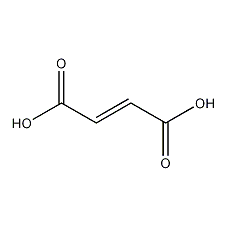
Structural formula
| Business number | 030Q |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H4O4 |
| Molecular weight | 116.07 |
| label |
(E)-Butenedioic acid, (E)-Butenedioic acid, fumaric acid, Corydalis acid, trans-1,2-ethylenedihydroxy acid, (E)-Butenedioic acid, (E)1,2-Ethylenedicarboxylic acid, Allomaleic acid, sour agent, sourness modifier, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:110-17-8
MDL number:MFCD00002700
EINECS number:203-743-0
RTECS number:LS9625000
BRN number:605763
PubChem number:24894967
Physical property data
1. Properties: white particles or crystalline powder. Odorless, with special sour taste and strong sour taste 2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.6353. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 1.6354. Melting point (ºC): 287 (dec) 5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 355.56. Boiling point (ºC, 0.23kPa): 165
7. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.635
8. Flash point (ºC): 230
9. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1470.0
10. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) ( kJ·mol-1): -675.8
11. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): – 1334.0
12. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -811.7
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol ): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (polymer) Log value of the partition coefficient (alcohol/water): Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V ): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in ethanol, slightly soluble in water and ether, insoluble in chloroform, carbon tetrachloride and benzene.
20. Refractive index (n20D): 1.526
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: LD50: 10700mg/Kg (orally in rats).
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 23.76
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 77.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 222.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/ cm): 67.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 9.42
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 74.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 119
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 1
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. No contact with oxides.
2.This product is non-toxic. LD505000mg/kg was administered orally to rabbits, and LD50200mg/kg was administered intraperitoneally to mice.
3. Exist in flue-cured tobacco leaves and smoke.
Storage method
Package in woven bags lined with plastic bags, net weight per bag 25kg, or in cardboard barrels lined with plastic bags, net weight per barrel 30kg or 50kg. Store in a cool and dry place.
Synthesis method
1. Use green-shaped bacteria of the genus Rhizopus to ferment sugar substances. After the fermentation is completed, remove bacteria and calcium from the fermentation liquid, concentrate it under reduced pressure and adjust the pH to acidic, to obtain crude crystals. Dissolve the crude crystals, then add activated carbon to decolorize, then crystallize and filter to obtain the product.
Glucose
Neutralize Rhizopus fermentation, add CaCO3 fermentation broth, add Na2SO4, stir, filter CaSO4, bacterial filtrate (sodium salt)
Vacuum pressure evaporation concentrate HCl filtration waste liquid crude crystal → dissolved activated carbon decolorization crystallization filtration product
(1) The catalytic method mainly converts benzene (or butene) in the presence of a catalyst ) is oxidized to generate maleic acid (or maleic anhydride), which is then obtained through isomerization.
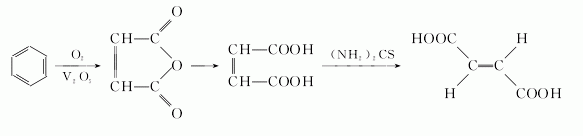
(2) Furfural method uses furfural as raw material and is obtained by oxidation with sodium chlorate. The reaction formula is as follows:
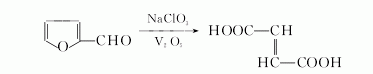
Make a solution of sodium chlorate , put it into the oxidation tank, add vanadium pentoxide, heat to 90~95℃, add furfural dropwise, control the temperature at about 105℃, complete the addition, keep it at 100℃ for 2~3 hours, cool and crystallize, filter and dry to obtain the reaction Butenedioic acid, yield 62.7%.
(3) Maleic acid method uses maleic acid as raw material and is produced through hydrolysis and isomerization. The reaction formula is as follows:
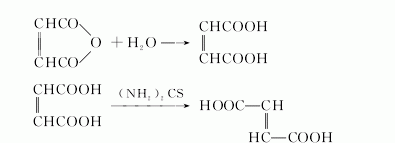
Absorb maleic anhydride with water to obtain about 35% maleic acid aqueous solution, use activated carbon to decolorize and remove tar at a temperature of 95°C; then use concentrated sulfuric acid medium to Thiourea is used as a catalyst and isomerized to generate fumaric acid at a temperature of 85 to 95°C. Industrial grade fumaric acid is then obtained through cooling, crystallization, filtration, washing, centrifugation and drying. In the above process, the washed fumaric acid is added to the dissolving pot, added with water and boiled to fully dissolve it. After recrystallization, filtration, washing and drying, food grade fumaric acid can be obtained.
(4). Obtain monoclinic, rhombic needle crystals or fronds from water.
(5). Tobacco: FC, 50, 54.
2. Preparation method:
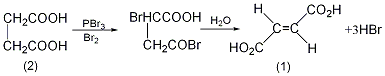
p>
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser (connected to a hydrogen bromide absorption device), dropping funnel, and thermometer, add 118g (1.0mol) of pre-dried succinic acid (2) and newly distill it 212g of phosphorus tribromide ① was added dropwise with 307g of dry bromine (98.5mL) under stirring, and the addition was completed in about 2 hours. During the dripping process, the system became so viscous that it was difficult to stir. Stop stirring and add all the bromine. Leave overnight. Heat in a water bath and stir for 4 hours to make the color of bromine disappear (do not allow bromine vapor to escape during heating). Slowly pour the reactant into 300 mL boiling water, stir thoroughly, and precipitate crystals. Add another 500 mL of water, heat to boiling, dissolve the solid matter, and filter. Cool and crystallize. Filter the precipitated crystals with suction, wash with water and dry to obtain 25-30g of fumaric acid. When the mother liquor is concentrated under reduced pressure to 1/2 volume, part of the product precipitates after cooling. A total of 58g of fumaric acid (1) was obtained, with a yield of 50%. Note: ① Phosphorus tribromide can be prepared by the following method: In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser (connected to a hydrogen bromide absorption device), dropping funnel, and thermometer, add 41g of red phosphorus and 250mL of carbon disulfide. Within 1.5h, 326g (105mL) of dry bromine and 250g of phosphorus disulfide (200mL) were added dropwise. The boiling point of phosphorus tribromide is 172.9°C. It should be kept in an airtight container. [1]
3. Preparation method:
Put 10g maleic acid (2) into the reaction bottle, add 10mL water and a few zeolites , after heating to dissolve, add 20mL concentrated hydrochloric acid. Install a reflux condenser and heat to reflux for 0.5h. Crystals precipitate quickly from hot solutions. After cooling, filter with suction and recrystallize from 1 mol/L dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain fumaric acid (1), mp 286~287°C. [2]
IV. Preparation method:
Equipped with stirrer, thermometer, reflux condenser, dripping liquid In the reaction bottle of the funnel, add 112.5g sodium chlorate (1.06mol), 250mL water, and 0.5g vanadium pentoxide, and heat to 70~75°C with stirring. Add 50g (0.52mol) of furfural (2) into the dropping funnel, and add about 4mL dropwise first to make the reaction occur vigorously. Add the rest of the furfural while keeping the reaction going vigorously, and finish the addition in about 30 minutes. After the addition is completed, continue the reaction at 70-75°C for 5-6 hours. Leave at room temperature overnight. The crystals were precipitated by suction filtration, washed with a small amount of cold water, recrystallized with about 300 mL (1 mol/L) hydrochloric acid, and dried at 100°C to obtain 26 g of fumaric acid (1), mp 282-284°C, yield 43%. [3]
Purpose
Can be used as acidulant, flavoring agent and antioxidant additive. Sodium fumarate has good water solubility and good flavor, and is often used in powdered foods. It is also a raw material for manufacturing various unsaturated alkyd resins and can also be used in fiberglass, paint, coating and plastics industries.
Place acid (2) in a reaction bottle, add 10 mL of water and a few grains of zeolite. After heating to dissolve, add 20 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Install a reflux condenser and heat to reflux for 0.5h. Crystals precipitate quickly from hot solutions. After cooling, filter with suction and recrystallize from 1 mol/L dilute hydrochloric acid to obtain fumaric acid (1), mp 286~287°C. [2]
IV. Preparation method:
Equipped with stirrer, thermometer, reflux condenser, dripping liquid In the reaction bottle of the funnel, add 112.5g sodium chlorate (1.06mol), 250mL water, and 0.5g vanadium pentoxide, and heat to 70~75°C with stirring. Add 50g (0.52mol) of furfural (2) into the dropping funnel, and add about 4mL dropwise first to make the reaction occur vigorously. Add the rest of the furfural while keeping the reaction going vigorously, and finish the addition in about 30 minutes. After the addition is completed, continue the reaction at 70-75°C for 5-6 hours. Leave at room temperature overnight. The crystals were precipitated by suction filtration, washed with a small amount of cold water, recrystallized with about 300 mL (1 mol/L) hydrochloric acid, and dried at 100°C to obtain 26 g of fumaric acid (1), mp 282-284°C, yield 43%. [3]
Purpose
Can be used as acidulant, flavoring agent and antioxidant additive. Sodium fumarate has good water solubility and good flavor, and is often used in powdered foods. It is also a raw material for manufacturing various unsaturated alkyd resins and can also be used in fiberglass, paint, coating and plastics industries.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

