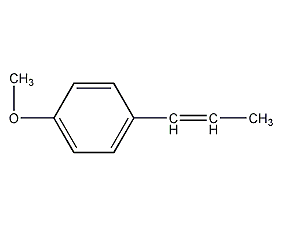
structural formula
| business number | 02q2 |
|---|---|
| molecular formula | c10h12o |
| molecular weight | 148.20 |
| label |
1-methoxy-4-propenylbenzene, p-propenyl anisole, anise essence, sheng bai ning, anethole, para methoxy alpha phenyl propene, p-methoxypropenylbenzene, p-propenylanisole, -1-methoxy-4-(1-propenyl)benzene, anise camphor |
numbering system
cas number:104-46-1
mdl number:none
einecs number:224-052-0
rtecs number:bz9275000
brn number:774229
pubchem id:none
physical property data
1. properties: trans form is crystalline, cis form is liquid. has a sweet anise aroma.
2. density (g/ml, 20℃): 0.9883
3. relative vapor density (g/ml, air=1): undetermined
4. melting point (ºc): 22.5
5. boiling point (ºc, normal pressure): 235
6. boiling point (ºc, 307pa): 81~81.5
7. refractive index: 1.56145
8. flash point (ºc): 90
9. specific rotation (º): undetermined
10. autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºc): not determined
11. vapor pressure (mmhg, ºc): not determined
12. saturated vapor pressure (kpa, ºc) : undetermined
13. heat of combustion (kj/mol): undetermined
14. critical temperature (ºc): undetermined
15. critical pressure (kpa): undetermined
16. log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: undetermined
17. explosion upper limit (%, v/v): undetermined determined
18. lower explosion limit (%, v/v): undetermined
19. solubility: miscible with chloroform and ether, soluble in benzene, ethyl acetate, acetone, carbon disulfide, petroleum ether and alcohol are insoluble in water.
toxicological data
1. acute toxicity: rat oral ld50: 2090mg/kg; rat peritoneal cavity ldlo: 70mg/kg; mouse oral ld50: 3050mg/kg; mouse peritoneal cavity ld50: 593mg/kg; rabbit skin contact ld 50: >5mg/kg; guinea pigs ld50: 2160mg/kg; wild birds pass the mouth ld50: 316mg/kg; 2. chronic toxic/carcinogenic: mouse peritoneal cavity tdlo: 2400mg/kg/8w-i;
ecological data
none yet
molecular structure data
1. molar refractive index: 48.82
2. molar volume (cm3/mol): 154.4
3. isotonic specific volume (90.2k ): 366.9
4. surface tension (dyne/cm): 31.8
5. dielectric constant:
6. dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. polarizability: 19.35
compute chemical data
1. hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (xlogp): 3.3
2. number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. number of tautomers:
6. topological molecular polar surface area (tpsa): 9.2
7. number of heavy atoms: 11
8. surface charge: 0
9. complexity: 121
10. number of isotope atoms: 0
11. determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters number: 1
14. number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. number of covalent bond units: 1
properties and stability
1. found in burley tobacco leaves.
2. it naturally exists in essential oils such as fennel oil, cumin oil and star anise oil, of which the trans form accounts for the majority.
storage method
none yet
synthesis method
1. there are many industrial preparation methods for anethole. here are the following ones. (1) cool fennel oil or anise oil to precipitate crystals, which can be obtained by distillation and recrystallization with alcohol. anise oil can also be distilled and the distillate at 230-234°c collected. or distill under reduced pressure and collect the 142°c (5.60kpa) or 110°c (2.7kpa) fraction to obtain anethole. (2) obtained from p-methoxyphenylbutenoic acid by heating at 220-240°c. (3) heating p-propenyl anisole and caustic alkali together to isomerize it into anethole. (4) derived from methylation of propenylphenol. (5) anisaldehyde reacts with g2h5mgx, and the product is dehydrated by heating water to obtain anethole. (6) anisaldehyde is heated together with propionic anhydride and sodium propionate to obtain anethole. (7) add concentrated hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid to the mixture of anisole and propionaldehyde at 0°c to saturate the hydrogen chloride gas. heat the product with pyridine to remove hydrogen chloride to obtain anethole. hydrobromic acid can also be used instead of concentrated hydrochloric acid. the product is treated with metallic sodium and dehydrobromated to obtain anethole. (8) prepare grignard reagent from p-bromoanisole and react with allyl bromide to generate p-methoxyphenylpropene, which is then heated with potassium hydroxide to isomerize to obtain anethole.
2. tobacco: bu, 14.
purpose
used for the preparation of perfume flavors and food flavors, and also used as raw material for the preparation of p-methoxybenzaldehyde (anisaldehyde).

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

