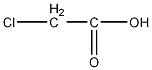
Structural formula
| Business number | 01PC |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H3ClO2 |
| Molecular weight | 94.5 |
| label |
Chloroacetic acid, Monochloroacetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, Monochloroacetic acid, Anhydrous chloroacetic acid, TZR-701 flame retardant lubricant, Melamine isocyanurate salt, Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:79-11-8
MDL number:MFCD00002683
EINECS number:201-178-4
RTECS number:AF8575000
BRN number:605438
PubChem number:24865140
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless crystals, deliquescent. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 50~63[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 189[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.4~1.58[4]
5 .Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.26[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.67 (71.5℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.78[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.22[8 ]
9. Flash point (℃): 126 (CC) [9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): >500[10]
11. Lower explosion limit (%): 8.0[11]
12. Solubility: Soluble in water, ethanol, ether, chloroform, carbon disulfide. [12]
13. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol, 61ºC): 19.3
14. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol, 56ºC): 18.8
15. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol, 51ºC): 15.9
16. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, solid): 726.4
17. Electrical conductivity Rate (S/m, 60ºC): 1.4×10-6
18. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.433060
19. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.435155
20. Relative density (25 ℃, 4℃): 1.37763
21. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.404340
22. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -435.2
23. The crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol -1):-510.5
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[13]
LD50: 76mg/kg (rat oral); 255mg/kg (oral in mice)
LC50: 180mg/m3 (inhaled in rats)
2. Irritating strong> No data yet
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[14] Rat feed contains 1% When treated with chloroacetic acid, the growth was slow during the 200-day experimental period, and liver glycogen was found to increase, but there was no other special damage.
4. Mutagenicity[15] Mammalian somatic cell mutation: mouse lymphocytes 400mg/L. Sister chromatid exchange: Hamster ovary 160mg/L. Cytogenetic analysis: Rat oral administration 0.5ppb
Ecological data
��Chloroform. The trichlorethylene hydration method carries out the addition and hydrolysis of water at the same time: the reaction temperature is 160-180°C, the sulfuric acid concentration during the reaction should be maintained at 93%, and the ratio of trichlorethylene and water should be controlled. Sulfuric acid consumption does not exceed 50kg, and 30% hydrochloric acid is a by-product of 2.57t. Industrial product chloroacetic acid is colorless or slightly yellowish crystal. Raw material consumption quota: glacial acetic acid (98%) 730kg/t, chlorine 860kg/t, sulfur 26kg/t.
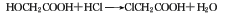
Refining method: use chloroform, tetrahydrofuran After recrystallizing carbon chloride, benzene or water, place it in a vacuum dryer and dry it with phosphorus pentoxide or concentrated sulfuric acid. If further purification is required, it can be distilled in the presence of magnesium sulfate. The distillate is melted and crystallized in stages, and the product is stored in vacuum or dry nitrogen.
(4)Chloroacetic acid can be produced by passing chlorine gas into acetic acid in the presence of acetic anhydride:
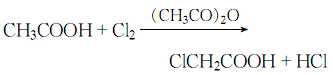
After distillation and refining, the finished product of chloroacetic acid is obtained.
(5) Take industrial chloroacetic acid and place it at 35-40°C for about half a month, dialyze out the liquid acetic acid and dichloroacetic acid in the crystals, then dissolve it in benzene, steam out part of the benzene, stop heating and then cool Recrystallize, filter the crystal to remove trichloroacetic acid, and wash with benzene and a small amount of ether to obtain anhydrous pure chloroacetic acid.
2. Preparation method:
In a container equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, reflux condenser (connected to a gas pipe to the hydrogen chloride gas absorption device), and a ventilation tube (extending into into the reaction bottle (pre-weighed), add 150g (2.5mol) of glacial acetic acid (2) and 6g of red phosphorus, heat to 100°C, slowly add chlorine gas, and keep the reaction temperature between 105 and 110°C . It takes about 5 hours until the mass increases to about 85g. During distillation, first collect acetyl chloride with a lower boiling point and unreacted acetic acid, and then collect the 150-200°C fraction. The liquid of this fraction solidifies upon cooling. Pour off the unsolidified liquid as much as possible, re-distill the solid, collect the fraction at 182-192°C, solidify at 63°C after cooling, and obtain 150-175g of chloroacetic acid (1) with a yield of 64%-74%. [26]
Purpose
1. Used in a wide range of organic synthesis raw materials. In the dye industry, it is used to produce indigo and naphthyl aminoacetic acid dyes; in the pharmaceutical industry, it is used to synthesize drugs and intermediates such as caffeine, barbiturates, epinephrine, vitamin B6, glycine, malonate, etc.; in the pesticide industry, it is used Production of herbicides 2,4-D, butyl ester, 2,4,5-T, thiocyanacetic acid, α-naphthyl acetic acid, glyphosate, alachlor, acetochlor, butachlor and the insecticide dimethoate and more than 20 kinds of pesticides; used in the synthetic fiber industry to produce carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and non-ferrous metal flotation agent Z-200#, and can also be used as chromatographic analysis reagents, etc., and can also be used in food additives and detergents , cold perm essence and other products.
2. Used as an acidifier for starch adhesives. It is also an intermediate for dyes, medicines, pesticides, synthetic resins and other organic synthetic materials. Used in the dye industry to produce indigo dye. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used to synthesize barbiturates, caffeine, epinephrine, vitamin B6 and glycine, etc. The pesticide industry is used to produce dimethoate, 2,4,D and its butyl ester (herbicide), 2,4,5,T (herbicide and growth stimulant), thiocyanacetic acid and naphthylacetic acid, etc. Chloroacetic acid is also an important carboxymethylating agent, used to prepare sodium carboxymethylcellulose, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, etc., and is also used as a non-ferrous metal flotation agent and chromatographic analysis reagent.
3. Used in the preparation of pesticides and as intermediates in organic synthesis. [25]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

