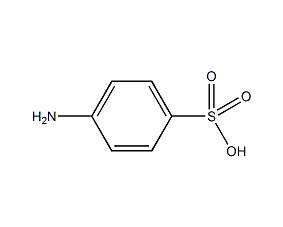
Structural formula
| Business number | 03DS |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H7NO3S |
| Molecular weight | 173.19 |
| label |
sulfamate, Para-aminobenzenesulfonic acid, 4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid, p-Aminobenzenesulfonic acid, anhydrous, Anhydrous p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid, Para-aminobenzenesulfonic acid (anhydrous), Anhydrous 4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid, Aniline-4-sulfonic acid, Aniline-4-sulfonic acid, Aniline p-sulfonic acid, 4-Sulfoaniline, 4-Aminobenzenesulphonic acid, 4-Anilinesulfonic acid, Sulphanilic acid, Sulfanilsaeure, whitening agent, Fungicide |
Numbering system
CAS number:121-57-3
MDL number:MFCD00007886
EINECS number:204-482-5
RTECS number:WP3895500
BRN number:908765
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: White crystalline powder. It changes color easily when exposed to light. Hydrates lose water at 100°C, and anhydrous substances begin to decompose and carbonize at 280°C.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.485
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 288
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
p>
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V /V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in cold water, soluble in ethanol.�Ammonia, carbonate, alkali metal hydroxide solution, ether and benzene are significantly acidic and can be dissolved in caustic soda solution and sodium carbonate solution.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 12300mg/kg Rat intravenous LD50: 6gm/kg
2. Mouse Oral LC50: >3200mg/kg. Harmful if ingested, inhaled or absorbed through the skin. Has a stimulating effect.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.71
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 114.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 328.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 67.5
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 16.14
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 80.4
p>
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 211
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Acidic and irritating. It decomposes when heated and releases toxic gases such as nitrogen and sulfur oxides. Decomposes upon exposure to light.
2. Harmful if inhaled, taken orally or in contact with skin. Avoid contact with eyes when using.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, dry place. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of aniline and sulfuric acid to form a salt and then translocation.
2.Put aniline dropwise into concentrated sulfuric acid to react, and pour the reaction mixture into cold water to obtain a colorless precipitate of p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid. After cooling, filter and dry to obtain p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid.
3.Water recrystallization and purification.
4. It can be obtained by reacting aniline and sulfuric acid to form a salt and transposition:
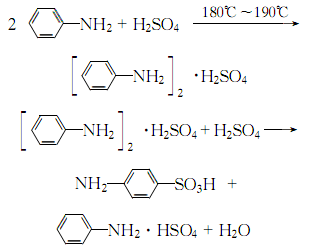
Purpose
1. Used in the manufacture of azo dyes, etc., and also used as pesticides to prevent and control wheat rust.
2. Mainly used in the manufacture of dyes, printing and dyeing auxiliaries, prevention and control of wheat rust, and as spices, Intermediates for food pigments, medicines, whitening agents, pesticides, etc.
3. Used in organic synthesis, and also used as chromatography reagents, etc.
4. Used as benchmark reagents , experimental reagents and chromatographic analysis reagents.
5.Benchmark reagents. Determination of aluminum, magnesium, potassium, sodium, iodine, iodide and nitrite. Used together with 1-naphthylamine to determine nitrite and test osmium and ruthenium. Potassium can be measured indirectly through potassium nitrite. Determination of serum bilirubin, soil analysis. It is also used in printing and dyeing auxiliaries, pesticides and fungicides, spices, food pigments, pharmaceuticalbuildingmaterials and other fields. span>
6.Used as an analytical reagent, such as a reference reagent for the determination of nitrite. It is also used as chromatographic analysis reagent, dye synthesis and pharmaceutical industry.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

