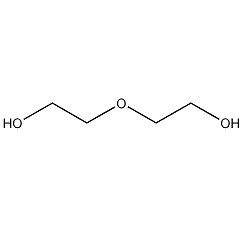
Structural formula
| Business number | 033L |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H10O3 |
| Molecular weight | 106.12 |
| label |
diethylene glycol, 2,2′-Oxodiethanol, Dihydroxydiethyl ether, Diethylene glycol ether, Diethylene glycol, 2-Hydroxyethyl ether, Digycol, 2,2′-Oxydiethanol, gas dehydrating agent, Aromatic hydrocarbon extraction solvent, textile softener, finishing agent, brake fluid compound, celluloid softener, antifreeze, Diluent during emulsion polymerization, alcohol solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-46-6
MDL number:MFCD00002882
EINECS number:203-872-2
RTECS number:ID5950000
BRN number:969209
PubChem number:24889810
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless, odorless, transparent, hygroscopic viscous liquid with pungent smell and non-corrosive.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 245
3. Melting point (ºC): -10.5
4. Relative density ( g/mL, 20/4ºC): 1.118
5. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 2.14
6. Refractive index (15ºC): 1.4490
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4472
8. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.446
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 35.7
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 30
11. Flash point (ºC, closed): 143
12. Ignition point (ºC): 229
13. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 52.297
14. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 2380.2
15. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 2.31
16. Conductivity (S/m, 20ºC): 5.86×10 -7
17. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): <0.0013
18. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC ): 0.000635
19. Explosion lower limit (%,V/V): 0.7
20. Explosion upper limit (%,V/V): 22
21. Solubility: Miscible with water, ethanol, ethylene glycol, acetone, chloroform, furfural, etc. Immiscible with ether, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, linear aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, etc.
22. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.1122
23. Critical temperature (ºC): 476.85
24. Critical pressure (MPa) : 4.7
25. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 27.775
26. van der Waals Area (cm2·mol-1): 8.920×109
27. van der Waals Volume (cm 3·mol-1): 60.700
28. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2432.0
29. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -571.2
30. Liquid phase standard Heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2374.7
31. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -628.5
32. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 258.4
Toxicological data
1. Irritation: Rabbit transdermal: 500mg Mild irritation.
Rabbit eye: 50mg Mild irritation.
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 12565mg/kg; rabbit dermal LD50: 11890mg/kg
3. It is slightly toxic. It can be absorbed through the skin and has little irritation to the skin and mucous membranes. Similar to ethylene glycol, it has a depressant effect on the central nervous system. Can cause pathological changes in the kidneys and urinary tract stones. The lethal dose of a single oral dose to humans is estimated to be 1mL/kg. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea may occur about 24 hours after taking diethylene glycol. The deceased subsequently developed headaches, pain in the kidney area, temporary polyuria and then oliguria, lethargy, and mild facial swelling. Coma and death occur within 2 to 7 days after anuria occurs. Therefore, this product should not be used for medicinal purposes and long-term contact with the skin should be avoided.
Ecological data
Slightly harmful to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 25.39
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 95.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 244.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 42.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.06
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -1.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 49.7
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 26.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with oxides and moisture. 2. Colorless, odorless, transparent, hygroscopic viscous liquid. There is a spicy sweetness. Its solubility is similar to that of ethylene glycol, but it has stronger solubility for hydrocarbons. Diethylene glycol is miscible with water, ethanol, ethylene glycol, acetone, chloroform, furfural, etc. Immiscible with ether, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, linear aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, etc. Rosin, shellac, cellulose acetate, and most oils and fats are insoluble in diethylene glycol, but nitrocellulose, alkyd resins, polyester resins, polyurethanes, and most dyes are soluble. Flammable, low toxicity. It has the general chemical properties of alcohol and ether. 3. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke. 4. Symptoms after ingestion are similar to ethylene glycol, see Ethylene Glycol. Used as aelixir to produce fatal poisoning effects.
Storage method
1. Store sealed in a cool, dry place. Make sure the workspace has good ventilation.
2. Keep away from fire and water sources. Store away from oxidizing agents.
Synthesis method
1. Diethylene glycol is a by-product when ethylene oxide is used to produce ethanol. 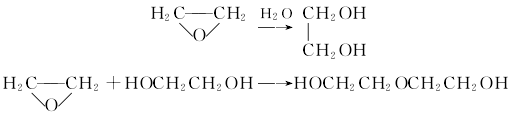 Process flow:Use direct hydration method to mix ethylene oxide and water at a ratio of 1:8 and send them to the mixing reaction In the reactor, react for 40-60 minutes at 150°C MPa to form a dehydration tower for further dehydration; the ethylene glycol mixture at the bottom of the tower is sent to the ethylene glycol tower, and more than 99.8% of ethylene glycol can be obtained at the top of the tower. The bottom liquid is sent to a distillation tower, and diethylene glycol is obtained from the top of the tower at a temperature of 135-140°C and a pressure of 4.0KPa. Continue the separation to obtain triethylene glycol and tetraethylene glycol. Refining method: Impurities contained include water, ethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, etc. It can be refined by distillation under reduced pressure followed by fractional crystallization. Take 1650 mL of diethylene glycol for fractional distillation under reduced pressure, discard 480 mL of the initial fraction, and collect 1000 mL of the middle fraction for fractional crystallization to obtain 700 mL of diethylene glycol. 2. When reacting with acid anhydride, it will generate ester, and when reacting with alkyl sulfate or halogenated hydrocarbon, it will generate ether. 3. Synthesis: Produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide and ethylene glycol. It is also a by-product when hydrating ethylene oxide to produce ethylene glycol.
Process flow:Use direct hydration method to mix ethylene oxide and water at a ratio of 1:8 and send them to the mixing reaction In the reactor, react for 40-60 minutes at 150°C MPa to form a dehydration tower for further dehydration; the ethylene glycol mixture at the bottom of the tower is sent to the ethylene glycol tower, and more than 99.8% of ethylene glycol can be obtained at the top of the tower. The bottom liquid is sent to a distillation tower, and diethylene glycol is obtained from the top of the tower at a temperature of 135-140°C and a pressure of 4.0KPa. Continue the separation to obtain triethylene glycol and tetraethylene glycol. Refining method: Impurities contained include water, ethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, etc. It can be refined by distillation under reduced pressure followed by fractional crystallization. Take 1650 mL of diethylene glycol for fractional distillation under reduced pressure, discard 480 mL of the initial fraction, and collect 1000 mL of the middle fraction for fractional crystallization to obtain 700 mL of diethylene glycol. 2. When reacting with acid anhydride, it will generate ester, and when reacting with alkyl sulfate or halogenated hydrocarbon, it will generate ether. 3. Synthesis: Produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide and ethylene glycol. It is also a by-product when hydrating ethylene oxide to produce ethylene glycol.
Purpose
1. Mainly used as gas dehydrating agent and aromatic hydrocarbon extraction solvent. It is also used as a solvent for nitrocellulose, resin, grease, printing ink, etc., as a softener and finishing agent for textiles, and for extracting coumarone and indene from coal tar. In addition, diethylene glycol is also used as a brake fluid compound, celluloid softener, antifreeze and diluent during emulsion polymerization. It is also used in the production of rubber and resin plasticizers; polyester resin; fiber glass; urethane foam; lubricating oil viscosity improver and other products. Used to synthesize unsaturated polyester resin, etc.
2.Used as synthetic unsaturated polyester resin, plasticizer, etc. It is also used in antifreeze, gas dehydrating agent, plasticizer, solvent, aromatic hydrocarbon extraction agent, cigarette hygroscopic agent, textile lubricant and finishing agent, anti-drying agent for paste and various glues, vat dye hygroscopic co-solvent, etc. It is a common solvent for grease, resin, nitrocellulose, etc.
��, triethylene glycol, etc. It can be refined by distillation under reduced pressure followed by fractional crystallization. Take 1650 mL of diethylene glycol for fractional distillation under reduced pressure, discard 480 mL of the initial fraction, and collect 1000 mL of the middle fraction for fractional crystallization to obtain 700 mL of diethylene glycol. 2. When reacting with acid anhydride, it will generate ester, and when reacting with alkyl sulfate or halogenated hydrocarbon, it will generate ether. 3. Synthesis: Produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide and ethylene glycol. It is also a by-product when hydrating ethylene oxide to produce ethylene glycol.
Purpose
1. Mainly used as gas dehydrating agent and aromatic hydrocarbon extraction solvent. It is also used as a solvent for nitrocellulose, resin, grease, printing ink, etc., as a softener and finishing agent for textiles, and for extracting coumarone and indene from coal tar. In addition, diethylene glycol is also used as a brake fluid compound, celluloid softener, antifreeze and diluent during emulsion polymerization. It is also used in the production of rubber and resin plasticizers; polyester resin; fiber glass; urethane foam; lubricating oil viscosity improver and other products. Used to synthesize unsaturated polyester resin, etc.
2.Used as synthetic unsaturated polyester resin, plasticizer, etc. It is also used in antifreeze, gas dehydrating agent, plasticizer, solvent, aromatic hydrocarbon extraction agent, cigarette hygroscopic agent, textile lubricant and finishing agent, anti-drying agent for paste and various glues, vat dye hygroscopic co-solvent, etc. It is a common solvent for grease, resin, nitrocellulose, etc.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

