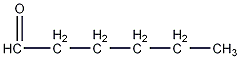
Structural formula
| Business number | 01E3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H12O |
| Molecular weight | 100.16 |
| label |
Hexanal, Hexanal, Caproic aldehyde, Hexaldehyde, Capronaldehyde |
Numbering system
CAS number:66-25-1
MDL number:MFCD00007027
EINECS number:200-624-5
RTECS number:MN7175000
BRN number:506198
PubChem number:24847229
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -56.3[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 128~131[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.83[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.45[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3946.3[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.46[ 8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.78[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 32 ( OC)[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 197[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.1[12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.3[13]
14. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in benzene and acetone, easily soluble in ethanol and ether. [14]
15. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.8096
16. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.4040
17. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4017
18. Critical density (g·cm-3 ): 0.265
19. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 378
20 .Critical compression factor: 0.266
21. Eccentricity factor: 0.439
22. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.079
23. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 9.890×109 sup>
24. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 69.700
25. Liquid phase Standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 211.2
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 4890 mg/kg; rat inhalation LCLo: 2000 ppm/4H; mouse oral LD50: 8292 mg/kg;
2. Cause Mutation: Mouse liver irregular DNA comprehensive test system: 30 mmol/L;
3. Acute toxicity[15] LD50: 4890mg/kg (rat oral)
4. Irritation[16]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 100mg (24h), mild irritation.
5. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Mouse inhalation 0.75~27mg/m3 , 2~4 hours a day, 1 month later, 2/13 died.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No information available
2. BiodegradationPerformance[18] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100ppm, sludge concentration 30ppm, 50% degradation after 4 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 13h (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 30.03
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 124.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 279.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 25.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.90
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 41.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[20] Stable
2. Incompatible substances [21] Strong oxidizing agent, strong reducing agent, strong alkali
3. Conditions to avoid contact[ 22] Heated, humid air
4. Polymerization hazard[23] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Stay away from China and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. It should not be stored for a long time to avoid deterioration. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Preparation method:
![]()
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser, and thermometer, add 22.5 mL of 2,3-dimethyl-2-butylborohydride in THF (containing 25 mmol of hydride), and cool to – 20℃ (dry ice-carbon tetrachloride). Then, a THF solution of 0.58g (5mmol) n-hexanoic acid (2) was slowly added dropwise under stirring (cooled to -20°C). After 10 minutes, slowly raise the temperature and heat to reflux. The content of n-hexanal (1) was determined at different reaction times. The yield of (1) when reacting for 12 hours was 68%; the yield of (1) when reacting for 24 hours was 88%; the yield of (1) when reacting for 36 hours was 98%. [26]
2. Preparation method:
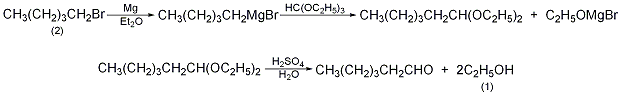
Into a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, dropping funnel, ventilation tube, and reflux condenser, add 200 mL of anhydrous ether and 57 g of anhydrous stannous chloride. Dry hydrogen chloride gas was introduced under cooling until saturated, and the reaction liquid was divided into two layers. 19.5g (0.2mol) of dry capronitrile (2) was added dropwise under stirring, and imine hydrochloride crystals precipitated during the reaction. After the addition is complete, continue stirring the reaction for 15 minutes. Strain out the solids. Add the solid matter to another reaction bottle, add about 50 mL of water, and heat to reflux until the hydrolysis is complete. Cool and extract with ether. Dry over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and perform fractional distillation. First, evaporate the diethyl ether, and then collect the fraction at 127-129°C to obtain 19g of hexanal (1), with a yield of 95%. [27]
3. Preparation method:
Equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser (installed with calcium chloride drying tube), dripping liquid In the reaction bottle of the funnel, add 15g of magnesium chips (0.675mol), 50mL of anhydrous ether, one grain of iodine, and 3g of dry 1-bromopentane (2). After the reaction started, 100 mL of anhydrous ether was added. Add a mixture of 91.5g 1-bromopentane (0.625mol in total) and 100mL anhydrous ether into the dropping funnel. Control the dropping speed to maintain reflux until all the magnesium metal reactants are present. Cool to 5°C, add 74g of triethyl orthoformate (82mL, 0.5mol) within 10min, and reflux for 6h. Steam off the ether and slowly add 6% dilute hydrochloric acid cooled with ice water while cooling. When all the solid matter enters the solution, separate the upper acetal layer. Mix acetal with dilute acid made of 50g concentrated sulfuric acid and 350mL water, distill it, collect hexanal in a receiving bottle containing a solution made of 50g sodium bisulfite and 150mL water, and separate the oil (1- pentanol). Steam distillation evaporates about 100 mL of water, which can further remove 1-pentanol and gas impurities. The residue is cooled to 45°C, a compound of 40g sodium bicarbonate and 100mL water is slowly added, steam is distilled, and the generated hexanal is evaporated. Separate the upper organic layer to obtain crude 1-hexanal. Wash three times with water, dry over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, fractionate, and collect the fractions at 127 to 129°C to obtain 25 g of 1-hexanal (1), with a yield of 50%. [28]
Purpose
1. Used to synthesize spices and prepare caproic acid. Also used as gas chromatography analysis reagent.
2. Used in high-end spices, beauty products, soaps, laundry and care products, and household use.
3. Commonly used in baked goods, frozen dairy products, and meat products.
4. Used as plasticizer and in the organic synthesis of rubber, resin and pesticides. [25]
Ingredients, beauty products, soaps, laundry and care products, and household use.
3. Commonly used in baked goods, frozen dairy products, and meat products.
4. Used as plasticizer and in the organic synthesis of rubber, resin and pesticides. [25]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

