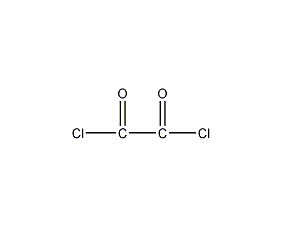
Structural formula
| Business number | 01PT |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2Cl2O2 |
| Molecular weight | 126.92 |
| label |
oxalyl chloride, Ethanedioyl dichlorid |
Numbering system
CAS number:79-37-8
MDL number:MFCD00000704
EINECS number:201-200-2
RTECS number:KI2950000
BRN number:1361988
PubChem number:24853204
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless fuming liquid
2. Relative density: 1.488
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Uncertain
4. Melting point (ºC): -12
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 63-64
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa ): Uncertain
7. Refractive index: 1.4340 (13℃)
8. Flash point (ºC): Uncertain
9. Specific rotation (º): Uncertain
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Uncertain
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Uncertain
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Uncertain
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Uncertain
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19. Solubility: Soluble in ether , can decompose violently when exposed to water and alcohol. It decomposes and releases carbon monoxide when heated to about 600°C. Soluble in n-hexane, benzene, ether, acetonitrile and halogenated solvents such as dichloromethane and chloroform.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity Rat inhalation LC50: 1840ppm/4H
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 21.07
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 78.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 198.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 40.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.35
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 34.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 75.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the atomic stereocenter�Number: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determined number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain Number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Oxalyl chloride is not only sensitive to air, but will decompose and release hydrogen chloride when encountering moisture, and it also has an unpleasant smell.
2. Oxalyl chloride is highly toxic and corrosive and can seriously irritate eyes, skin and respiratory tract. Reagent bottles containing oxalyl chloride must be stored in a cool, dry environment, tightly sealed, and strictly prohibited from contact with moisture. Oxalyl chloride can react violently with water and release toxic gases CO, CO2 and HCl.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dark place.
Synthesis method
Mix anhydrous oxalic acid and phosphorus pentachloride, slowly heat to about 64°C, and react until there is no hydrogen chloride. Oxalyl chloride is obtained after distillation of the crude product.
Purpose
1. Used as an intermediate for the synthesis of benzoylurea pesticides such as flufluturon and flufenuron, etc., and also as an intermediate for the sulfonylurea herbicides metsulfuron-methyl, bensulfuron-methyl, pyrazosulfuron-methyl, etc. intermediate.
2. Oxalyl chloride is a widely used acylating reagent for the preparation of phosgene, phosphoryl dichloride, chlorinated alkanes and acyl isocyanates.
Oxalyl chloride is a very effective acylating reagent and can be widely used in the preparation of acyl azides, brominated alkenes, carbon amides, o-naphthalenes, azoketones, lactones, and the realization of ethylene Cycloaddition reaction of ketones, intramolecular Fridel-Crafts acylation reaction.
Similar to thionyl chloride, the reaction between oxalyl chloride and acid will give gas by-products, and the generated chloride can be easily separated (formula 1)[1].
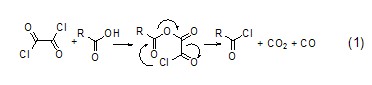
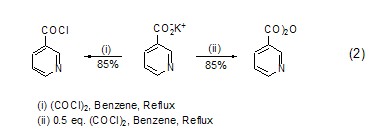
The relationship between oxalyl chloride and carboxylate ion The mechanism of action includes nucleophilic substitution and intramolecular charge transfer, thereby forming the corresponding acid chloride product. An acid anhydride compound (formula 2)[2] can also be obtained by adjusting the ratio of oxalyl chloride and carboxylate ions.
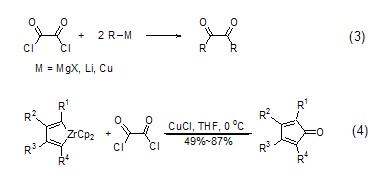
Oxalyl chloride and metal organic compounds such as Grignard reagent and alkyl lithium react to generate ortho-dicarbonyl compounds (formula 3)[3]. Oxalyl chloride and zircocyclopentadiene generate cyclopentadienone derivatives (formula 4)[4] under the action of CuCl.
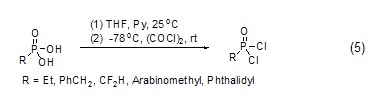
Oxalyl chloride can be used to prepare phosphorus oxychloride derivatives. For example, phosphoric acid can be converted into the corresponding phosphorus oxychloride with high yield under the action of oxalyl chloride and pyridine at low temperature ( Formula 5)[5].
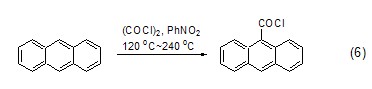
Oxalyl chloride can also be directly converted into an alkane Or a chlorocarbonyl group is introduced into a cycloalkane compound, but usually the reaction results in a mixture. Aromatic hydrocarbon compounds can also undergo chlorocarbonylation reaction under the action of oxalyl chloride and Lewis acid. Among them, anthracene can also react directly without a catalyst (Formula 6)[6].
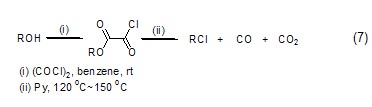
Alcohol compounds react with oxalyl chloride to obtain oxalyl monoalkyl ester, which is then converted into chlorinated alkane compounds (formula 7) under heating conditions. [7]
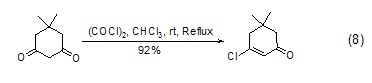
Oxalyl chloride and 1,3 -Diketone reaction can generate β-chloroolefin cyclide (Formula 8)[8] with high yield.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

