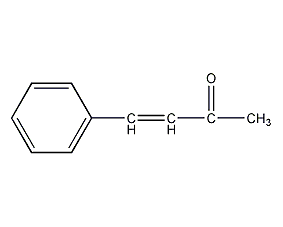
Structural formula
| Business number | 03F6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H10O |
| Molecular weight | 146 |
| label |
α-phenbutene-γ-one, Styrobutene-[1]-one-[3], Stenbutenone, Methyl styryl ketone, Methyl styrene ketone, Methylcinnamyl ketone, 4-phenyl-3-buten-2-one, (3E)-4-Phenyl-3-buten-2-one, 1-Buten-3-one-1-phenyl, 2-Phenylvinyl methyl ketone, 4-phenyl-3-buten-2-one, 4-Phenylbutenone, Acetocinnamone, Aromatic aldehydes, ketones and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:122-57-6
MDL number:MFCD00008779
EINECS number:204-555-1
RTECS number:EN0330000
BRN number:742046
PubChem number:24848836
Physical property data
1. Properties: white or light yellow crystal. Combustible. Has a coumarin smell.
2. Density (g/mL, 15/15℃): 1.0377
3. Refractive index (nD20): 1.5836
4. Flash point (℃): 65
5. Melting point (℃): 41.5
6. Boiling point (ºC): 260-262℃, 161℃ (5.3 kPa), 126-128℃ (1.2kPa)
7. Solubility: Easily soluble in sulfuric acid, ethanol, ether, benzene and chloroform, slightly soluble in water and petroleum ether.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 2030 mg/kg
Mouse peritoneal cavity LC 50: 1210 mg/kg
Mouse intravenous injection LC50: 112 mg /kg
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 46.80
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 144.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 355.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.9
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 18.55
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3.�Number of � bond receptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecules Polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 152
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Number of determined atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Number of uncertain atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 1
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. However, it can irritate the skin and mucous membranes and cause blistering.
2.The color becomes darker when exposed to light. It is easy to decompose when heated for a long time.
3. Found in flue-cured tobacco leaves.
Storage method
1. Production equipment should be sealed, and operators should wear protective gear to avoid contact with skin. Maintain good ventilation in the workshop.
2. Packaged in iron drums lined with plastic bags. Flammable, should be stored away from light. Store in a cool, ventilated place.
Synthesis method
1. It is obtained by condensing benzaldehyde with acetone. Mix acetone, benzaldehyde, and water. After cooling, slowly add 10% sodium hydroxide solution. Control the temperature at 25-31°C. Continue stirring for 1 hour after the addition. Then add dilute hydrochloric acid to neutralize to pH 6-7, leave it for 1 hour, and separate a yellow oil. The lower layer is extracted with benzene, the extract and the oil are combined, washed twice with water, the water layer is separated, the benzene is recovered, dried with calcium chloride, added with dry decolorizing carbon, filtered, and the filtrate is distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product. Reference specifications of this product: melting point 40-42℃, boiling point 123-126℃ (1.07kPa). The melting point of 99% of products in the international market is 39-41°C. Raw material consumption quota: benzaldehyde 1700kg/t, acetone 2900kg/t, liquid caustic soda (40%) 500kg/t.
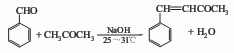
2. Tobacco: FC, 18 .
3. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, reflux condenser, and dropping funnel, add newly distilled benzaldehyde ① (1) 15.8g (0.15mol), acetone ② 24g (0.4mol), water 15mL. Add 4 mL of 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution dropwise while stirring, control the dropping speed, and maintain the reaction temperature between 25 and 31°C ③. After the addition was completed, the reaction was stirred at room temperature for 2 h. Neutralize to neutrality with dilute hydrochloric acid. The upper oil layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted twice with benzene. Combine the organic layers, wash with water, and dry over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. First steam out the benzene, and then distill under reduced pressure. Collect the fractions at 148~160℃/3.33kPa or 133~143℃/2.13kPa, 4-phenyl-3-butene. -2-one (1) 20g, solidified after cooling, yield 91%, mp40~42℃. Note: ① Benzaldehyde is washed and dried with 5% sodium carbonate solution before distillation. ②Increasing the dosage of acetone can reduce the occurrence of side reactions. ③The reaction temperature should be strictly controlled. If the temperature is too high, the reaction solution will turn black and the yield will decrease. [1]
Purpose
1. Organic synthesis intermediates. Can be used as an anti-volatile agent for spices. In the dyeing industry, it is used as a mordant and fixing agent, to prepare spices or flavoring agents, and to prepare galvanizing brightening agents.
2. Used as an additive for electroplating zinc to increase the brightness of the coating.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

