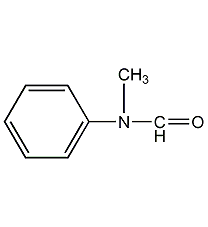
Structural formula
| Business number | 026L |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H9NO |
| Molecular weight | 135.16 |
| label |
N-Methyl-N-phenylcarboxamide, N-methylfumaamine, Methylformanilide, N-formyl-N-methylaniline, N-Formyl-N-methylaniline, N-Methyl-N-phenylformamide, MFA, N-Methyl-N-Phenylformamide, Vilsmier-Haack reagent |
Numbering system
CAS number:93-61-8
MDL number:MFCD00003283
EINECS number:202-262-3
RTECS number:None
BRN number:636496
PubChem number:24896936
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow liquid
2. Density: 1.095 g/cm3
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, Air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 8~13
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 243~244
6. Boiling point (ºC): 131℃ (2.93kPa), 128-129℃ (2.0kPa).
7. Refractive index: 1.5589
8. Flash point (ºC): 126
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure ( kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/ V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in most organic solvents, can be dissolved in a variety of organic solvents used in solvents.
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.75
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 124.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 318.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 42.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 16.15
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic ginsengReference value for numerical calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.3
7. Number of heavy atoms :10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 108
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11 .Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Relatively stable to air and moisture.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, dry place.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of N-formanilide and dimethyl sulfate. Mix N-formanilide and dimethyl sulfate, add potassium hydroxide solution dropwise while stirring and cooling, and control the temperature below 15°C. After the dropwise addition is completed, continue stirring for 1 hour at 20-25°C. The reaction mixture becomes slightly alkaline. Slowly add concentrated ammonia solution dropwise to decompose excess dimethyl sulfate. Then let it stand for layering, take the upper oil and distill it under reduced pressure, and collect the 130-133°C (2.13kPa) fraction, which is N-methylformanilide, with a yield of about 90%. 2. Obtained from the reaction of N-methylaniline and formic acid. Mix N-methylaniline, formic acid and toluene, heat and distill. After steaming out the water, the temperature is raised to 108-110°C to steam out the toluene. The residue is distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
2. Install a water trap with a piston on the 2-liter round-bottomed flask, and connect a reflux condenser to the water trap. The bottle contains 321 grams (3 moles) of N-toluidine, 300 grams of formic acid (85-90%) and 200 ml of benzene. Heat to reflux until no more water separates (collect 140-150 ml). Transfer the residue into a Kirschner flask, distill under reduced pressure, and collect the 114-121/8mm fraction.
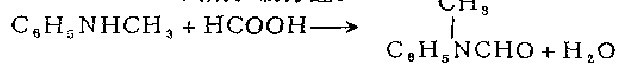
3. Use N-methyl Aniline is prepared by heating the raw material with formic acid in toluene [1].
Purpose
1. Used as an intermediate in organic synthesis.
2.N-Methyl-N-phenylformamide (MFA) is mainly used in Vilsmeier-Haak reaction in organic synthesis. of formylation reagents. It seems to have exactly the same function as DMF, but because the presence of aryl groups in the MFA molecule makes the reaction intermediate more stable, the yield of the product obtained is higher than using DMF. At the same time, MFA does not have a large solubility in water like DMF, so post-processing is more convenient than using DMF.
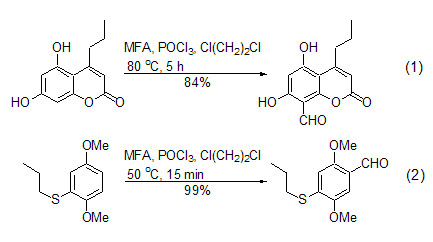
The Vilsmeier-Haak reaction conditions using MFA are very mild. 1,2-dichloroethane is the most commonly used reaction solvent, and sometimes the reaction can be carried out under solvent-free conditions. The reaction can be carried out at room temperature or at the reflux temperature of the reaction solvent, and the yield is generally moderate to high. For example: in the presence of POCl3, MFA can react with activated aromatic compounds to introduce formyl groups on the aromatic ring. The benzene ring substituted by amino, hydroxyl or alkoxy groups can be conveniently generated by the Vilsmeier-Haak reaction of this reagent to generate the corresponding benzaldehyde derivatives (Formula 1, Formula 2)[2~5].
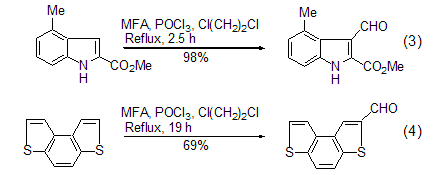
The reactions of heteroatom aromatic compounds are more It is easy and has important application value, such as indole, pyrrole or thiazole derivatives (Formula 3, Formula 4) [6~10].
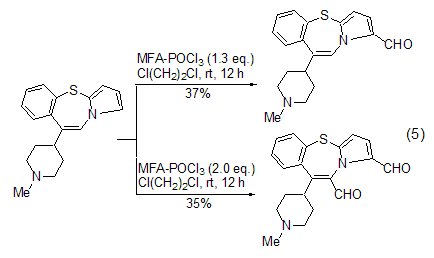
Vilsmeier-Haak using MFA The selectivity of the reaction mainly comes from two aspects. When the reaction substrate contains multiple aromatic rings, using a limited amount of MFA can make the formylation reaction preferentially proceed on the most reactive ring (Formula 5)[11]. When the reaction substrate contains multiple identical reaction sites, using an excess of MFA can cause formylation reactions to occur simultaneously at these sites to generate polyformyl compounds [12].

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

