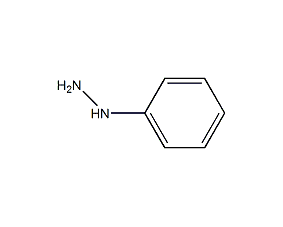
Structural formula
| Business number | 02JD |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H8N2 |
| Molecular weight | 108.14 |
| label |
benzene hydrazinate, phenylhydrazine, phenylhydrazine, phenylhydrazine oxalate, phenylhydrazine oxalate, phenylhydrazine, Hydraminophen, Phenylhydrazine, hydrazinated benzene, phenylhydrazine, 1-Phenylhydrazine, Fenilidrazina, Fenylhydrazine, Hydrazine,Phenyl-, Hydrazine-Benzene, Phenyldiazane, Phenylhydrazin, Phenyl-Hydrazin |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-63-0
MDL number:MFCD00007573
EINECS number:202-873-5
RTECS number:MV8925000
BRN number:606080
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow crystal or oily liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 19.4[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 243.5 (Decomposition) [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.10[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 3.7[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (115℃)[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.9[7]
8. Flash point (℃): 89 (CC) [8]
9. Ignition temperature (℃): 615[9]
10. Explosion upper limit (%): Temporary No information
11. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.3[10]
12. Solubility: insoluble in cold water, slightly soluble in hot water, Miscible in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and benzene. [11]
13. Refractive index: 1.6084
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[12]
LD50: 188mg/kg (rat oral); 175mg/kg (mouse Oral); 80mg/kg (rabbit oral); 90mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
2. Irritation No data yet p>
3. Mutagenicity [13] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 4600nmol/dish. Gene transformation and mitotic recombination: Saccharomyces cerevisiae 25mg/L. DNA damage: mice were given 350 μmol/kg intraperitoneally.
4. Others[14] The lowest toxic dose in rat abdominal cavity (TDLo): 30mg/kg (gestation 17~19d), for newborn rats Behavior has consequences.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15]
LC50: 0.16~0.26mg/L (96h) (zebrafish); 21.4mg/L (24h), 15.7mg/L (48h) (medaka, static)
EC50: <1200μg/L (24h) (Daphnia, static)
2. Biodegradability [16] Static Zahn-Wellens test, 85% degradation in 9~13 days.
3. Non-biodegradability[17] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 9h (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 34.76
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 96.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 255.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 49.9
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 13.78
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 38
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 57.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Combustible in case of open flame or high heat. Can react with strong oxidizing agents. It decomposes when heated and releases toxic nitrogen oxide fumes.
2. It turns reddish brown in the air, is toxic, and can cause hemolysis of red blood cells.
3. Stability[18] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[19] Strong oxidizing agent
5. Conditions to avoid contact [20] Heat, light, contact with air
6. Hazards of aggregation[21] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Prepared by reduction of diazobenzene chloride.
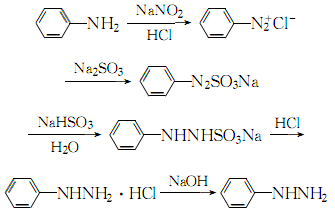
2. Mix aniline and 30% hydrochloric acid aqueous solution at a molar ratio of 1:2, cool to 2°C, and slowly add 6 mol/l sodium nitrite while controlling the temperature at 0 to 5°C. Stir the solution until the starch potassium iodide test paper turns blue, continue stirring for 30 minutes, and obtain a diazonium salt solution for later use. At 10 to 15°C, use concentrated sodium hydroxide to adjust the 40% sodium bisulfite solution to a pH of 6 to 7, and cool it to 0 to 5°C. Add the above diazonium salt quickly while stirring, and then continue Stir for 15 minutes. When the ph value is 6 to 7, raise the temperature to 70 to 80°C, and slowly pass the concentrated hydrochloric acid through a catheter below the reaction liquid level. After adding, keep the temperature constant for 1 to 2 hours, cool to below 20°C, and filter. The resulting crystal is phenylhydrazine hydrochloride. Dissolve the obtained phenylhydrazine hydrochloride with a small amount of water, add activated carbon for decolorization, add excess sodium hydroxide solution to the filtered filtrate, cool to 15-20°C and extract several times with benzene or ether, combine the extracts, and add anhydrous carbonic acid The potassium is dried, and then benzene or ether is recovered. The crude phenylhydrazine obtained is distilled at 2399Pa, and the 137-138°C fraction is collected, which is pure phenylhydrazine. The process reaction is as follows:
Purpose
1. It is used in the preparation of dyes, drugs, developers, etc. It is also an important reagent for identifying carbonyl groups and is used to identify aldehydes, ketones and sugars.
2. Used as a reducing agent for the photometric determination of phosphorus and selenium. Also used as a characteristic derivatization reagent for aldehydes and ketones.
3. Used in organic synthesis, analytical reagents and the manufacture of dyes and drugs. [23]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

