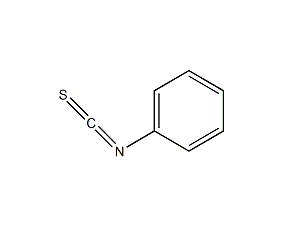
Structural formula
| Business number | 02P3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H5NS |
| Molecular weight | 135.19 |
| label |
phenylthioisocyanate, Phenyl isothiocyanate, phenyl mustard oil, Phenyl mustard oil phenyl isothiocyanate, Phenyl isocyanate, Phenyl isothiocyanate/PITC, Phenyl isothiocyanate, isothiocyanine, Benzene,isothiocyanato-, Benzene-1-isothiocyanate, Fenylisothiokyanat, Iso-Thiocyana-tobenaene, Isothiocyanato-benzen, Isothiocyanatobenzene, Isothiocyanato-Benzene, Phenyl thiocyanate |
Numbering system
CAS number:103-72-0
MDL number:MFCD00004798
EINECS number:203-138-1
RTECS number:NX9275000
BRN number:471392
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or light yellow liquid with a strong pungent odor. [13]
2. Melting point (℃): -21[14]
3. Boiling point (℃): 221[15]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.13[16]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 4.65[17]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (47.2℃)[18]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 3.28[19]
8. Flash point (℃): 87.8[20] sup>
9. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether. [21]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat peritoneal cavity LDLo: 150mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 87mg/kg; mouse peritoneal cavity LD50: 100mg/kg; mouse subcutaneous LD50: 250mg/kg;
2. Reproductive toxicity: subcutaneous TDLo in mice 6-14 days pregnant: 225mg/kgSEX/DURATION;
3. Mutagenicity:
Mutation test: lactation Animal skin contact, 800 μg/L;
Cell production assay test: Mammalian skin contact, 800 μg/L.
4. Acute toxicity [22] LD50: 87mg/kg (mouse oral)
5 .Others [23] Minimum subcutaneous toxic dose in mice (TDLo): 225mg/kg (gestation 6~14d), causing abnormal development of the central nervous system, abnormal eye and ear development, Causes abnormal development of the craniofacial area (including nose and tongue).
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .��Biodegradability No information available
4. Other harmful effects[24] This substance is harmful to the environment, so special attention should be paid pollution of water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 42.63
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 129.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 318.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.1
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 16.90
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 44.4
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 121
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[25] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[26] Water, alcohols, strong alkalis, amines, acids, strong oxidants
3. Conditions to avoid contact[27] Exposure to heat and humid air
4. Polymerization hazard[28] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[29] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of diphenylthiourea and hydrochloric acid. Add diphenylthiourea to hydrochloric acid and heat to dissolve, distill out the resulting phenyl isothiocyanate, add an equal volume of water to the distilled oil, wash it, separate the aqueous layer, and then wash it with dilute alkali solution. After washing with a large amount of water, it is dried with anhydrous calcium chloride and collected at 120-121°C (4.66kPa), which is the finished product.
2. It is obtained by dehydrating 1,3-diphenylthiourea under the action of concentrated sulfuric acid. It can also be obtained by trichloromethyl carbonate and sulfur powder, N< under the catalysis of selenium. [1] is prepared by reacting /em>-phenylformamide.
3. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer and distillation device, add 1.15kg (5.0mol) of diphenylthiourea (2), 25% 4L of hydrochloric acid, stir and heat to dissolve. Then the temperature continues to rise, and the generated phenyl isothiocyanate is continuously evaporated. Cook until no oil comes out. Add an equal volume of water to the distilled solution. Separate the aqueous layer, wash the organic layer with dilute alkali, then wash with water, dry over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and distill under reduced pressure. Collect the fraction at 120~121℃/4.66kPa to obtain 420g of phenyl isothiocyanate (1), yield 62 %. [31]
4. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser, and dropping funnel, add concentrated ammonia water 90mL, add 54g (0.71mol) of pure carbon disulfide while cooling in an ice-salt bath, then slowly add 56g (0.71mol) of aniline (2) dropwise, and finish the addition in about 20 minutes. After the addition is complete, continue stirring the reaction for 30 minutes and leave it for another 30 minutes. Separate the resulting salt. Transfer the salt to a 5L reaction bottle and add 800mL of water to dissolve. Add a solution of 200g (0.605mol) of sales lead dissolved in 400mL of water under stirring to generate lead sulfide precipitation. Steam distillation, put 10mL (0.5mol/L) dilute sulfuric acid into the receiving bottle. Evaporate about 2 to 3L of distillate. The oil layer was separated, dried over anhydrous calcium chloride, and distilled under reduced pressure. The fraction at 120~121°C/4.66kPa was collected to obtain 62g of phenyl isothiocyanate (1), with a yield of 76%. [32]
Purpose
1. Phenyl isothiocyanate can be used to synthesize phenylthiourea derivatives [2~4] and heterocyclic compounds [5,6] .
Synthesis of phenylthiourea Phenyl isothiocyanate reacts with amine to form phenylthiourea derivatives (Formula 1, Formula 2)[7 ,8].
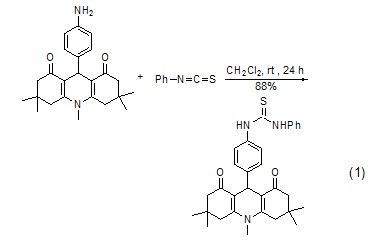
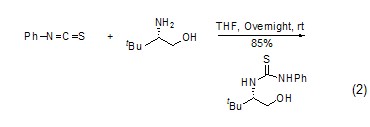
Under the action of n-butyllithium, aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives can also react with phenyl isothiocyanate Reaction occurs on the benzene ring (Formula 3)[9].
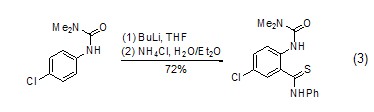
Cyclization reaction Phenyl isothiocyanate can be incorporated into the ring structure to produce a variety of heterocyclic compounds (Formula 4~Formula 6)[10,11].
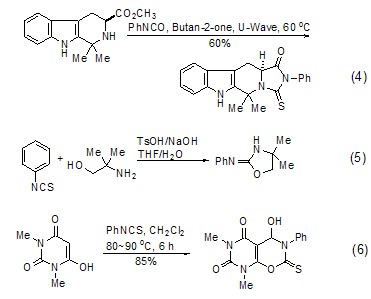
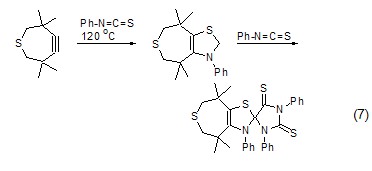
[3+2 ] Cycloaddition reaction Phenyl isothiocyanate can undergo cycloaddition reaction with alkynes, and the organic active intermediate carbene formed reacts with excess phenyl isothiocyanate to form the corresponding heterocyclic compound (Formula 7 )[12].
2. Used as an intermediate for organic synthesis bodies, and synthetic drugs, and are also used in biochemical analyses. [30]
chem.org/internal/day_120516/201205161653544768.jpg” alt=”” />
2. Used as organic synthesis intermediates, synthetic drugs, and biochemical analysis.[30]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

