Background and overview[1]
Phenylbenzyl sulfide can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate. Aryl sulfoxides and thioether compounds are two very important compounds. They are widely present in various drug molecules and natural products. In the process of drug development, sulfur-containing compounds in various oxidation states are generally studied at the same time because they contain similar Compounds with different oxidation states of the skeleton may all be active molecules, and may also target different subspecies of diseases. Therefore, it is particularly important to selectively construct sulfoxides and thioethers from some structurally simple and commercially available raw materials.
The traditional method of synthesizing aryl sulfide compounds is mainly through thiol or thiophenol compounds. In this type of method, the organic sulfur used is easily oxidized and is toxic to metal catalysis; the raw materials taste too strong and are harmful to the environment and human body to varying degrees; the raw materials are relatively expensive, and complex substrates require pre-preparation; Many of the above shortcomings restrict the in-depth application of such methods in the fields of process research and medicinal chemistry research. Moreover, the synthesis of traditional aryl sulfide compounds needs to be carried out under high temperature conditions, which consumes a lot of energy and is not in line with the development trend of green chemistry, restricting the large-scale application of this method in industry. Sulfoxide compounds are produced by the oxidation of thioether compounds. The required oxidants are generally peroxides or high oxidation state compounds, which have poor atom economy, high pollution, and are more dangerous. In view of this, constructing a new green and efficient vulcanization reaction has become a technical problem to be solved.
Preparation[1]
Phenylbenzyl sulfide is prepared as follows:
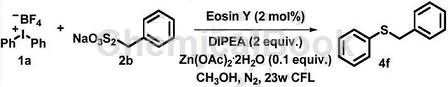
The specific steps are as follows: In the 25mL reaction tube, evacuate and replace nitrogen, add Eosin Y (2.5mg, 4*10-3mmol), substrate 1a (73.6mg, 0.2mmol), substrate 2b ( 135.8mg, 0.6mmol), zinc acetate [Zn(OAc)2·2H2O] (4.3mg, 0.02mmol), diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) (66μL, 0.4mmol), methanol (MeOH) (0.5mL ), stir for 24 hours under the irradiation of a 23-watt spiral lamp. After the reaction is completed, filter, concentrate, and separate by column chromatography (PE) to obtain colorless liquid 4f (29.2 mg, 73%), Rf = 0.4 (PE).
Main reference materials
[1] CN201710939889.3 Aryl sulfoxides, thioether compounds and their synthesis methods and applications

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

