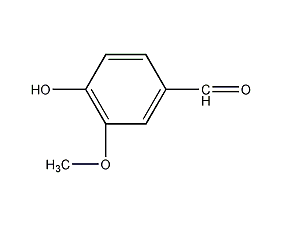
Structural formula
| Business number | 03DE |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H8O3 |
| Molecular weight | 152.15 |
| label |
vanillin, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, With Vanilla aldehyde, With Vanilla pigment, 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde, natural flavors |
Numbering system
CAS number:121-33-5
MDL number:MFCD00006942
EINECS number:204-465-2
RTECS number:YW5775000
BRN number:472792
PubChem number:24901469
Physical property data
1. Appearance: White to light yellow crystalline powder or needle-like crystals. 2. Melting point (℃): 81~82 3. Boiling point (℃): 285 4. Relative density: 1.056 5. Solubility: soluble in 125 times of water, 20 times of ethylene glycol and 2 times of 95% ethanol. Soluble in chloroform.
Toxicological data
Oral LD50: 2~2.8g/kg (rat)
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 41.56
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 123.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 324.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 47.3
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24 cm3):
7. Polarizability: 16.47
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: 5
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 46.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 135
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1.Reacts with higher alcohols and ketones to produce blue-green color, and reacts with deoxysaccharides, amino acids, and amines to produce color or fluorescence.
2. Found in tobacco leaves.
3. Naturally found in asparagus, coffee, and vanilla.
Storage method
Packaging lined with polyethylene bags and iron cans. Store in a dry and ventilated warehouse.
Synthesis method
1. Acidify N,N-dimethylaniline with hydrochloric acid to form a salt, and nitrate it with sodium nitrite to obtain p-nitroso-N,N-dimethylaniline hydrochloride. It is condensed with guaiacol and formaldehyde at 41-43°C. Then extract with benzene. First�� Distillation, recrystallization with benzene, and then distillation a second time, recrystallization with water. The finished product is obtained by drying at 50℃. In the sulfurous acid pulp waste liquid, the lignosulfonate containing the structural unit of chapus alcohol is oxidized under alkaline conditions and then hydrolyzed to obtain vanillin. Raw material consumption (kg/t) Guaiacol (98%) 1460 sodium nitrite 640N, N-dimethylaniline (98%) 974 hydrochloric acid (30%) 6000 formaldehyde (99%) 320
2.N,N-dimethylaniline is processed in the presence of30% hydrochloric acid and sodium nitrite Nitrosation reaction, the obtained nitroso compound is condensed with o-methoxyphenol and formaldehyde, and then hydrolyzed to obtain crude vanillin:
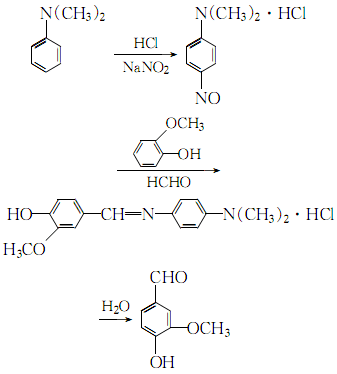
Contains para-amino group N,N- The crude vanillin of dimethylaniline hydrochloride is extracted, distilled twice, recrystallized with petroleum ether, and dried to obtain purification.
3. Add 2-methoxyphenol, sodium glyoxylate, and sodium hydroxide to water under stirring, and maintain the reaction at 25°C for 24 hours [2-methoxyphenol: sodium glyoxylate: sodium hydroxide ∶Water=40∶24∶13∶950 (mass ratio)]. After the reaction is completed, the pH value of the mixture is adjusted to 5 with sulfuric acid, and unreacted 2-methoxyphenol is extracted with benzene. Then mix it with water, sodium hydroxide and copper oxide in the autoclave, add 175℃, control the pressure to 303.9kPa, and introduce air at a speed of 2L/min for 90 minutes while stirring. Carry out oxidation reaction. After the reaction is completed, the copper oxide is removed by filtration. The obtained reaction product was extracted with sulfuric acid to a pH of 1.5 with methyl isobutyl ketone 5 times. After the water layer was separated, the pH was adjusted to 7.0 with sulfuric acid and extracted with methyl isobutyl ketone for another 5 times at 20°C. Next, separate the water layer. The methyl isobutyl ketone layer is heated to evaporate the methyl isobutyl ketone, and then distilled at 666 Pa to collect the 149-151°C fraction as the target product vanillin finished product.
4.Using clove oil as the basic raw material, after isolating eugenol using the phenol sodium salt method, press The following reaction is used to prepare vanillin.
Isomerization of eugenol produces isoeugenol:
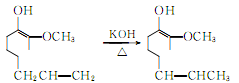
Acetylation of isoeugenol to acetylisoeugenol:
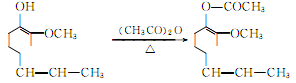
The oxidation reaction of acetyl isoeugenol produces acetyl vanillin:
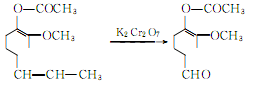
Hydrolysis of acetyl vanillin to produce vanillin potassium salt:
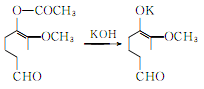
Vanillin potassium hydrochloride generates vanillin:
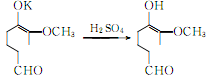
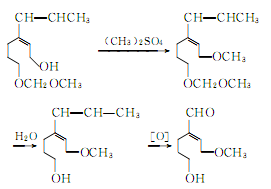
② Prepared from safrole. Isomerization of safrole to produce isosafrole phenolic ether:
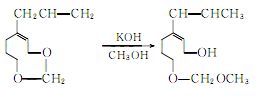
Isosafrole phenolic ether is methylated, hydrolyzed and oxidized to produce vanillin
③ Made from lignin as raw material. In recent years, many countries have used lignin in the sulfite pulp waste liquid from the papermaking industry to produce vanillin. Due to the rich sources of raw materials, it is a promising synthesis method. The reaction process is as follows:
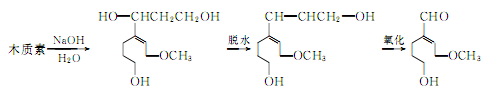
④ Prepared from guaiacol as raw material.
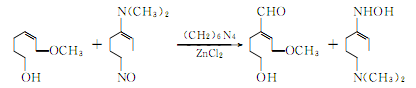
Purpose
1. It can be used to prepare flavors such as vanilla, chocolate and cream. The dosage is 25% to 30% of the total flavor. The prepared flavors can be used in the pharmaceutical and food industries. In addition, vanillin can also be used in other products such as cosmetics.
2. Used as a marker for detecting higher alcohols, ketones, deoxysugar, amino acids, amines and sterols by thin layer chromatography. Toner. Also used in synthetic fragrances.
3.Vanillin is one of the important spices. As a foundation fragrance, it is used in almost all fragrance types. Such as violets, orchids, sunflowers, roses, jasmine, etc. However, because it can easily cause discoloration, you should be careful when using it in white scented products. Vanillin is also widely used in food, tobacco and alcohol, and is an essential spice in vanilla, chocolate, and toffee flavors. The dosage in candy is 200×10-6, the dosage in syrup is (370~20000)×10-6, the dosage in chewing gum is 270×10-6, and the dosage in chocolate is 970×10-6.
4. It is an organic synthetic raw material, used in the pharmaceutical industry to synthesize TMP, the anthelmintic drug Ditrizozin, etc.; it is also used in metal plating brighteners, rubber deodorants, etc. In agriculture, vanillin can be used as a herbicide after it matures, and can also be used as a ripening agent for sugar cane.
type of color developer. Also used in synthetic fragrances.
3.Vanillin is one of the important spices. As a foundation fragrance, it is used in almost all fragrance types. Such as violets, orchids, sunflowers, roses, jasmine, etc. However, because it can easily cause discoloration, you should be careful when using it in white scented products. Vanillin is also widely used in food, tobacco and alcohol, and is an essential spice in vanilla, chocolate, and toffee flavors. The dosage in candy is 200×10-6, the dosage in syrup is (370~20000)×10-6, the dosage in chewing gum is 270×10-6, and the dosage in chocolate is 970×10-6.
4. It is an organic synthetic raw material, used in the pharmaceutical industry to synthesize TMP, the anthelmintic drug Ditrizozin, etc.; it is also used in metal plating brighteners, rubber deodorants, etc. In agriculture, vanillin can be used as a herbicide after it matures, and can also be used as a ripening agent for sugar cane.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

