Background and overview[1]
2-Amino-4,6-dichlorobenzoic acid is a carboxylic acid derivative, which is mainly used in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates.
Structure
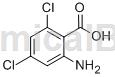
Preparation[1]
To a solution of 4,6-dichloro-1H-indole-2,3-dione (5.0g, 23.1mmol) in 75ml 1NNaOH at room temperature was partially added hydrogen peroxide (28% v/v, 10ml) . After the mixture was stirred for 2 hours, the insoluble dark brown solid was removed by filtration. The filtrate was acidified to pH 2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. The resulting yellow precipitate was harvested, washed with distilled water, and dried in vacuo. Recrystallization from benzene gave the title compound as an ivory solid (3.90 g, 82%). TLCRf=0.1 (ethyl acetate:n-hexane=1:1); melting point 188-189℃; 1HNMR (DMSO-de) δ6.76 (d, IH5J =1.9Hz5ArH), 6.85 (d, IH5J=1.9Hz, ArH); MS (EI) m/e206[M+], 162[M+-CO2].
Apply[1]
2-Amino-4,6-dichlorobenzoic acid is mainly used in the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, such as the preparation of 5,7-dichloro-3-methyl-1H-quinazoline-2,4-dione, The specific steps are: react triphosgene (0.4mmol) in a solution of 2-amino-4,6-dichlorobenzoic acid (1.0mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (20ml) or tetrahydrofuran (20ml) 2 hours, while fluxing is carried out. After the starting material benzamide was dissolved, the solvent was removed in vacuo. The residue was washed with 1N hydrochloric acid (100 ml) and recrystallized from methanol and ethyl acetate (or purified by flash column chromatography (eluent: n-hexane and ethyl acetate)) to give a yellow solid (96%) . Melting point: 47-250℃;
1HNMR (200MHz, DMSO) δ0.96 (t, 3H, J=6.5Hz, CH3), 1.73 (m, 2H, CH2), 3.97 (t, 2H, J=6.5Hz, NCH2), 7.02 (d, IH, J=2.0Hz5ArH) , 7.24 (m, IH, ArH), 9.84 (brs, IH, NH); MS (EI) m/e272 [M+1, 231, 160, 72.
Main reference materials
[1](WO2008004716) NOVEL SUBSTITUTED-1H-QUINAZOLINE-2,4-DIONE DERIVATIVES, PREPARATION METHOD THEREOF AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION CONTAINING THE SAME

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

