
Structural formula
| Business number | 02GV |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H6O3 |
| Molecular weight | 138.12 |
| label |
p-phenol formic acid, p-Hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-Carboxyphenol, 4-Hydroxy-benzoic acid, Acidop-idrossibenzoico, Paraben, p-Salicylic acid, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:99-96-7
MDL number:MFCD00002547
EINECS number:202-804-9
RTECS number:DH1925000
BRN number:970950
PubChem number:24878885
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow crystal.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.46
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 214~216
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 45mmHg): Undetermined
p>
7. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.483
8. Flash point (ºC): 199
9. Specific rotation Degree (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC) : Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble In water, easily soluble in hot water and ethanol, soluble in ethanol and ether. Insoluble in carbon disulfide.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: >10mg/kg; rat peritoneal cavity LD50: 340mg/kg; mouse oral LC50: 2200mg/kg; mouse peritoneal cavity LC50: 210mg/kg; small Rat subcutaneous LC50: 1050mg/kg;
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: rat oral TDLo: 42mg/kg/6W-I; rat oral TDLo: 15mg/kg/30D-I;
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment and can cause pollution to water bodies and the atmosphere. Organic acids can easily form acid rain during atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physical changes. Therefore, when the pH value drops below 5, it will cause serious harm to animals and plants. The reproduction and development of fish will be seriously affected, and the soil and water bodies in the basin will be severely affected.Metals in mud can be dissolved into water and poison fish. Acidification of water bodies will also lead to changes in the composition and structure of aquatic organisms. Acid-resistant algae and fungi will increase, while root plants, bacteria and vertebrates will decrease, and the decomposition rate of organic matter will decrease. Acidification will seriously lead to the reduction or death of fish in lakes and rivers.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.06
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 100.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 284.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 64.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 13.90
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 4
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 57.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 125
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid light and contact with strong oxidants.
2. Exist in flue-cured tobacco leaves, burley tobacco leaves, oriental tobacco leaves and smoke.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed.
2. They should be stored separately from oxidants and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage.
3. Equipped with corresponding varieties and quantities of fire-fighting equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. There are many methods for producing parahydroxybenzoic acid. The potassium phenolate carboxylation method is more suitable for industrial production. This method is divided into the potassium phenolate solid phase carboxylation method, the potassium phenolate solvent carboxylation method, and the potassium phenolate and carbon dioxide method. Continuous gas-liquid phase method. Add about 40% potassium hydroxide solution and phenol into the reaction pot and mix, and stir at 100°C for 0.5h until the free base of the potassium phenolate solution is 0.3-1.2%. Heating, perform normal pressure dehydration, change to reduced pressure dehydration when the internal temperature reaches 140°C, and steam water under a pressure of 10.6kPa for about 0.5-1h until the internal temperature reaches above 170°C. Add the solvent phenol and carry out azeotropic dehydration. The dehydration is completed at 200°C (2.67kPa) to obtain a complex salt of potassium phenolate and phenol. Continue to heat the prepared above-mentioned composite salt to 220-230°C, pass in purified anhydrous carbon dioxide, maintain the pressure at 0.5MPa, react for 2.5 hours, cool to 200°C and add phenol, keep stirring for 30 minutes, and then recover phenol under reduced pressure to All. Then carbon dioxide is introduced for the second carboxylation, which takes about 2 hours. After the carboxylation is completed, recover the phenol, cool it to below 180°C, add water to dissolve it, and obtain the carboxylated liquid (dipotassium p-hydroxybenzoate). Gradually add sulfuric acid to the carboxylation solution and neutralize it to pH 6.7 below 70°C. The potassium sulfate is removed by cooling and filtration, and the resulting crude filter cake is recrystallized with water and decolorized with activated carbon to obtain parahydroxybenzoic acid with a content of more than 99%. Dipotassium p-hydroxybenzoate can also be obtained by translocation of dipotassium salicylate. Therefore, p-hydroxybenzoic acid can also be obtained industrially from salicylic acid through salt formation, translocation, and neutralization, but the cost is relatively high. In addition, p-toluenesulfonyl chloride, a by-product during the production of saccharin, can also be obtained through ammoniation, oxidation, acid precipitation, alkali fusion, and acid precipitation. This method has low yield and high cost, and the saccharin by-product often contains toxic impurity o-sulfonamidotoluene.
2. Stir ethyl paraben, water, and NaOH evenly, then reflux until there is no oil. After cooling, add HCL to pH=1~2, and filter the crude crystals obtained. Recrystallize from 50% ethanol to obtain the finished product:
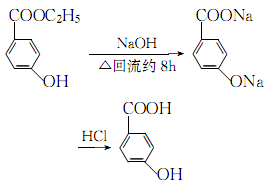
3. Tobacco: OR, 41, 44; FC, 54; BU, 26.
Purpose
1. Mainly used in organic synthesis, dyes, spices and other industries, and also used in the preparation of efficient preservatives.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

