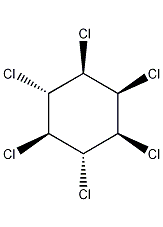
Structural formula
| Business number | 019W |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H6Cl6 |
| Molecular weight | 290.83 |
| label |
γ-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane, (1α,2α,3β,4α,5α,6β)-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane, C body six hundred and sixty-six, γ-666, Aalindan, Aficide, Agrocide, Ameisentod, Aparasin, γ-1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexachlorocyclohexane, Organochlorine pesticides |
Numbering system
CAS number:58-89-9
MDL number:25842
EINECS number:175135-73-6
RTECS number:24849491
BRN number:MFCD00013385
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: white to light yellow crystal or powder. Slightly musty smell.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.87
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 111.8~112.8
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 288
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: 1.644
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 1.2×10-3
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol ): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (polymer) Log value of the partition coefficient (alcohol/water): Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V ): Undetermined
19. Solubility: at 20°C, solubility (g/100g): acetone 43.5, benzene 28.9, chloroform 24.0, ether 20.8, ethanol 6.4. Insoluble in water.
Toxicological data
The acute daily LD50 of rats is 88-270mg/kg (125mg/kg), and that of mice is 59-246mg/kg. Feed rats at 625 mg/lcg, about 50 % had symptoms of convulsions and poisoning, the serum helium-transferase activity of male rats increased, and the red blood cell count decreased significantly. The maximum allowable concentration in the production workshop is 0.5mg/m3
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 56.64
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 182.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 462.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 41.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 22.45
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 104
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Irritating to the skin, causing rashes and swelling. There is an accumulation effect in the animal body,
Storage method
This product should be kept sealed.
Synthesis method
1. The industrial production method of lindane is based on the different solubility of each isomer of 666 in methanol at different temperatures and the difference in crystallinity of various isomers. Under the appropriate amount of methanol and extraction temperature , C-body, D-body and oily impurities are extracted in methanol, and A and B-body are separated into residues. The methanol solution that is saturated and dissolved with butyl and oily substances is cooled and crystallized. Due to the difference in crystallization speed, the 666-propanol crystals separate out. Generally, a second purification is required to obtain lindane products with a propyl propyl content of more than 99%.
Purpose
Gas chromatography analysis standards. Organic Synthesis. Pesticides. This product is a broad-spectrum insecticide that acts on the nerves of insects. It has stomach poisoning, contact killing, and fumigation effects. It is generally processed into powder or wettable powder for use. Due to its wide range of uses and simple manufacturing process, BHC was widely produced and used around the world in the 1950s and 1960s. It was once the most produced pesticide in my country and played an active role in eliminating locust plagues and preventing forest pests and household hygiene pests. effect. Due to the long-term and large-scale use of 666, pests have become resistant to pesticides, and the drug supply is decreasing day by day. Moreover, because it is not easy to degrade, it causes residue accumulation in the environment and organisms. Many countries stopped using it in the 1970s. Our country stopped production in 1983, but a small amount of it is still produced as a raw material for other household medicines.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

