The influence of chain extenders and cross-linking agents
For chemical cross-linking of polyurethane foam, the main way to achieve it is covalent bonding. Reactive isocyanates can react with many functional groups. Generally speaking, small molecule substances with two such functional groups are called chain extenders, while small molecule substances with more than two such functional groups are called cross-linking agents, because the former can change the main chain of the matrix molecule. Long, the latter makes it easier for the matrix molecular chain to form a network structure. The chain extender and cross-linking agent are used together to speed up the curing process of the foam, increase the cross-linking degree of the molecular network, and evenly distribute the cross-linking points, resulting in a foam with high density and small cells, thus improving its mechanical properties.
The increase in chain extender will lengthen the main chain of the molecule and enhance its mobility. When subjected to external force, it can absorb energy through chain segment movement. The elasticity and toughness of the foam plastic will be improved, but the rigidity will decrease. The increase in cross-linking agent will increase the cross-linking density of the system, hinder the movement of chain segments, enhance the ability to maintain the body structure, and be able to resist larger external forces. The strength of the foam will increase and the flexibility will become worse. However, there are some hydrogen bonds in foam plastics, and the increase in cross-link density will lead to enhanced chain separation. This non-covalent bond attraction effect between molecules will be destroyed by the increase in chemical cross-links. At the same time, the introduction of cross-linking bonds destroys the regularity of the molecular chain and reduces the crystallization ability of the soft segment of polyurethane foam. These effects will relatively reduce the strength of foam plastics, so the amount of cross-linking agent cannot be too large. By using chain extenders and cross-linking agents together, foam with excellent comprehensive properties can be obtained.

Alcohol chain extenders and cross-linking agents
Commonly used glycol chain extenders and curing agents mainly include 1,4-butanediol, ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, 1,6-hexanediol, HQEE, etc.
Commonly used polyol cross-linking agents include glycerin, trimethylolpropane, pentaerythritol and low molecular weight polyether polyols.
Dimethylol propionic acid, dimethylol butyric acid and some homemade carboxyl-containing diols are a type of chain extender containing hydrophilic groups, used to prepare water-based polyurethane.
Most structurally specific diols and polyols are described in the Polyols section. Some special polyhydroxy cross-linking agents are introduced below.
Vibracure A250 from Chemtura in the United States is a glycol mixture with a hydroxyl equivalent weight of 45.0. It is mainly used for curing PPDI prepolymers and is easier to mix with prepolymers than BDO. The obtained elastomer has high tensile strength and elongation, high tear strength, rebound rate and dynamic mechanical properties. Vibracure A931 is a glycol mixture with a melting point of approximately 93°C and a hydroxyl equivalent weight of 87.6. The hardness of the cured elastomer ranges from Shore A55 to 60, with high tensile strength, elongation, tear strength and low compression set.
Small molecular weight glycols are conventional chain extenders, but some companies recommend higher molecular weight glycol chain extender (curing agent) products.
For example, Vibracure A120 from Chemtura in the United States is a liquid polyether glycol (Mw=1000), used as a flexible chain extender for low-hardness polyurethane elastomers such as rollers. It can be used alone or with BDO, HQEE or MOCA, etc. Use together with curing agent. Vibracure A122 is a white waxy solid polyether glycol (PTMEG-2000) that can be used in TDI or MDI-based prepolymers with a curing temperature of 55 to 115°C. Vibracure A125 is a polyester diol (Mw=1000) with a melting point of 49°C. It can be mixed with BDO in certain proportions and used as a curing agent for MDI-polyester prepolymer; it is mixed with MOCA as a TDI prepolymer. Body curing agent to obtain softer elastomer.
Addolink 3530 from Rhein Chemie Rheinau GmbH is a polyester diol with a hydroxyl value of approximately 245 mg KOH/g, a viscosity (25°C) of approximately 300 mpa.s, and a pour point of approximately – 4℃, used as curing agent for polyurethane elastomer.
In addition, a small amount of low molecular weight polyether is used as a chain extender and cross-linking agent for foam or elastomer, which has been briefly introduced in the product uses in Chapter 2 “Polyether Polyols” and other chapters. Many polyether manufacturers supply low molecular weight polyether polyol cross-linking agents with molecular weights in the hundreds for use in polyurethane foam systems and “CASE” elastic polyurethane systems. Application areas include rigid foam, semi-rigid foam, high resilience, soft Foams, coatings, adhesives, elastomers, etc.
For example, the American Perstorp Polyol Company (a subsidiary of Swedish Perstorp Company) produces a series of cross-linking agents that can be used for polyurethane foams and elastomers, and some products are also used in polyurethane coatings. They are low molecular weight adducts of one trimethylol molecule or pentaerythritol molecule and 3 to 8 ethylene oxide or propylene oxide. Among them, polyol cross-linking agent Polyol 3610 is ethoxylated trimethylolpropane, with the structural formula CH3CH2C (CH2OCH2CH2OH) 3, which is the adduct of one trimethylolpropane molecule and three ethylene oxide molecules. The corresponding product brands of the original American Upjoin Company and DOW Company were Isonol 93 and Voranol 234-630 respectively (both have now ceased production). Products with very low moisture content (such as 0.03% moisture content) can be used as curing agents for polyurethane prepolymers for non-foam polyurethane.
HP-Link 600 produced by Shanghai Hongpu Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. is a liquid polyol cross-linking agent based on trimethylolpropane. It is a colorless, transparent and viscous liquid with a viscosity (25°C) of 600~800mPa. s, the hydroxyl value is (600±20) mg KOH/g, which has been widely used in high recovery polyurethane.�Foam, microcellular foam, elastomer and high-density hard foam can improve the resilience of foam plastic products and produce a dense skin. HP-Link 105C is a polyol starting from fatty amines. It is a brown viscous liquid with a viscosity (25℃) of 500~700mPa.s and a hydroxyl value of (500±20) mg KOH/g. It can replace conventional diethanolamine. , triethanolamine cross-linking agent, used to improve the resilience of high-resilience foam in high MDI systems, while also accelerating product maturation and demoulding.
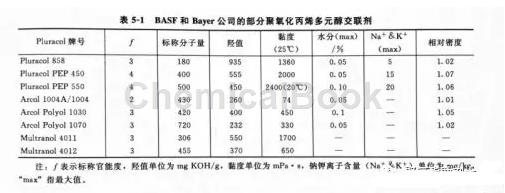
BASF’s Pluracol PEP series is a secondary hydroxyl polyether tetraol obtained by the reaction of pentaerythritol and propylene oxide. Pluracol 858 is a small molecule polyether triol. Bayer’s Arcol Polyol 1004A/1004, Arcol Polyol 1030, Arcol Polyol 1070, Multranol 4011 (Desmophen 4001T), and Multranol 4012 (equivalent to the company’s Desmophe 4012R) are also polyoxypropylene polyols, of which Arcol Polyol 1004A is a low acid value polyether glycol used for elastomer chain extenders and curing agents. The typical physical properties of these polyethers are shown in Table 5-1.
In addition, Solvay’s low molecular weight polycaprolactone, such as CAPA2054, 2043, 3031, 3022, 3050, 3091 and 4101, can also be used as chain extenders and crosslinking agents for polyurethane elastomers, coatings, adhesives, etc. combination agent. Their physical properties can be found in the section “Polycaprolactone Polyols”.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

