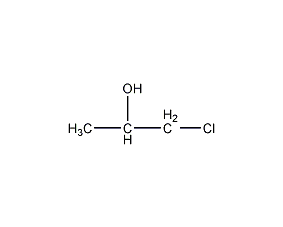
Structural formula
| Business number | 03KJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H7ClO |
| Molecular weight | 94.54 |
| label |
Chloropropanol, Propylene chlorohydrine, β-Chloroisopropyl alcohol, CH2ClCH(OH)CH3, Hydroxypropylation reagent, aliphatic compounds, Multifunctional solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:127-00-4
MDL number:MFCD00004530
EINECS number:204-819-6
RTECS number:UA8942000
BRN number:773653
PubChem number:24857557
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless transparent liquid with a slight ether smell.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 126.5750
3. Relative density (g/mL, 20/20ºC): 1.1128
p>
4. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.4392
5. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 4.67
6. Flash point (ºC, opening): 51.7
7. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): 0.65
8. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 55ºC): 0.00097
9. Solubility: Miscible with water, also soluble in alcohol.
10. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.1123
11. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.1075
12. Normal temperature Refractive index (n25): 1.4366
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity data: Rat inhalation LC50: 1000 ppm/4H
2. Mutagenicity data: Bacteria – Salmonella typhimurium: 1100 ug/plate
Fruit fly specific trajectory test: 1 ppb
3. It is of low toxicity. Strongly irritating to eyes. The oral LD50 in mice is 220mg/kg. Poisoning can occur through inhalation, ingestion or skin absorption.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 22.29
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 87.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 204.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 29.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.83
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4.���Number of rotational chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Heavy atoms Number: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 22.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Can burn and decompose to produce toxic gases when heated.
Chemical properties: It has the properties of alcohol and chlorinated alkyl. When heated to 140~160℃ in a sealed tube, 1,2-dichloropropane and acetone are generated. When its aqueous solution is heated, acetone and propionaldehyde are generated. When heated in an alkali aqueous solution, hydrogen chloride is easily removed to produce propylene oxide. Chloroacetone and acetic acid are produced when 1-chloro-2-propanol is oxidized.
2.Poisonous. Inhalation of high concentrations may damage internal organs and nervous system, and may be fatal in severe cases. Rat LC0.08g/m3. The maximum allowable concentration in the air in the workplace is 16 mg/m3. When handling and using, neoprene gloves, protective clothing and a mask should be worn to prevent inhalation or skin absorption.
Storage method
Reacts with a variety of metals and should be stored in glass or ceramic lined carbon steel containers to prevent contamination and discoloration. It is flammable and can decompose into highly toxic phosgene, so it should not be in contact with open flames. Store and transport according to regulations for flammable and toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
(1) It is obtained by hypochlorous acidification of propylene. Propylene, chlorine and water are passed into the hypochlorous acidification reaction tower in a certain proportion. Generally, when the propylene is excessive so that there is no free chlorine in the reaction liquid and tail gas, and the chlorohydrin concentration in the tower reaction liquid is less than 5%, the chloropropylene reacts. Alcohol selectivity can reach 90%. After washing with water and alkali, part of the tail gas is vented to prevent the accumulation of inert gases, and the rest is compressed and mixed with fresh propylene and returned to the reaction system. When reacting at a reaction tower temperature of 45-60°C, about 0.12-0.13MPa and an excess of propylene, the propylene conversion rate is 97%. Among them, 93.5% is chloropropanol, 4.5% is dichloropropane, 1.7% is 2.2′-dichlorodiisopropyl ether, and 0.3% is propionaldehyde, acetone and other by-products. Among the obtained chloropropanol, 1-chloro-2-propanol accounts for about 90%, and 2-chloropropanol accounts for about 10%.
![]()
(2) By chloropropene and Derived from the action of sulfuric acid. At low temperature, add sulfuric acid dropwise to propylene chloride and stir the reaction. The reaction solution was slowly added to ice water, and then the finished product was obtained through distillation, with a yield of 86.5%. In addition, 1-chloro-2-propanol can also be obtained by reacting propylene oxide with hydrogen chloride.
![]()
Refining method: 1-Chloro- 2-Propanol is produced by the acid-catalyzed addition of allyl chloride to water. Industrially produced by the reaction of propylene, chlorine and water. The product contains 75% 1-chloro-2-propanol and 25% 2-chloro-1-propanol, which can be separated by distillation under reduced pressure (about 6.67kPa).
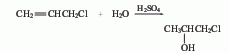
Purpose
Organic synthesis intermediates. Mainly used in the manufacture of propylene oxide and propylene glycol. Widely used in the production of polyurethane and other unsaturated polyester resins. Used in medicine to synthesize chlorpromazine. Mainly used in organic synthesis as raw material for propylene oxide and hydroxypropylation reagent.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

