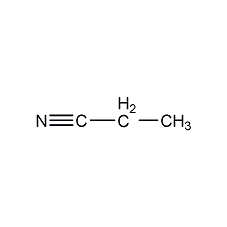
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UQ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H5N |
| Molecular weight | 55.08 |
| label |
Ethyl cyanide, Ethyl cyanide, Propionic nitrile, Ether cyanatus, Chromatographic analysis standard materials, selective solvents, synthetic raw materials, Intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-12-0
MDL number:MFCD00001948
EINECS number:203-464-4
RTECS number:UF9625000
BRN number:773680
PubChem number:24853188
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless transparent liquid with ether-like odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -92[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 97.2[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.78[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 1.9[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 5.2 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1910.62[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 291.2[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.18[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.16 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): 2 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃) ): 512[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 14[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%): 3.1[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol, ether, dimethylformamide, etc. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.389
17. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol, -91.8ºC): 6.07
18. Heat of formation (KJ/mol): -1909
19. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), constant pressure): 2.17
20. Conductivity (S/m): (0.8~2.5)×10-7
21. Solubility (%, 25ºC, water): 10.3
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 39mg/kg (rat oral); 36mg/kg (mouse oral Oral); 210mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 500ppm (rat inhalation, 4h); 367mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 1h)
2. Irritation [17]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
Rabbit eye: 100mg (24h), moderate irritation.
3. Mutagenicity [18] Sex chromosome deletion and non-disjunction: Drosophila melanogaster inhalation 51ppm.
4. Teratogenicity [19] Rats inhaled the lowest toxic dose (TCLo) 100ppm (6h) 6 to 20 days after pregnancy, causing urinary tract disease Developmental abnormalities of the reproductive system. Hamsters given 238 mg/kg intraperitoneally on the 8th day after pregnancy caused developmental malformations in the central nervous system and musculoskeletal system.
5. Others[20] The lowest oral toxic dose in rats (TCLo): 1120mg/kg (gestation 6~15d), affecting every The number of fetuses in the litter can cause embryotoxicity.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[21]
LC50: 1450~1580mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow)
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non-biodegradability[22] In the air , when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 83d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 15.86
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 71.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 159.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 25.0
5. Polarizability: 6.28
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 23.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 38.5
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Form addition compounds with various metal salts such as titanium tetrachloride, tin tetrachloride, platinum dichloride (in the presence of amines), etc. It produces propionic acid during hydrolysis and propylamine during reduction. It is a selective solvent for separating hydrocarbons and refining petroleum fractions.
2. This product is toxic, much more toxic than hydrogen cyanide and acrylonitrile. Propylonitrile, like other fatty nitriles, has an anesthetic effect on the central nervous system because it can decompose into hydrogen cyanide in the body, thereby stopping the respiration and oxidation of tissue cells and causing death. The oral LD50 for rats is 39mg/kg. The LD50 for rabbits injected subcutaneously is 210mg/kg. Production equipment should be sealed and operators should wear protective equipment.
3. It is a highly toxic substance that rapidly releases cyano groups in the body. Its toxic effects are similar to those of hydrocyanic acid, but the symptoms develop slowly. All rats died within two minutes of inhaling its saturated vapor. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 13.5 mg/m3 (USA).
4. Stability[23] Stable
5. Incompatible substances[24] Strong acid, strong alkali, strong oxidizing agent, strong reducing agent
6. Polymerization hazard[25] No polymerization
Storage method
1. Storage precautions [26] Store in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement the “two people to send and receive, and two people to keep” system. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C and the container should be kept sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. This product is available in barrels, 150kg each, and in cans, 14kg each. This product is a first-class flammable liquid and should be stored and transported in accordance with Danger Regulation No. 61137.
Synthesis method
1. Produced by direct catalytic hydrogenation of acrylonitrile. Propylonitrile is produced by hydrogenating acrylonitrile in the gas phase or liquid phase in the presence of catalysts copper phosphate, rhodium, and Raney nickel.
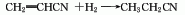
2. Acrylonitrile is added electrolytically When adiponitrile is prepared by hydrogen dimerization, propionitrile is produced as a by-product while dicyanethyl ether is produced.
3. Obtained from the ammoniation of propionic acid. Pour ammonia gas into an iron pipe filled with silica gel, heat it with an electric heating wire, maintain ammonia activation at 400°C for 8 hours, adjust the ammonia gas flow rate and slowly Drop propionic acid into the reaction pipe through a 320-380°C preheater, and control the temperature at 380-400°C. The resulting crude propionitrile condensation bottle is divided into two layers, and the upper layer is a 12% aqueous propionitrile solution. Separate the water layer, add a little solid potassium permanganate to propionitrile, shake well, and leave it for about 4 hours. When the color does not fade, pour the supernatant liquid into another container, add potassium carbonate to dry, and leave it for 8 hours with stirring. Carry out fractional distillation (magnetic ring in the fractionation column), collect the fractions at 95.8-97.5°C to obtain the finished product, with a yield of 59.8%. In addition, propionitrile can also be produced by the reaction between propionamide and phosphorus pentoxide. Refining method: Treat with a small amount of concentrated hydrochloric acid to remove isonitrile, then wash with saturated potassium carbonate solution and calcium chloride solution, dry over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and distill.
Purpose
1. Used as a selective solvent for separating hydrocarbons and refining petroleum fractions. Used as raw materials for organic synthesis; solvents and resin additives. A small amount of it is used as a pharmaceutical raw material, mainly for the synthesis of antispasmodic drugs 2,4,6-trihydroxypropiophenone; sulfisoxazole and other drugs. Also used as standard material for chromatographic analysis. Propylamine can be obtained by catalytic hydrogenation. Also used as an intermediate for pesticides and herbicides.
2. Used as solvent, intermediate and insulating liquid. [27]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

