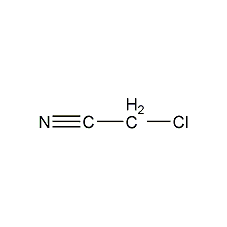
Structural formula
| Business number | 02US |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H2ClN |
| Molecular weight | 75.50 |
| label |
Methyl cyanide chloride, Chloroacetonitrile, polyacetonitrile, Chloroacetonitrile, Chloromethyl cyanide, Chloroacetonitrile, Monochloroacetonitrile, Chlorocyanomethane, 2-Chloroacetonitrile, α-Chloroacetonitrile, CH2ClCN, Chlorocyanomethane, Dichloroethanenitrile, analytical reagents, fumigant, Multifunctional solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-14-2
MDL number:MFCD00001885
EINECS number:203-467-0
RTECS number:AL8225000
BRN number:506028
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless to light yellow liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): <25[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 124~126[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.193[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.0[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.064 (20℃)[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.45[7]
8. Flash point (℃): 47.8[8]
9. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.0[9]
10. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in hydrocarbons , alcohols. [10]
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation
Open irritation test: rabbit, skin contact: 14mg/24H, severity of reaction: mild.
Standard Draize test: rabbit, skin contact: 500mg/24H, severity of reaction: mild.
Standard Draize test: rabbit, skin contact: 20mg/24H, severity of reaction: moderate.
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 220mg/kg; rat inhalation LCLo: 250ppm/4H; mouse oral LD50: 139mg/kg; mouse abdominal LD50: 100mg/ kg; Rabbit skin contact LD50: 71μL/kg;
3. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity: Mouse skin TDLo: 4800mg/kg/2W-I;
4. Mutagenicity: Microbial Salmonella typhimurium mutation: 20 mg/L; DNA damage to human lymphocytes: 15 μmol/L; Non-mammalian multiplex micronucleus test: 1250 μg/L; Rat oral DNA synthesis: 115 mg/L kg; sister chromatid exchange in hamster ovary: 79100 μmol/L;
5. It has strong stimulating and tear-inducing effects. Toxic by inhalation, oral administration or in contact with skin.
6. Acute toxicity��[11] LD50: 220mg/kg (rat oral); 71mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
7. Irritation[12]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
Rabbit eye: 20mg (24h), moderate irritation.
8. Subacute and chronic toxicity[13] Rat inhalation, 60.2mg/m3 , 6 hours each time, 20 times in total, no signs of poisoning were seen, and autopsy showed mild renal congestion.
9. Mutagenicity[14] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 30mg/L. DNA damage: human lymphocytes 15 μmol/L. Unprogrammed DNA synthesis: Rat oral administration: 115 mg/kg. Sister chromatid exchange: hamster ovary 79100nmol/L. DNA damage: human HeLa cells 10μmol/L (30min)
10. Carcinogenicity[15] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, there is insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[16] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 238d (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects[17] This substance is harmful to the environment. Pollution of water bodies should be particularly pursued.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 16.07
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 66.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 158.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.5
5. Polarizability: 6.37
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 23.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 41.2
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[18] Stable
2. Incompatible substances [19] Strong oxidants, strong reducing agents, strong acids, strong bases
3. Conditions to avoid contact[20] Heating
4. Polymerization hazard[21] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[22] Hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
It is obtained by reacting chloroacetic acid with ethanol to generate ethyl chloroacetate, which is then reacted with ammonia water to generate chloroacetamide, and finally dehydrated: Add chloroacetic acid to ethanol, add concentrated sulfuric acid under stirring, heat to reflux, stop stirring, and react 8-10h, filter and wash with water, separate the water layer, and obtain ethyl chloroacetate. Add it to 0-2°C ammonia water, the temperature should not exceed 15°C, stir for 10-15 minutes after the addition, cool, let stand, filter, and dry to obtain chloroacetamide. Then, add phosphorus pentoxide to chloroacetamide, heat and dehydrate, steam out chloroacetonitrile while heating, and finally distill under reduced pressure to steam out all chloroacetonitrile. The obtained crude product is dried with phosphorus pentoxide and magnesium oxide, and fractionated under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
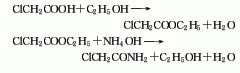
![]()
Purpose
1. Used as analytical reagents, fumigants, and solvents.
2. Used as pesticides and organic synthesis intermediates. [24]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

