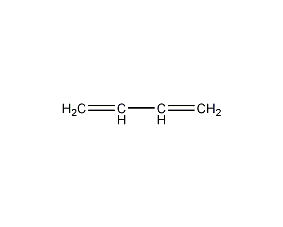
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UD |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H6 |
| Molecular weight | 54.09 |
| label |
butadiene, diethylene, vinyl vinyl, Butadiene, United ethylene, Butadiene, Butadiene residue, Two ethylene, Vinyl ethylene, bivinyl, Erythrene, Aliphatic hydrocarbons |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-99-0
MDL number:MFCD00008659
EINECS number:203-450-8
RTECS number:EI9275000
BRN number:605258
PubChem number:24857754
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: slightly aromatic colorless gas. [11]
2. Melting point (℃): -108.9[12]
3. Boiling point (℃): -4.4[13]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.62[14]
5. Relative Vapor density (air=1): 1.87[15]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 245.27 (21℃)[16]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2541.0[17]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 161.8[18 ]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.33[19]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.99[20]
11. Flash point (℃): -76[21]
12. Ignition temperature (℃) :415[22]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 16.3[23]
14. Explosion lower limit (%) %): 1.1[24]
15. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents such as acetone, benzene, acetic acid, and esters. [25]
16. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5:15.607
17.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 5.880×109
18. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 40.820
19. Critical density (g·cm-3 ): 0.245
20. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 221
21 .Critical compression factor: 0.270
22. Eccentricity factor: 0.193
23. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2541.49
24. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 110.0
25. Phase standard entropy (J·mol -1·K-1): 278.78
26. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1 ): 150.6
27. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 79.88
28. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2519.4
29. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 87.9
30. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 199.07
31. Liquid phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1)mages.basechem.org/internal/day_101009/201010090931194593.gif” alt=”” />
2. Extraction method The C4 fraction produced by the ethylene cracking unit is extracted by solvent extraction method. According to the different solvents used, it can be divided into acetonitrile extraction method and N, N-dimethylformamide extraction method. (1) Acetonitrile extraction method uses acetonitrile as the extractant. The C4 fraction produced by the ethylene cracking unit is sent to Enter the butadiene extractive distillation tower, add acetonitrile at the top, and butene and a small amount of butane are discharged from the top of the tower; butadiene, alkynes and acetonitrile enter the first desorption tower, and the acetonitrile is desorbed and returned to the extractive distillation tower. Butadiene and alkynes enter the second extraction tower, and acetonitrile is added to the top of the tower. Butadiene comes out from the top of the tower and enters the water washing tower, and then undergoes distillation and dehydration to obtain polymer grade butadiene. (2) N,N-Dimethyl The methyl formamide extraction method uses N, N-dimethylformamide as the extractant. The C4 fraction is extracted twice and distilled twice to prepare qualified butadiene products. The first extraction removes more than butadiene. Impurities that are difficult to dissolve in N, N-dimethylformamide, such as butene and butane; the second extraction removes impurities that are more soluble in N, N-dimethylformamide than butadiene, such as vinyl Acetylene. The first distillation removes components lighter than butadiene, such as methyl acetylene; the second distillation removes components heavier than butadiene, such as cis-2-butene, 1,2- Butadiene, C5 fraction and high boiling point products, finally obtain more than 99.5% of 1,3-butadiene finished product.
3. Preparation from petroleum gas in large quantities, that is, from butene or butene-butadiene Catalytic dehydrogenation of alkane mixture can also be obtained directly by cracking naphtha and light oil.
Purpose
1. In terms of synthetic rubber, it is used to produce styrene-butadiene rubber, butadiene rubber, ethylene-propylene rubber, nitrile rubber, chloroprene rubber, styrene-butadiene latex, etc.; in terms of synthetic resin, it is used to produce ABS, BS, SBS, MBS, epoxidized polybutadiene resin, liquid butadiene oligomer, etc.; in organic chemical production, used to synthesize sulfolane, 1,4-butanediol, adiponitrile, anthraquinone, 1 , 4-hexadiene, cyclooctadiene, cyclododecatriene, etc.
2. Used to manufacture styrene-butadiene rubber, butadiene rubber, butadiene rubber, nitrile rubber and ABS resin, etc. It is an important monomer for synthetic rubber and synthetic resin, and also a raw material for the preparation of butanol and butanediol. Emulsion polymerization with styrene, acrylonitrile, etc. can produce styrene-butadiene latex and nitrile-butadiene latex used in adhesives and coatings; it can also be used as raw materials for manufacturing plasticizers, curing agents, and flame retardants.
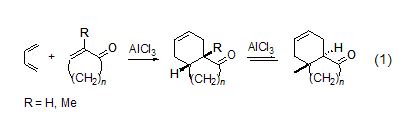
3. Butadiene is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. It is a synthetic intermediate and Diels-Alder reaction for elastic polymers, polybutadiene, polychloroprene and nylon. diene reagents in . It is mainly used in the synthesis of six-membered carbocyclic and heterocyclic compounds in organic synthesis [1]. Lewis acid, such as: AlCl3, SnCl4, BF3, FeCl3 or TiCl4 , which is beneficial to the cycloaddition reaction of 1,3-butadiene and α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. Under the action of AlCl3, cycloenone (n =2,3,4) undergoes cycloaddition reaction with butadiene to generate the expected cis adduct (Formula 1)[2]. When R = H, the cis adduct is partially or completely isomerized into the more stable trans isomer.
Asymmetric Diels- Alder reactionThe cycloaddition reaction of 1,3-butadiene and methacrylate dienophile using camphoractimide in the presence of Lewis acid produces cyclohexene carboxylate adduct. The larger stereocoordinated metal will cause the methacrylate to produce the S-trans conformation (Formula 2)[3].
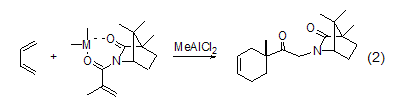
With 1,3-D In the cycloaddition reaction of dienes, the addition reaction using sugar as a chiral auxiliary compound has stereoselectivity [4]. The reaction of 3-O-acryloyldihydro-L-rhamnose (R = pivaloyl) gives (R)-cycloadduct (R /S=95:5) (Formula 3).
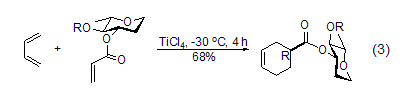
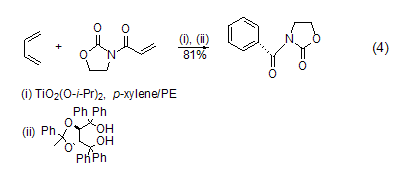
Chiral titanium catalysts are used in Asymmetric Diels-Alder reaction of 1,3-butadiene. Under better asymmetric induction, other dienes can undergo stereoselective cycloaddition reactions. This catalyst can assist the exchange of the alkoxy group of the compound through diisopropoxytitanium dichloride and tartaric acid derivatives, and treat it with a cycloaddition compound for 24 hours at room temperature to obtain cyclohexene carboxylate with an optical purity of 93% ( Formula 4)[5].
Butadiene can be passed through Diels- Alder reaction synthesizes the thiopyran ring structure in the molecule (Formula 5)[6]. The Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction of disulfide methyl phosphate and 1,3-butadiene is a new synthesis method of thiopyran derivatives. Lewis acid catalyst controls the reaction rate and selectivity (Formula 6)[7].
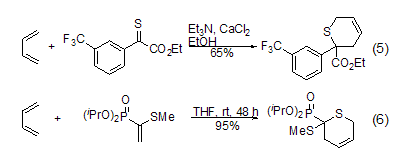
New diene affinity compounds 2-(Trimethylsilyl)vinyl-9-BBN easily undergoes Diels-Alder reaction with butadiene. After the trihydroxyborane of the intermediate is oxidized, 2-(trimethylsilyl)cyclic ring is obtained. Hexenol (Formula 7)[8].
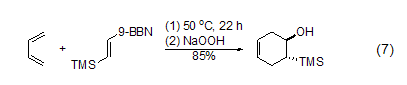
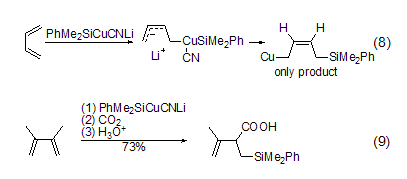
1,3-Butadiene Reacting with cyanocuprate reagent (PhMe2SiCu- CNLi), copper attacks the carbon atoms of the olefin end chain to generate an intermediate product, which is then reduced and eliminated, and copper (I) captures the anion. 1 , 4-addition reaction to generate cis product (Formula 8). When CO2 is used as the nucleophile for this reaction, a 1,2-addition reaction occurs (Formula 9)[9].
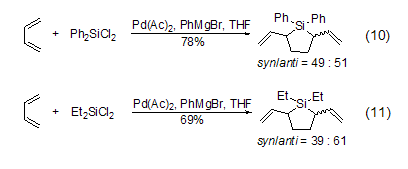
In the catalyst Pd(Ac)2, dichlorosilane and 1,3-butadiene only undergo a cyclization reaction to generate 2,5-divinylsilane (Formula 10, Formula 11)[10].
4. Used for synthetic rubber, ABS resin, acid anhydride, organic synthesis intermediates, etc. [42]
0208/201202081426548423.gif” alt=”” />
Reaction of 1,3-butadiene with cyanocuprate reagent (PhMe2SiCu- CNLi), copper Attack the carbon atom of the end chain of the olefin to generate an intermediate product, which is then reduced and eliminated. Copper (I) captures the anion and undergoes a 1,4-addition reaction to generate a cis product (Formula 8). And with CO2If this reaction is carried out as a nucleophile, a 1,2-addition reaction will occur (Formula 9)[9].

Under the catalysis of the catalyst Pd(Ac)2, dichlorosilane and 1 , 3-butadiene only undergoes cyclization reaction to generate 2,5-divinylsilane (Formula 10, Formula 11)[10].

4. Used in synthetic rubber, ABS resin, acid anhydride, organic synthesis intermediates, etc.[42]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

