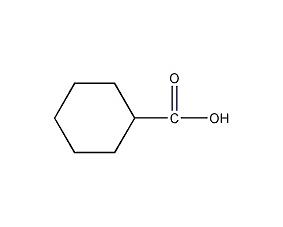
Structural formula
| Business number | 02ES |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H12O2 |
| Molecular weight | 128.17 |
| label |
Hexahydrobenzoic acid, cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, Hydrogenated benzoic acid, Hexahydrobenzoic acid, Fema 3531, Akosbbs-00003723, Rarechem al bo 1301, Timtec-bb sbb008550, Cyclohexancarbonsaeure, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:98-89-5
MDL number:MFCD00001461
EINECS number:202-711-3
RTECS number:GU8370000
BRN number:970529
PubChem number:24901765
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless flake or columnar crystals.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.033
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.033422
4. Melting point (ºC): 31
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 229~234
6. Boiling point (ºC, 1.7kPa): 120-121
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.4530
8 . Flash point (ºC): >110
9. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.027430
10. Refractive index at room temperature ( n20): 1.459922
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor Pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in most organic solvents.
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 3265mg/kg;
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 33.77
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 118.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 300.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 41.2
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. ExtremeTransformation rate: 13.39
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.9
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 104
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants.
2. Exist in smoke.
Storage method
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from catalytic hydrogenation of benzoic acid. 2. Obtained from cyclohexanol through chlorination and carboxylation.
2. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, reflux condenser, and dropping funnel, add 13.4g (0.55mol) clean magnesium chips. One grain of iodine, add 50mL of anhydrous ether. Slowly add 20 mL of a solution composed of 59.5 g (0.5 mol) of cyclohexyl chloride (2) and 300 mL of anhydrous ether, and slowly heat to start the reaction. Keep boiling and add the rest of the solution dropwise. After the addition was completed, the reaction was continued with reflux and stirring for 0.5 h. The ice-salt bath was cooled to -10°C, dry carbon dioxide gas was introduced, and the reaction was exothermic. After about 2 hours of passage, the reaction temperature dropped, indicating the end of the reaction. Add 100g of ice water to the reaction solution, and adjust it with dilute hydrochloric acid until it becomes acidic to the Congo red test paper. The ether layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted once with ether. Combine the ether layers and extract the ether layer with excess sodium hydroxide solution. Separate the ether layer. Acidify the aqueous layer with dilute hydrochloric acid, separate the organic layer, and distill the aqueous layer until no oil is distilled out. The eluate was saturated with sodium chloride, and the organic layer was separated. The organic layers were combined, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and distilled under reduced pressure. The fractions at 120-121°C/1.7kPa were collected to obtain 54g of cyclohexylcarboxylic acid (1), with a yield of 85%. [1]
3. Preparation method:
Add 122g (1mol) of benzoic acid (2) into the high-pressure reaction kettle ), cyclohexane carboxylic acid, 10% Pd-C catalyst, remove the air and introduce hydrogen to a pressure of 3.92Mpa, slowly heat to 105°C, stir and hydrogenate, keep the reaction temperature at 145~160°C, and the pressure drops. Then add hydrogen until no more hydrogen is absorbed. After cooling, vent, filter to remove the catalyst, distill under reduced pressure, and collect the fraction at 48°C/3.0kPa to obtain product (1) with a yield of 95%. [2]
Purpose
Used to synthesize medicines, pesticides, dyes and other organic compounds

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

