
Structural formula
| Business number | 02EM |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C9H10 |
| Molecular weight | 118.18 |
| label |
2-Phenylpropene, α-Methylthrothylene, isopropenylbenzene, 1-methyl-1-styrene, cumene, methylstyrene, 1-Methyl-1-phenylethylene, β-Phenylpropylene, Isopropenylbenzene, For plasticizer synthesis, modifier, hydrocarbon solvents, Organic synthetic raw materials |
Numbering system
CAS number:98-83-9
MDL number:MFCD00008859
EINECS number:202-705-0
RTECS number:WL5075300
BRN number:969405
PubChem number:24885891
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid, with a pungent odor, polymerizes when heated, and is flammable.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 165.38
3. Melting point (ºC): -23.21
4. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4ºC): 0.9106
5. Relative density (g/mL, 25/25ºC): 0.9046
6. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 4.1
7. Refractive index(n20D): 1.5386
8. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.940
9. Flash point (ºC): 45
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC) :494
11. Critical temperature (ºC): 384
12. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.36
13. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC) : 0.253
14. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): 4.1
15. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): 3.4
16. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): 0.7
17. Solubility: Miscible with ethanol, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, benzene and chloroform, insoluble in water.
18. Temperature refractive index (n20): 1.5386
19. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.345
20. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 9.920×109
21. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1) : 76.460
22. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -5041.18
23. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (Enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 70.46
24.��� phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 212.6
25. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) ( kJ·mol-1): -5089.4
26. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 118.7
27. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 372.56
28. Gas phase standard generation is free Energy (kJ·mol-1): 217.9
29. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1 ):140.49
Toxicological data
Toxicity classification Poisoning
Acute toxicity Oral administration – rat LD50: 4900 mg/kg; Oral administration – mouse LD50: 4500 mg/kg.
Irritation Data Skin – Rabbit 100% Moderate; Eyes – Rabbit 91 mg Mild.
This product has medium toxicity, similar to vinyl toluene. Inhalation or contact with skin should be avoided. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 375mg/m3. Operators should wear protective gear Utensils, chronic experiments on animals (600×10-6) can cause damage to liver and kidneys and stagnant growth.
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.45
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 135.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 312.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.4
5. Dielectric constant: 2.27
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 16.03
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 96.6
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Can be copolymerized with styrene, acrylonitrile, butene and divinylbenzene. Flammable, explosion limit in air is 0.7%-3.4% (volume fraction). poisonous.
2. Exist in smoke.
Storage method
Usually products contain polymerization inhibitors. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse with a temperature not exceeding 30°C. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. It should not be stored in large quantities or for long periods of time. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
(1) By-product recovery method When phenol and acetone are produced by the cumene method, α-methylstyrene is a by-product. A device with an annual output of 10,000 tons of phenol and acetone will produce about 500t of α-methylstyrene as a by-product. (2) Cumene catalytic dehydrogenation method This product can also be obtained by dehydrogenating cumene in the presence of a catalyst. 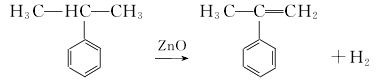 However, in industry, the by-product α-methylstyrene is often hydrogenated and converted into isoforms propylbenzene. Usually Fe2O3 is used as the main catalyst, and Cr2O3 and K2O are used as cocatalysts. An isothermal integrating single tubular reactor is used, with a 1 mm × 8 mm thermocouple tube in the center of the reactor and a catalyst inside. The reaction materials and water are injected into the catalyst layer by a micro-metering pump. After the reaction product is cooled by the cooler, it is separated by the separator. The oil sample composition is analyzed and the gas is measured and vented. The main factors affecting the conversion rate are reaction temperature, space velocity, and water-oil volume ratio. Temperature 610-620℃; air speed 10-15h-1; water-oil volume ratio 20-25.
However, in industry, the by-product α-methylstyrene is often hydrogenated and converted into isoforms propylbenzene. Usually Fe2O3 is used as the main catalyst, and Cr2O3 and K2O are used as cocatalysts. An isothermal integrating single tubular reactor is used, with a 1 mm × 8 mm thermocouple tube in the center of the reactor and a catalyst inside. The reaction materials and water are injected into the catalyst layer by a micro-metering pump. After the reaction product is cooled by the cooler, it is separated by the separator. The oil sample composition is analyzed and the gas is measured and vented. The main factors affecting the conversion rate are reaction temperature, space velocity, and water-oil volume ratio. Temperature 610-620℃; air speed 10-15h-1; water-oil volume ratio 20-25.
Purpose
Monomers or modified monomers commonly used in polymerization reactions to produce adhesive base materials. It is one of the important monomers for synthetic resins and plastics, and is also a modifier for polyester resin, alkyd resin and ABS resin. It can also be used in the production of coatings, plasticizers, solvents, and organic synthesis.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

