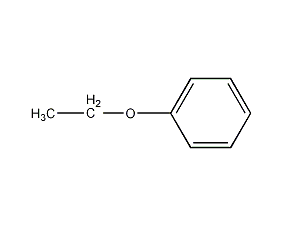
Structural formula
| Business number | 02P4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H10O |
| Molecular weight | 122.16 |
| label |
ethoxybenzene, Phenethyl ether, Ethyl phenyl ether, ethoxybenzene, Ethylphenyl ether, Ethoxybenzene, Phenetol, Phenoxyethane, spices, Ether solvents, Test reagents for aromatic sulfinic acid |
Numbering system
CAS number:103-73-1
MDL number:MFCD00009090
EINECS number:203-139-7
RTECS number:SI7700000
BRN number:636270
PubChem number:24854525
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless oily liquid with aromatic smell.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 170
3. Melting point (ºC): -30
4. Relative density (g/mL, 0/4ºC): 0.9852
5. Relative density (g/mL, 20.2/4ºC): 0.9666
6. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 4.2
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.5075
8. Refractive index (25ºC): 1.5049
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC) : 1.158
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 45ºC): 0.825
11. Flash point (ºC, closed): 63
12. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 44.80
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/kg, constant pressure): 4423.4
14. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant Pressure): 1.8672
15. Critical temperature (ºC): 374.0
16. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.4
17. Conductivity (S/ m, 25ºC): <1.7×10-8
18. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): 0.17
19. Vapor pressure (kPa, 18.1ºC): 0.13
20. Solubility: Insoluble in water, miscible with alcohol and ether. The solubility is similar to that of anisole.
21. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.9651
22. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.9605
23. Eccentricity Factor: 0.415
24. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 19.393
25. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 9.280×109
26. van der Waals volume ( cm3·mol-1): 72.640
27. Gas phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy)(kJ·mol-1): -4475.63
28. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -101.60
29. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -4424.59
30. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) )( kJ·mol-1): -152.64
31. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K -1): 120.1
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: Rat subcutaneous LDLo: 3500mg/kg; Mouse oral LD50: 2200mg/kg; Guinea pig oral LD50: 3mg/kg; acute toxicity is very low, but irritating. The minimum lethal dose for subcutaneous injection in rats is 400mg/kg.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 37.56
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 129.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 303.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 29.8
5. Dielectric constant (20ºC): 4.22
6. Dipole moment (10-30C·m): 3.33
7. Polarizability: 14.89
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 9.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 65
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with strong oxidizing agents. Compared with aliphatic ethers, it is relatively stable in aqueous solutions of amines or alkalis, and only 20% decomposes when heated with sodium alkoxide. When heated with sodium or potassium in pyridine, more than 90% is converted into phenol. It is unstable to acids, especially the ether bond is easily broken under the action of concentrated hydroiodic acid and hydrobromic acid, and decomposes to produce phenol and ethyl iodide or ethyl bromide. Refluxing with anhydrous aluminum trichloride in carbon disulfide or nitrobenzene, heating with aluminum tribromide in benzene, heating with aniline hydrochloride or pyridine hydrochloride and hydrolysis all produce haloethane and phenol. . When heated to 400°C, phenol and ethylene are generated.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Obtained from the reaction of sodium phenolate and ethyl bromide. Dissolve phenol in the sodium alkoxide solution, cool to below 20°C, and slowly add ethyl bromide. After the reflux reaction for 3 hours, the ethanol was recovered, and the sodium bromide generated by the reaction was filtered off. The crude product was washed with water, the oil layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with diethyl ether. Combine the extract and the oil layer, recover the ether and then steam out the 170-173°C fraction, which is phenylethyl ether.
Refining method: wash away the remaining phenol with sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, then wash with water, dry with calcium chloride, and distill.
Purpose
Used in organic synthesis, spices and testing aromatic sulfinic acid, used in the manufacture of medicines, dyes, etc.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

