Background and overview[1]
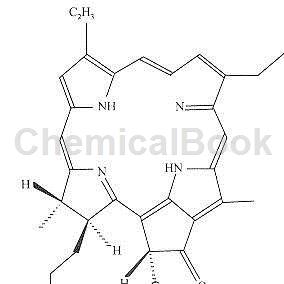
The degradation products of chlorophyll under heat or acidic conditions. Including pheophytin a and pheophytin b. The chemical formulas are C55H74O5N4 and C55H72O5N4 respectively; the colors are dark brown and yellowish brown respectively. All insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether and acetone. It is the main component that reflects the appearance and color of tea leaves and the color of the leaf base. The ratio of chlorophyll to pheophytin is positively correlated with the color and quality of green tea. Among the green tea drying methods, “frying” can retain more chlorophyll and form less pheophytin than “baking”. Pheophytin is an important component of the appearance color of black tea. A higher ratio of pheophytin to thearubigin can obtain a dark and oily dry tea color.
Apply[2-3]
Pheophytin is widely found in higher plants, marine algae, silkworms, liverworts and photosynthetic bacteria. Pheophytin can absorb light with a wavelength above 670nm, penetrate tissues through radiation, and produce singlet oxygen, hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anions, thereby playing antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antioxidant and other pharmacological effects. Some studies have analyzed the effect of pheophytin on the absorption characteristics of phytoplankton. It was inferred from the measured data and related literature that the blue and red light absorption peaks of pheophytin are located in the 412 and 670 nm bands respectively, and multiple linear regression was used to study the specific absorption coefficients of pheophytin and chlorophyll a. The results show that the specific absorption coefficient of pheophytin in the 412nm band is much larger than chlorophyll a; in the 440nm band, the specific absorption coefficient of chlorophyll a is slightly larger than pheophytin; in the 670 and 675nm bands, the specific absorption coefficient of chlorophyll a is about 3 times that of pheophytin times. As the proportion of pheophytin in the total pigment concentration increases, the blue light absorption peak on the phytoplankton absorption curve deviates from the 440nm band and gradually approaches the 412nm band, and the height of the blue light band absorption peak is determined by the pheophytin concentration, while the red light band The height of the absorption peak is determined by the chlorophyll a concentration. The power function fitting analysis of pigment concentration and absorption coefficient shows that the fitting correlation between the absorption coefficient and pheophytin concentration in the 412 and 440 nm bands is higher than that of chlorophyll a, while the opposite is true for the 675 nm band.
Preparation[2]
Extract pheophytin from mulberry leaf residue. The specific method is as follows:
a. Take 50g of mulberry leaf residue, mix it evenly with 400ml of recovered ethanol in a 1000ml beaker, adjust the pH to 7.5-8.5 with 2mol/L sodium hydroxide solution, and place it under ultrasonic conditions for leaching at a constant temperature of 60°C for 10 minutes. , the extraction power is 120W, and then filtered with 400 mesh filter cloth while hot to obtain the filtrate and filter residue;
b. Repeat the ultrasonic extraction operation of step a on the filter residue, filter, combine the filtrate from the two ultrasonic extractions, add concentrated hydrochloric acid to the filtrate to adjust the pH of the filtrate to 3.5-4.5, let it stand for 24 hours, and rotary evaporate under reduced pressure until the solution is Stop concentrating when the concentration reaches 45-50 ml. Pour the concentrated solution into a 100 ml beaker and let it stand for 1 hour. You can see yellow-green precipitate. Filter to obtain a yellow-green solid. Dry the yellow-green solid in a vacuum drying oven for 4 hours. The drying temperature is 50°C. That is, pheophytin is obtained.
Desalination and sedimentation method[4]
A desalination and sedimentation method that can reduce the pheophytin content in salina. Salina algae cultured in liquid medium were centrifuged at high speed, diluted with water and desalted. By controlling the pH of the algae liquid, ethanol was added to the algae liquid and allowed to settle naturally. After centrifugation at low speed, salina algae paste was made and its desalination was measured. Magnesium chlorophyll. The present invention chooses to add ethanol. Since ethanol is a non-toxic and easily removed solvent, its cost is relatively low compared with other solvents. Pheophytin is formed by the degradation of chlorophyll. The chlorophyll is partially extracted by ethanol, so the pheophytin content will inevitably decrease. Moreover, the selected pH value is weakly acidic, which can reduce the content of pheophytin, while reducing the amount of acid added and reducing the cost. This method selects an appropriate salinity in order to achieve better desalination and sedimentation speed under natural conditions without introducing any flocculant.
Main reference materials
[1] Chinese Tea Dictionary
[2]CN201510062483.2 Preparation and application method of pheophytin
[3] Effect of pheophytin on absorption characteristics of phytoplankton
[4]CN201510706826.4 A desalination and sedimentation method for reducing pheophytin in salina

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

