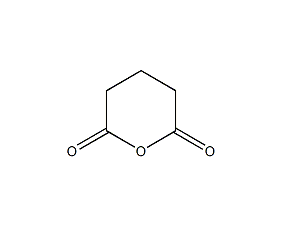
Structural formula
| Business number | 02XF |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H6O3 |
| Molecular weight | 114.10 |
| label |
Gel anhydride, glutaric anhydride, Subic acid anhydride, glutaric anhydride, Glutaric anhydride, Plastic anhydride, GTA, Hardener, Polymerization initiator |
Numbering system
CAS number:108-55-4
MDL number:MFCD00006679
EINECS number:203-593-6
RTECS number:MA3850000
BRN number:110051
PubChem number:24895139
Physical property data
1. Character: needle-like crystal
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.429
3. Melting point (ºC): 56
4. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 15010
5. Boiling point (ºC ,1.33kpa): 287
6. Solubility: soluble in ether, ethanol and tetrahydrofuran
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 540mg/kg; rabbit skin contact LD50: 1780mg/kg
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 24.92
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 90.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 231.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 42.6
5. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
6. Polarizability: 9.88
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 43.4
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 114
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with oxides and water. Needle crystals. Soluble in ether, ethanol and tetrahydrofuran. After absorbing water, glutaric acid is produced. Very low toxicity.
See glutaric acid.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire, heat and water sources. The packaging requires sealing and should be stored separately from oxidants. Mixed storage is strictly prohibited. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. This product can be packed in polypropylene woven bags lined with polyethylene plastic bags. 25kg per bag. Store and transport according to general chemical regulations.
Synthesis method
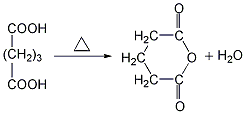
1. Dehydrate glutaric acid by heating it with a dehydrating agent such as hepatitis B. ① Preparation from γ-butyrolactone Add γ-butyrolactone and potassium cyanide to the reaction kettle, heat to 190-195°C with stirring, and react for 2 hours to generate potassium cyanobutyrate. 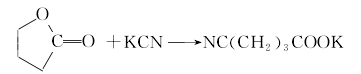 After cooling, add concentrated hydrochloric acid for acidification to generate glutaric acid monoamide.
After cooling, add concentrated hydrochloric acid for acidification to generate glutaric acid monoamide.  Heat again for hydrolysis to generate glutaric acid, with a yield of 71%-75%.
Heat again for hydrolysis to generate glutaric acid, with a yield of 71%-75%. ![]() Finally, the glutaric acid is heated to above 300℃ for dehydration to obtain the finished product.
Finally, the glutaric acid is heated to above 300℃ for dehydration to obtain the finished product. 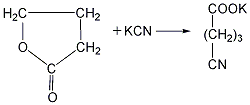 ②Prepared from dihydropyran Mix dihydropyran and 0.2mol nitric acid on a boiling water bath Heat to dissolve and then cool in an ice-water bath, then add concentrated nitric acid, hydrolyze dihydropyran to generate hydroxyvaleraldehyde and release nitrogen dioxide. Reduce the temperature to 0°C and add sodium nitrate, stir vigorously for 3 hours, and allow the temperature to naturally rise to 25-30°C. The reaction product is evaporated under reduced pressure and cooled to obtain glutaric acid. The yield is 70%-75%. Finally, the glutaric acid is heated to above 300°C for dehydration, and the finished product is obtained after cooling.
②Prepared from dihydropyran Mix dihydropyran and 0.2mol nitric acid on a boiling water bath Heat to dissolve and then cool in an ice-water bath, then add concentrated nitric acid, hydrolyze dihydropyran to generate hydroxyvaleraldehyde and release nitrogen dioxide. Reduce the temperature to 0°C and add sodium nitrate, stir vigorously for 3 hours, and allow the temperature to naturally rise to 25-30°C. The reaction product is evaporated under reduced pressure and cooled to obtain glutaric acid. The yield is 70%-75%. Finally, the glutaric acid is heated to above 300°C for dehydration, and the finished product is obtained after cooling. 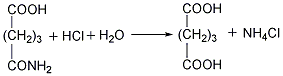 ③Prepared from glutaronitrile Heat glutaronitrile and hydrochloric acid to reflux for 4 hours, then evaporate to remove water. Glutaric acid and ammonium chloride are produced. Continue to add hot ether to extract glutaric acid, ammonium chloride precipitates as a solid, and the extract is heated to evaporate the ether to obtain glutaric acid. The finished product is obtained after heating glutaric acid to 300°C and dehydrating it.
③Prepared from glutaronitrile Heat glutaronitrile and hydrochloric acid to reflux for 4 hours, then evaporate to remove water. Glutaric acid and ammonium chloride are produced. Continue to add hot ether to extract glutaric acid, ammonium chloride precipitates as a solid, and the extract is heated to evaporate the ether to obtain glutaric acid. The finished product is obtained after heating glutaric acid to 300°C and dehydrating it. 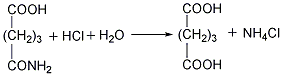 ④Recover glutaric acid from the by-product of oxalic acid production, and then dehydrate to produce glutaric acid .
④Recover glutaric acid from the by-product of oxalic acid production, and then dehydrate to produce glutaric acid . 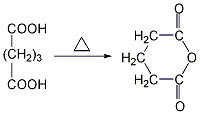
2. Heat and mix dicarboxylic acids (succinic acid, glutaric acid, hexane Diacid), directly dehydrate and anhydride succinic acid and glutaric acid, and take the fraction at a certain temperature to obtain glutaric anhydride.
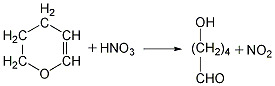
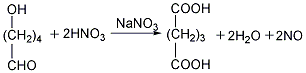
Purpose
Used in the production of plastics, rubber, resins, medicines, etc. and in the preparation of amides. Peroxyglutaric acid can be obtained by oxidizing valeric anhydride with hydrogen peroxide. Stir and mix 420ml of distilled water and 221.7g of 30% hydrogen peroxide, then add 342g of glutaric anhydride, stir vigorously, maintain the reaction at 15°C, add 7.6g of hydrogen peroxide and continue to keep it warm for 1 hour, let it stand for 24h, and filter out the crystals. After washing with water and drying with an infrared lamp, a white powdery peroxide is obtained into diacid with a melting point of 89-90°C (it starts to decompose at 90°C). Used as a curing agent for epoxy resins. It is also a polymerization initiator for the polymerization production of some synthetic resins and synthetic rubbers.
Mainly used as curing agent for epoxy resin. It is also a polymerization initiator for the polymerization production of some synthetic resins and synthetic rubbers.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

