate, active oxidation Any kind of aluminum, the vacuum distillation described in step (i), the pressure is 1.8-1.9kPa.
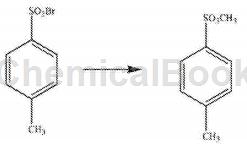
Method 2: A synthesis method of methyl p-toluenesulfonate, which method includes the following steps:
Step 1. Add 50g of toluene into a four-necked flask with a stirring reflux device, heat to 120°C, add 35g of 98% concentrated sulfuric acid dropwise under reflux, add dropwise evenly within 30 minutes, and continue to reflux and heat. ;
Step 2: When water no longer separates from the reflux liquid, react for 4 hours to end the reaction. Lower the temperature and add 10g of water and 20g of ethanol as a mixed solvent at 60°C to precipitate crystals and perform vacuum filtration to obtain p-toluenesulfonic acid;
Step 3. Add 100g methanol to the reaction kettle, add 3.0g high-efficiency catalyst Fe-Zn/SBA-15, and 100g p-toluenesulfonic acid, slowly heat up to 70°C, start stirring, raise the temperature to 85°C and reflux for 3 hours; continue Raise the temperature to 135°C and start adding 150g of methanol dropwise;
Step 4. During the dropwise addition process, raise the temperature to a slight boil, steam out high-concentration methanol, and keep it at 135°C for half an hour after the dropwise addition. Distillate under reduced pressure. When there is almost no distillate, stop the distillation to obtain pure product Methyl tosylate.
Detection method[6]
Method 1: A method for determining the content of methyl p-toluenesulfonate, which includes the following steps:
(1) Prepare a mixed aqueous solution containing 50.5-60.5g of sodium iodide and 0.0005-0.005g of vitamin C per 50mL solution as the derivatization solution;
(2) Prepare a mixed solution with a volume ratio of acetonitrile and derivatization solution of 1:4 to 4:1 as a blank solution;
(3) Prepare for concentrationThe acetonitrile solution of methyl p-toluenesulfonate is 0.25 to 1.0 μg/mL; the mixed solution of the acetonitrile solution of methyl p-toluenesulfonate and the derivatization solution with a volume ratio of 1:4 to 4:1 is used as p-toluenesulfonate. Acid methyl ester derivatization control solution;
(4) Dissolve the sample to be tested in a mixed solution with a volume ratio of acetonitrile and derivatization solution of 1:4~4:1 to obtain a derivatization solution of the test product containing 0.005~0.1g/ml of the sample to be tested;
(5) Take equal volumes of the blank solution, the methyl p-toluenesulfonate derivatization control solution and the test product derivatization solution and inject them into the headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometer, and subtract the blank according to the external standard method. Calculate the peak area of methyl iodide to obtain the content of methyl p-toluenesulfonate in the derivatization solution of the test product.
Main reference materials
[1] Concise Dictionary of Fine Chemicals
[2] CN201811092752.X A synthesis method of methyl p-toluenesulfonate
[3] CN201410570172.2 A high-yield, high-purity DAST source powder synthesis process
[4] CN201310473733.2 Preparation method of 4-(4-dimethylaminostyryl)methylpyridine-p-toluenesulfonate
[5] CN201510976362.9 A synthesis method of selective methylation reagent methyl p-toluenesulfonate
[6] CN201710693255.4 A method for determining methyl p-toluenesulfonate in drugs

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

