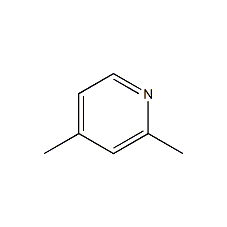
Structural formula
| Business number | 02X9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H9N |
| Molecular weight | 107.15 |
| label |
2,4-Dimethylazepine, 2,4-lutidine, 2,4-dimethylpyridine, 2,4-Dimethylpyridine, 2,4-Dimethyl-Pyridine, 2,4-Lutidene, Alpha,Gamma-Dimethylpyridine, 2,4-Dimethylpyridine, rubber catalyst, analytical reagents, Nitrogen-containing compound solvents, Heterocyclic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:108-47-4
MDL number:MFCD00006337
EINECS number:203-586-8
RTECS number:OK9400000
BRN number:1506
PubChem number:24896348
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or light yellow oily liquid with peppery smell and hygroscopicity. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -60.0[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 157~158[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.93[4]
5. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 4740 (76.3℃)[5]
6. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.90[6]
7. Flash point (℃): 37.22[7]
8. Solubility: soluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents. [8]
9. Refractive index: 1.5012
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.887
11 . Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 38.9
12. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, liquid): 16.07
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, liquid) : 4059.5
14. Vapor pressure (kPa, 76.3ºC): 4740
15. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 25ºC): 0.000945
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 200mg/kg;
2. Mutagenicity: loss and non-separation of yeast sex chromosomes: 5000ppm;
3. Acute toxicity[9] LD50: 200mg/kg (rat oral)
4. Irritation No information yet
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 33.99
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 115.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 276.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 33.2
5. Polarizability: 13.47
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 1.6
2. Hydrogen bond donorNumber: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 12.9
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 70.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain atomic stereocenter Number of stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Total Number of price key units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Its chemical properties are alkaline and can form salts with inorganic acids and organic acids. Form addition compounds with inorganic salts, alkyl halides, etc. 2,4-dimethylpiperidine is generated during electrolytic reduction. Isonicotinic acid is produced during oxidation.
2. Health hazards: Invasion route: inhalation, ingestion, percutaneous absorption. Health Hazards: Harmful to the body if inhaled, taken orally or absorbed through the skin. Strongly irritating to eyes. Exposure can cause coughing, chest pain, difficulty breathing, and gastrointestinal disorders. Toxicological information and environmental behavior Toxicity: Moderately toxic. Acute toxicity: LD50400~800mg/kg (rat oral administration). Hazardous characteristics: Flammable, there is a risk of combustion and explosion when exposed to high heat, open flame or contact with oxidants. It decomposes when heated and releases toxic nitrogen oxide fumes. Combustion (decomposition) products: carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides. Protective measures Respiratory protection: A filtering gas mask (half mask) should be worn when there is a possibility of contact with its vapors. During emergency rescue or evacuation, it is recommended to wear an isolation respirator. Eye protection: Wear chemical safety glasses. Body protection: Wear tape protective clothing. Hand protection: Wear rubber gloves. Others: Smoking is strictly prohibited at the work site. After work, take a shower and change clothes. Conduct pre-employment and regular physical examinations. Maintain good hygiene habits. First aid measures Skin contact: Take off contaminated clothing and wash skin thoroughly with soap and water. Eye contact: Lift eyelids and rinse thoroughly with plenty of running water or saline for at least 15 minutes. Seek medical attention. Inhalation: Move quickly to fresh air. Keep your airway open. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. If breathing stops, perform artificial respiration immediately. Seek medical attention. Ingestion: Drink plenty of warm water, induce vomiting, and seek medical attention.
3. Stability[10] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[11] Strong oxidants, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides
5. Conditions to avoid contact[12] Heating
6. Hazards of aggregation[13] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[14] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Mainly recovered from coal coking by-products. Pyridine and its homologues are widely distributed in crude coking chemicals. Approximately 23% of lutidine is present in coke oven gas, 22% is present in crude benzene, and 55% is present in tar.
Refining method: Heat and dissolve the lutidine fraction in coal tar with o-cresol and then cool it to collect the precipitated crystals. After washing with a solution composed of o-cresol, 2,4-dimethylpyridine and water, decompose it with sodium hydroxide, steam distillation, add sodium hydroxide solution to the distillate, separate the oil layer, and use solid sodium hydroxide After drying and distillation, 2,4-dimethylpyridine with a purity of 99% can be obtained.
Purpose
1. Used as medicine; pesticide intermediate, rubber catalyst, analytical reagent. Used as solvent and raw material for organic synthesis.
2. Used in organic synthesis, drug synthesis and as solvent. [15]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

