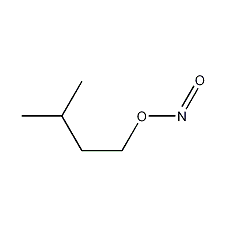
Structural formula
| Business number | 0319 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H11NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 117.15 |
| label |
amyl nitrite, Isoamyl nitrite, 3-Methyl-1-butylnitrite, 3-Methylbutanol nitrite, Isoamyl nitrite, Diazotization reagent |
Numbering system
CAS number:110-46-3
MDL number:MFCD00002057
EINECS number:203-770-8
RTECS number:NT0187500
BRN number:969510
PubChem number:24849038
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow transparent liquid with fruity aroma and volatility. [1]
2. Boiling point (℃): 97~99[2]
3. Relative density (water =1): 0.87 (25℃)[3]
4. Relative vapor density (air=1): 4.0[4]
5. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.77[5]
6. Flash point (℃): 3[6]
7. Ignition temperature (℃): 208.9[7]
8. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, Chloroform, gasoline. [8]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Rat oral LD50: 505mg/kg; rat inhalation LD50: 716ppm/4H; mouse inhalation LC50: 1430ppm/30M; mouse intraperitoneal LC50: 505mg/ kg; mouse venous LC50: 51mg/kg; dog venous LDLO: 167mg/kg;
2. Mutagenicity: Salmonella mutation: 333ug/plate; mouse lymphocyte mutation: 3740nmol/L; hamster ovary Cytogenetic analysis: 160mg/L; hamster ovary sister chromatid exchange: 16mg/L;
3. Inhalation and ingestion can dilate blood vessels, causing lowering of blood pressure and tachycardia. Large doses can Produces methemoglobinemia.
4. Acute toxicity [9]
LD50: 505mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 716ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
5. Mutagenicity[10] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 333μg/dish. Sister chromatid exchange: Hamster ovary, 16mg/L. Mammalian somatic mutations: mouse lymphocytes 3740nmol/L. Cytogenetic analysis: Hamster ovary 160mg/L. Sister chromatid exchange: Hamster ovary 16mg/L.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
4. Other harmful effects[11] This substance may be harmful to the environment and is harmful to the environment. Bodies of water should be given special attention.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 30.50
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 119.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 276.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 28.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 12.09
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 38.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 63.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[12] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[13] Strong oxidizing agent
3. Conditions to avoid contact[14] Heating
4. Polymerization Hazards[15] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[16] Nitrogen oxides p>
Storage method
Storage Precautions[17] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated non-combustible warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep away from light. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, alkalis, and alcohols, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency response equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of isoamyl alcohol and sodium nitrite. There are different operating methods according to actual production conditions. 1. The reaction is carried out in the synthesis tube. Pour the sodium nitrite aqueous solution, isoamyl alcohol, and hydrochloric acid into the high-level tank respectively. First, sodium nitrite solution and hydrochloric acid solution are dropped into the synthesis pipeline at the same speed. When chlorine bubbles are generated in the pipeline, isoamyl alcohol is slowly added dropwise from the top of the pipeline, and the crude product is synthesized in the pipeline. After washing, drying and fractionation, the finished product is obtained. 2. The reaction is carried out in the reaction tank. Add sodium nitrite, isoamyl alcohol and water to the reaction tank, stir, cool to below 5°C and add hydrochloric acid dropwise. Incubate at 5°C for 1 hour, then let stand and separate the water layer. Wash the ester layer with water, then with sodium carbonate solution, and then with water. After separating the aqueous layer, dehydrate with anhydrous sodium carbonate and filter. The filtrate is distilled, and the 97-99°C fraction is collected to obtain isoamyl nitrite.
2. Isoamyl alcohol reacts with sodium nitrite in an acidic environment, and is washed, dried, and distilled to obtain the finished product.
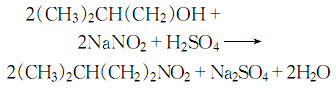
Purpose
1. Used as nitrosating agent and oxidizing agent in organic synthesis, used to prepare drugs, and also used to treat cyanide and carbon monoxide poisoning. [18]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

