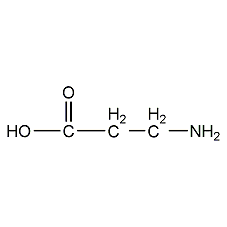
Structural formula
| Business number | 02W3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H7NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 89.09 |
| label |
3-aminopropionic acid, Beta-aminopropionic acid, β-Serine, β-Cross amino acid, 3-Aminopropionic acid, Abufene, β-Aminopropionic acid, β-Alaine, Intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-95-9
MDL number:MFCD00008200
EINECS number:203-536-5
RTECS number:UA2369200
BRN number:906793
PubChem number:24891409
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless crystals.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.437
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 200
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index (D20): Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): 204-206
9. Specific rotation (ºC): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 20ºC ): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined Determined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in ether and acetone. Slightly sweet.
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 21.04
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 76.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 202.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 49.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.34
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Tautomerism.�Number: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 63.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 52.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. No Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants.
2. This product is non-toxic, but contact with eyes and skin should be avoided.
3. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
It can be packed in plastic bags, 30kg per bag, or in fiberboard drums, 50kg per drum.
Synthesis method
1.. Acrylonitrile reacts with ammonia in a solution of diphenylamine and tert-butyl alcohol to form β-aminopropionitrile, which can be obtained by alkaline hydrolysis. Add acrylonitrile, diphenylamine, and tert-butanol in sequence to the dry autoclave, stir for 5 minutes, add liquid ammonia, control the temperature to 100-109°C, the pressure to about 1MPa, and keep stirring for 4 hours. Cool to below 10°C and stop stirring when the pressure drops to normal pressure. At 65-70℃/(8.0-14.7kPa), recover tert-butanol under reduced pressure to obtain crude β-aminopropionitrile. The crude product is then distilled under reduced pressure and collect the 66-105℃/(1.33-4.0kPa) fraction to obtain β -Aminopropionitrile. The alkaline hydrolysis operation is carried out in the reaction tank. First, add liquid alkali, control the temperature to 90-95°C, slowly add β-aminopropionitrile dropwise with stirring, complete the addition, and keep warm for 1 hour. Evaporate under reduced pressure for half an hour to drive out the ammonia in the reaction solution, add an appropriate amount of water, and add hydrochloric acid dropwise to pH 7-7.2. Filter to remove small amounts of insoluble impurities. The filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure until a large amount of solid is precipitated, and the material is discharged while hot, cooled to below 10°C, filtered, and dried under vacuum to obtain β-alanine. This method consumes 982kg of β-aminopropionitrile per ton of product, and the yield in the alkaline hydrolysis stage is 90%.
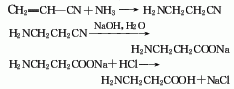
2. From succinimide Obtained from degradation (Hawley reaction). Put alkaline sodium hypochlorite solution (containing 14% sodium hypochlorite, 8% sodium hydroxide, 30% sodium carbonate) and ice into the reaction tank, add succinimide under stirring, and react at 18-25°C 0.5h. Raise the temperature to 40-50°C and react for 1 hour. Add hydrochloric acid to adjust pH to 4-5, and concentrate under reduced pressure. After the concentrated liquid is cooled, add 3 times the amount of 95% ethanol to precipitate the inorganic salt, filter, and repeat once more. Then dilute the filtrate with 4 times the amount of distilled water and reflux for 1 hour. Add activated carbon for decolorization, filter, and exchange the filtrate through exchange resin. The exchange liquid obtained is decolorized by adding activated carbon, filtered, and the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure, crystallized by cooling, filtered, and recrystallized once with distilled water, β-aminopropionic acid.

3.β-Aminopropionitrile It is obtained by hydrolysis and acid precipitation of β-aminopropionitrile.
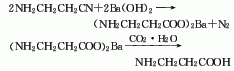
4. Can be made of sericin, gelatin It is obtained by hydrolyzing and refining proteins such as corn and corn. It can also be synthesized by chemical methods.
5. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer and reflux condenser, add 1000g of 30% sodium hydroxide solution and stir. Heat to 90~95°C, slowly add 500g (7.14mol) of β-aminopropionitrile (2), and continue the heat preservation reaction for 2 hours after the addition. The generated ammonia is extracted under reduced pressure. Add an appropriate amount of water, adjust the pH to 7~7.2 with hydrochloric acid, and filter out the insoluble matter. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure until solid precipitated and cooled to below 10°C, filtered with suction, and dried under vacuum to obtain β-aminopropionic acid (1) with a yield of 90%. [1]
Purpose
1. Used as electroplating corrosion inhibitor and biochemical reagent.
2. Calcium pantothenate, an intermediate used in the preparation of chloramphenicol cold sour plum.
3. Can be used for research in microbiology and biochemistry.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

