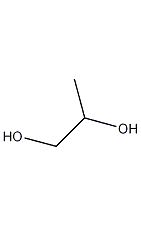
Structural formula
| Business number | 018S |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H8O2 |
| Molecular weight | 76.10 |
| label |
propylene glycol, 1,2-Dihydroxypropane, α-propylene glycol, Methyl glycol, propylene glycol, One propyl alcohol, 1,2-Dihydroxypropanol, Propylene glycol, 1,2-Dihydroxy-propane, Methyl glycol, Aliphatic alcohols, ethers and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:57-55-6
MDL number:MFCD00064272
EINECS number:200-338-0
RTECS number:TY2000000
BRN number:1340498
PubChem number:24864713
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless, viscous and stable water-absorbing liquid, almost tasteless and odorless, flammable, low toxicity.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 187.3
3. Melting point (ºC, pouring point): -60
4. Relative density (g /mL, 20/20ºC): 1.0381
5. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.0362
6. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.4329
7. Viscosity (mPa·s, 0ºC): 243
8. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 56.0
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 40ºC) : 18
10. Flash point (ºC, closed): 98.9
11. Flash point (ºC, open): 107
12. Fire point (ºC ): 421.1
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant pressure): 1827.5
14. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant volume): 1825.0
15. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 20ºC, 101.3kPa): 1853.1
16. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg): 538.1
17. Heat of generation (KJ/ mol, 20ºC): 500.3
18. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 2.48
19. Critical temperature (ºC): 351
20. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.9
21. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)): 0.217714
22. Lower explosion limit (% ,V/V): 2.6
23. Explosion upper limit (%,V/V): 12.5
24. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1 , 20ºC): 0.000695
25. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 55ºC): 0.000743
26. Vapor pressure (kPa, 55ºC): 0.19
27. Solubility: can be dissolved with water and ethanolh, 80% propylene glycol is obtained. Control the feeding speed of dichloropropane, that is, the feeding speed is fast at high temperature and slow at low temperature. Example: Add 60g calcium carbonate and 150g water into a 300ml autoclave, stir and heat to 230°C, continuously add dichloropropane at a rate of 0.03g/(min·100gH2O) for 11.5h; continue stirring at this temperature for 30min, and then quench At room temperature, the propylene glycol yield is about 95%. By controlling the temperature within 130-300°C and changing the feed rate of dichloropropane accordingly, the yield of propylene glycol can reach over 95%. (2) Two-step hydrolysis process: The raw materials are first reacted in a kettle reactor. After the dichloropropane reaches a certain conversion rate, the material is then pumped into a plug flow reactor to continue the reaction, and finally hydrolyzed into propylene glycol. Example: Add 606kg of dichloropropane into a 2 cubic meter reaction kettle, then add 800kg of sodium acetate, 556kg of 1,2-propanediol, 10kg of acetic acid and 1kg of water, stir and raise the temperature to 180°C, cool to 120°C after 4 hours, and extract the material. After the preheater is heated to 180°C, it passes through a plug flow reactor with a length of 400m, an inner diameter of 25mm, and a volume of 230L at a speed of 500L/h. The product is collected in the second stirred tank and cooled to room temperature. The analyzed product is: 44kg dichloropropane, 334kg propylene glycol, 32kg sodium acetate, 44kg acetic acid, 234kg 1,2-diacetoxypropane, 693kg propylene glycol monoacetate, 45kg 1-chloropropene, 547kg NACL and 1kg water.
Purpose
1. Propylene glycol is an important raw material for unsaturated polyester, epoxy resin, polyurethane resin, plasticizer, and surfactant. The amount used in this aspect accounts for about 45% of the total consumption of propylene glycol. This unsaturated polyol Esters are used extensively in surface coatings and reinforced plastics. Propylene glycol is widely used as a hygroscopic agent, antifreeze, lubricant and solvent in the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries due to its good viscosity, hygroscopicity and non-toxic properties. In the food industry, propylene glycol reacts with fatty acids to form propylene glycol fatty acid esters, which are mainly used as food emulsifiers; propylene glycol is an excellent solvent for condiments and pigments. Due to its low toxicity, it is used as a solvent for spices and food colorings in the food industry. Propylene glycol is commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry as a solvent, softener and excipient in the manufacture of various ointments and ointments. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used as a solvent for blending agents, preservatives, ointments, vitamins, penicillins, etc. Because propylene glycol has good miscibility with various fragrances, it is also used as a solvent and softener in cosmetics. Propylene glycol is also used as a tobacco humidifier, antifungal agent, food processing equipment lubricant, and solvent for food marking ink. Aqueous solutions of propylene glycol are effective antifreeze agents. It is also used as tobacco wetting agent, antifungal agent, fruit ripening preservative, antifreeze and heat carrier.
2.Used in organic synthesis as solvent, dehydrating agent, plasticizer, antifreeze, and gas chromatography stationary solution.
3.Commonly used organic synthetic raw materials for the manufacture of unsaturated polyester resin. It can also be used as emulsifier, preservative and antifreeze. It is also used in the manufacture of alkyd resins, polypropylene glycol, plasticizers, surfactants and lubricants. Due to its good hygroscopicity and low toxicity, it is used in the pharmaceutical industry as a solvent for blenders, preservatives, ointments, ointments, pills and vitamins, as well as softeners and excipients. Used as a solvent for spices, condiments and food colorings in the food industry. It is also used as tobacco humidifier, antifungal agent, fruit ripening preservative, coating film-forming additive, antifreeze and heat transfer medium. It is also often used as a substitute for ethanol and glycerin, and can be used as a wetting agent in combination with glycerin or sorbitol in toothpaste and cosmetics.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

