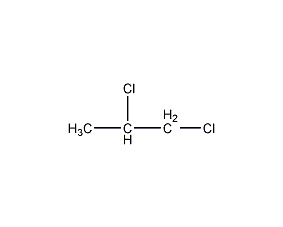
Structural formula
| Business number | 01NT |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H6Cl2 |
| Molecular weight | 112.99 |
| label |
Propylene-o-dichloride, propylene dichloride, Chlorinated propylene, Propylene dichloride, Propylene chloride, Solvent for resins and waxes, metal degreaser, soil fumigant, pesticides, Medium for chlorination and sulfonation reactions, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-87-5
MDL number:MFCD00000868
EINECS number:201-152-2
RTECS number:TX9625000
BRN number:1718880
PubChem number:24845325
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with chloroform smell.
2. Boiling point (ºC): 95~96
3. Melting point (ºC): -100
4. Relative density (g/mL, 20ºC ): 1.156
5. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 3.9
6. Refractive index: 1.4388
7. Viscosity ( mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.865
8. Flash point (ºC): 4
9. Fire point (ºC): 557.2
10. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, b.p.): 323.2
11. Heat of fusion (KJ/kg): 56.6
12. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 1545.4
13. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC): 1.30
14. Critical temperature (ºC): 304.3
15. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.4
16. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): 5.33
17. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): 3.4
18. Upper explosion limit ( %, V/V): 14.5
19. Body expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC): 0.001108
20. Solubility: insoluble in Water is miscible with most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, benzene, and carbon tetrachloride. Can dissolve grease, wax, rubber, resin and various dyes. The solubility in water at 20℃ is 0.26%.
21. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.395
22. van der Waals area ( cm2·mol-1): 7.640×109
23. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 54.540
24. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1) :-162.8
25. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -198.8
26. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1):145.8
Toxicological data
Can irritate eyes and mucous membranes and cause dermatitis. High concentrations have a depressant effect on the central nervous system. And damage the liver and kidneys. The olfactory threshold concentration is 231 mg/m3, and the maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 350 mg/m3 (USA). The oral LD50 of mice is 860mg/kg, and the lethal concentration of inhalation in rats is 9240mg/m3.
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 25.60
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 101.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 225.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 24.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.15
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 20.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Its vapor and air form an explosive mixture, which can cause combustion and explosion when exposed to open flames and high heat. The explosion limit is 3.4~14.5 (volume) and is decomposed by high heat to produce toxic corrosive gases. Pure and dry 1,2-dichloropropane is non-corrosive to metals. When water is present, it releases highly corrosive hydrogen chloride. Light can accelerate the decomposition reaction. Heating to 540~750℃ generates a mixture of 3-chloropropene and 1-chloropropene. It is heated to above 96°C in an aqueous alkali solution under pressure to generate 2-chloropropene. The alcohol solution with alkali is heated to 60~75°C to generate a mixture of 2-chloropropene and 1-chloropropene. Reacts with lower fatty acid salts to form esters of 1,2-propanediol. Heated with concentrated ammonia to 80°C to obtain the hydrochloride of 1,2-diaminopropane.
Storage method
Seal and save. The warehouse is ventilated and dried at low temperature; stored separately from oxidants and acids. It can be stored in iron, mild steel or aluminum containers.
Synthesis method
Obtained from liquid phase low-temperature chlorination of propylene and chlorine in dichloropropane. This product is also produced during the high-temperature chlorination of propylene to produce chloropropane.
[Preparation method] Propylene and chlorine are obtained by low-temperature chlorination of propylene and chlorine in dichloropropane.
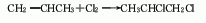
Purpose
Used as raw materials for organic synthesis, solvents for oils and fats, raw materials for detergents, resins, and pesticides. Propylenediamine can be obtained by amination. 1,2-Dichloropropane and 1,3-Dichloropropene, as pesticide drop-mixing agents, D-D, Vidden D, [8003-19-8]. D-D is a pre-sowing nematicide that can effectively control soil nematodes, including root knot nematodes, meadow nematodes, stinging nematodes, sword nematodes, spiral nematodes and beet nematodes. The effect is best when the pesticide is applied to a soil depth of 15-20cm. This product is phytotoxic, and there must be at least 15 days between application and planting. Less toxic to bees. Used as a solvent for resins and waxes, a degreasing agent for metals, a fumigant for soil, a pesticide, a medium for chlorination and sulfonation reactions, and a raw material for manufacturing amines, rubber, medicine, etc. Mixtures with acetone can be used as solvents for cellulose ethers and cellulose esters.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

