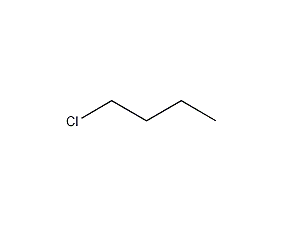
Structural formula
| Business number | 02ZJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H9Cl |
| Molecular weight | 92.57 |
| label |
1-Chlorobutane, Chlorobutane, n-butyl chloride, Butyl chloride, n-Butane chloride, n-butyl chloride, 1-Butylchloride, Butyl chloride, Aliphatic halogenated derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-69-3
MDL number:MFCD00001009
EINECS number:203-696-6
RTECS number:EJ6300000
BRN number:1730909
PubChem number:24865930
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -123.1[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 78.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.89[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.20[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 10.7 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2696.7[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 269[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.68[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.39 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -9 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature ( ℃): 460[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 10.1[13]
14. Explosion Lower limit (%): 1.9[14]
15. Solubility: Insoluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents such as ethanol and ether. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.469
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 30.02
18. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 298.16K, liquid): 186.7
19. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 298.16K, gas): 152.8
20. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 17.2ºC, constant volume): 2701.07
21. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 1.89
22. Conductivity (S/m, 30ºC): 10-101
23. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00080
24. Solubility (%, water, 20ºC): 0.08%
25. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.8857
26. Relative Density (25℃, 4℃): 0.8804
27. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4001
28. Solubility parameter (J· cm-3)0.5: 17.297
29. van der Waals area (cm2·mol– 1): 7.970×109
30. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 55.980
31. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -154.63
32. Liquid phase standard Claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -188.15
33. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1· K-1): 158.1
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16] LD50: 2670mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation No data available
3. Mutagenicity[17] Mammalian somatic cell mutation: mouse lymphocytes 500mg/L.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18] LC50: 97ppm (7d) (rainbow killifish); 79mg/L (48h) (green Medaka)
2. Biodegradability No data available
3. Non-biodegradability[19] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 7d (theoretical ).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 25.42
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 105.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 229.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 22.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.08
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 13.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Can dissolve wax, various rubbers, natural resins and polyvinyl acetate. It dissolves in stearic acid and paraffin when heated. The solubility in water at 20°C is 0.08%, and the solubility of water in chlorobutane is 0.11%. Dry chlorobutane has no obvious corrosive effect on metals. In the presence of water, it decomposes and releases highly corrosive hydrogen chloride. Solvents that have been stored or recycled should be checked for acidity before use. It is easy to catch fire and will produce highly toxic phosgene when heated.
2. Heating to 450~650℃ to remove hydrogen chloride, mainly producing 1-butene. Heating to 450°C under the catalysis of calcium chloride produces a mixture of 1-butene (20%) and cis and trans-2-butene (80%). Reacts with aniline to produce N-butylaniline and N,N-dibutylaniline. Reacts similarly with N-methylaniline, N-ethylaniline, o-toluidine, p-toluidine, etc. In the presence of anhydrous aluminum trichloride, it reacts with benzene to form butylbenzene, and reacts with toluene to form butyltoluene.
3. Stability[20] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidizing agent, strong alkali
5. Conditions to avoid contact[22] Heating
6. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
7. Decomposition products[24] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of n-butanol and hydrogen chloride: n-butanol and concentrated hydrochloric acid are heated and refluxed in the presence of zinc chloride. The reactants are washed with water, dried, fractionated, and the 75-78.5°C fraction is collected as the finished product. Raw material consumption quota: n-butanol (95%) 1600kg/t, hydrochloric acid (30%) 2780kg/t.
2. The preparation method is to react butanol and hydrogen chloride in the presence of catalyst ZnCl2. After the reaction is completed, the product is washed, dried and fractionated. Reaction equation:
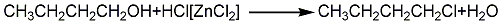
3. From positive It is prepared by heating butanol and concentrated hydrochloric acid in the presence of anhydrous zinc chloride.
4. Preparation method:
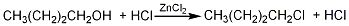
In a 3L reaction bottle, add 860mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, add 1363g (10mol) of anhydrous zinc chloride in batches while cooling, and shake to dissolve the zinc chloride as much as possible. Add 371g (5mol) of n-butanol (2) and a few grains of zeolite. Install a vertical upward reflux condenser with a distillation device at the top. The receiving bottle is connected to the gas absorption bottle with an elbow pipe to absorb the escaping hydrogen chloride gas. Heat the oil bath temperature to 150°C, the solution begins to boil, and 1-chlorobutane is evaporated. Control the flow rate of water in the vertically upward reflux condenser to maintain the temperature of the condenser at 75 to 80°C. When the evaporation is slow, the bath temperature can be slowly increased to about 165°C until there is almost no distillation. The distillate was washed successively with 100 mL cold water, 50 mL cold concentrated sulfuric acid (four times), water, and 10% sodium carbonate solution, dried with anhydrous calcium chloride, and distilled. The fractions at 75.5 to 77.5°C were collected to obtain 1-chlorine. Butane (1) 355g, yield 76%. [27]
Purpose
1. Used in organic synthesis and as polymerization inhibitor. Used as a solvent for grease, rubber, natural resins, polyvinyl acetate, alkylating agent (such as in the manufacture of butylcellulose) and insect repellent.
2. Used as solvent and butylation reagent in organic synthesis. It can also be used to make butyl cellulose, insect repellent, celluloid, phenylbutazone, etc.
3. Used in organic synthesis and as solvent. [26]
. Used as a solvent for grease, rubber, natural resins, polyvinyl acetate, alkylating agent (such as in the manufacture of butylcellulose) and insect repellent.
2. Used as solvent and butylation reagent in organic synthesis. It can also be used to make butyl cellulose, insect repellent, celluloid, phenylbutazone, etc.
3. Used in organic synthesis and as solvent. [26]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

