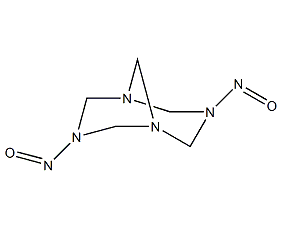
Structural formula
| Business number | 02KB |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H10N6O2 |
| Molecular weight | 186.17 |
| label |
Foaming agent H, 3,7-dinitroso-1,3,5,7-tetraazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane, N,N’-dinitrosopentamethyltetramine, Foaming agent H, Foaming agent BN, Foaming agent DPT, Blowing agent H, 3,7-2-nitroso-1,3,5,7-4-azabicyclo[3.3.1] nonane, N, N’-2-nitroso-five tetramine, Foaming agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:101-25-7
MDL number:MFCD00023882
EINECS number:202-928-3
RTECS number:XA5250000
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow powder, no odor. [1]
2. Melting point (ºC): 207 (decomposition) [2]
3. Relative density ( Water = 1): 1.4~1.45[3]
4. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, insoluble in ether, slightly soluble in ethanol, chloroform, soluble in acetone. [4]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[5] LD50: 940mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability No data
3. Non-biodegradability No information yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 44.12
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 103.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 325.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 98.5
5. Polarizability: 17.49
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 8
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 71.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 189
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Soluble in ethyl acetoacetate and dimethylformamide, slightly soluble in water and ethanol, slightly soluble in chloroform, pyridine, methyl ethyl ketone and acrylonitrile, almost insoluble inEther. When stearic acid or urea is mixed in, the decomposition temperature can be lowered. The gas production volume is 260-270ml/g. The decomposition products are mainly nitrogen, with a small amount of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and other gases. Adding urea can eliminate odor. It is flammable and will quickly catch fire when in contact with acid or acid mist. May spontaneously ignite when rubbed or knocked. It is hydrolyzed in concentrated acid, concentrated alkali and hot water. It is flammable and the product has odor. Adding urea compounds can prevent the odor from appearing in the product. Adding weakly acidic or amphoteric metal oxides, urea, and borax will stabilize the foaming agent. The addition of cyanoguanidine, phthalamide, polyols, glycerin and salts of lead, chromium, zinc, calcium, barium, aluminum and magnesium lowers the decomposition temperature and accelerates the foaming process.
2. Stability[6] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[7] Strong oxidants, acids, alkalis
4. Conditions to avoid contact [8] Heat, friction, Vibration or impact
5. Polymerization hazard[9] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products [10] Nitrogen oxides
Storage method
Storage Precautions[11] Stored in a cool, dry and well-ventilated non-combustible warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 35℃. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
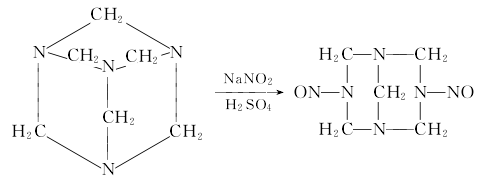
It is obtained by nitrosation of hexamethylenetetramine (urotropine). After dissolving urotropine and sodium nitrite in water, add dilute sulfuric acid (or dilute hydrochloric acid) dropwise while stirring, and control the reaction temperature at about 0°C. After nitrification is completed, add a small amount of ammonia and sodium nitrite. The product is filtered, washed, spin-dried, dried and sieved to obtain the finished product. The purity of industrial foaming agent H is ≥98%. Raw material consumption (kg/t) methenamine 720 sodium nitrite 1018 sulfuric acid (93%) 800 chlorine water (20%) 650
Purpose
1. This product is one of the widely used foaming agents. It is mainly used to make sponge rubber and is mostly used in polyvinyl chloride in plastics. This product is decomposed into nitrogen when heated to cause pores. It has a large amount of gas and high non-foaming efficiency. Using organic acids such as salicylic acid, adipic acid, phthalic acid or urea as foaming aids can reduce the decomposition temperature and adjust it to the range of 90-130°C. The product generates a large amount of heat when decomposed, so it is easy to carbonize the center of thick products, and the decomposition products have a foul odor. Used with urea to eliminate odor. Can be used as polyvinyl chloride and its copolymers, polyolefins, polystyrene, polyamide, polyester, phenolic resin, polyvinylidene chloride, polysiloxane, polychloroprene, ethylene and propylene copolymers, Foaming agent for polyethylene oxide and its elastomers.
2. It is a foaming agent widely used in the field of rubber foaming. It has the advantages of high foaming efficiency, no discoloration, and no pollution. Can be used as a foaming agent for adhesives or sealants. It is also a commonly used organic microporous foaming agent in the manufacture of sponge rubber and foam plastics. It is easy to disperse in the rubber material and has no pollution, but the decomposition temperature is high and the decomposition products have a smell. Using salicylic acid, adipic acid, phthalic acid, etc. as foaming aids, the decomposition temperature can be adjusted between 90 and 130°C. Use urea to eliminate odor. The dosage in polyvinyl chloride is 7% to 25%, and the dosage in rubber is 3% to 5%.
3. Used as a foaming agent for rubber, polyvinyl chloride and other plastics to produce microporous plastics. [12]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

