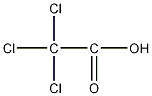
Structural formula
| Business number | 01KN |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2HCl3O2 |
| Molecular weight | 163.39 |
| label |
trichloroacetic acid, TCA, Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:76-03-9
MDL number:MFCD00004177
EINECS number:200-927-2
RTECS number:AJ7875000
BRN number:970119
PubChem number:24900586
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: Colorless crystals, pungent odor, easy to deliquesce. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 57.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 197.5 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.63[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 5.65[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (51℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -387.9[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.81[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.33[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 197[ 10]
11. Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol, ether, slightly soluble in carbon tetrachloride. [11]
12. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol, 59.1ºC): 5.9
13. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, solid): 514.1
14. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 3×10-9
15. Vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): 6.2×10 -9
16. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -503.3
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[12] LD50: 3300mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation[13]
Rabbit transdermal: 210μg, mild irritation.
Rabbit eye: 3500μg (5s), severe irritation.
3. Sensitization[14] Has sensitizing effect
4. Mutagenicity [15] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 250μg/dish. Micronucleus test: mice were administered 300mg/kg intraperitoneally (24h). Cytogenetic analysis: Mice take 500mg/kg orally. DNA adduct: mice were intraperitoneally administered 2000 nmol/L (1 week) (intermittent). DNA damage: Orally administered 500mg/kg in mice
5. Teratogenicity [16] Oral exposure of rats 1 to 22 days after pregnancy The lowest toxic dose (TDLo) is 6402 mg/kg, which can cause developmental malformations of the cardiovascular system.
6. Carcinogenicity [17] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18]
LC50: 2000mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow); 277mg/L (48h ) (Medaka); 2000mg/L (48h) (Daphnia)
IC50: 200~250mg/L (72h) (Algae)
2. Biodegradation Performance [19] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, 7% degradation after 4 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability No information available
Molecular structure�Data
1. Molar refractive index: 27.39
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 90.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 243.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 53.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.85
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 83.4
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Trichloroacetic acid is a strong acid (Ka=0.2159~0.2183 at 20°C), and its acidity is comparable to hydrochloric acid. It is unstable in aqueous solution and decomposes into chloroform and carbon dioxide. The same decomposition also occurs when heated together with sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate. Under the action of excess sodium hydroxide, sodium formate is produced. Esterification can occur with methanol, ethanol, etc.
2. Stability[20] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidizing agent, strong alkali
4. Conditions to avoid contact[22] Heating
5. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[24] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging should be sealed and should be stored separately from oxidants and alkalis. Mixed storage should be avoided. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Separate after chlorination of acetic acid, use chloroacetic acid mother liquor as raw material, sulfur powder as catalyst, continue chlorination at 90-100℃, and then recrystallize.
2. The trichloroacetaldehyde method is obtained by the eutectic oxidation of trichloroacetaldehyde and fuming nitric acid. Trichloroacetic acid can be produced by oxidizing trichloroacetaldehyde with nitric acid or potassium permanganate, and directly chlorinating acetic acid under the catalysis of iodine or phosphorus trichloride and light.
![]()
Refined method: from its melting After the material is crystallized step by step, it is refined by repeated recrystallization with dry benzene. Pure product should be stored in a vacuum desiccator containing concentrated sulfuric acid. It can also be recrystallized with chloroform or cyclohexane and dried with a vacuum dryer containing phosphorus pentoxide or magnesium perchlorate. Trichloroacetic acid can also be purified by fractional distillation under reduced pressure in the presence of magnesium sulfate. Or add benzene to trichloroacetic acid, first remove the water by azeotropic distillation, and then crystallize and refine it from the remaining benzene solution. ![]()
3. Combine trichloroacetaldehyde with fuming Nitric acid is mixed and eutectic, and the oxidation reaction is carried out until no more nitrogen dioxide is generated to obtain crude trichloroacetic acid:
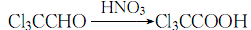
The crude product is distilled at 89.3kPa, and the fractions are collected, which is the finished product.
4. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, reflux condenser, and dropping funnel, heat 330g of nitric acid (d1.5), slowly Heat, add anhydrous trichloroacetaldehyde ① (2) 296g (2mol) dropwise with stirring, keep the temperature of the reaction solution at 80~85°C, and complete the addition in about 1.5 hours. After the addition, continue to keep warm and stir the reaction for 3 hours. until very little nitrogen dioxide escapes. Distill until brown without nitrogen dioxide. Fractional distillation under reduced pressure gave 185g of trichloroacetic acid (1) with a yield of 56%. [27]
Purpose
1. This product is a wart remover and astringent in medicine. Sodium trichloroacetate is a selective herbicide. It is mainly used as an extractant for biochemical drugs, such as adenosine triphosphate, cytochrome c and placental ester polysaccharide and other highly effective drugs. It is also used as a raw material for pesticides, a protein precipitant and a fixative for microscope samples. Used as selective herbicide (sodium salt), local corrosive agent, astringent, disinfectant, keratinolytic agent, protein precipitating agent and raw material of medicine, etc.
2. Used as analytical reagents, such as thin layer chromatography for determination of menthafuran and protein precipitating agent. Color developer for glucosides. Fixatives in microscopic analysis.
3. Used in organic synthesis and pharmaceuticals, chemical reagents, and pesticides. [26]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

