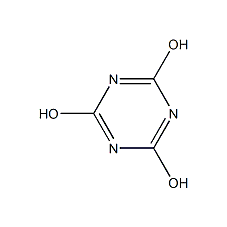
Structural formula
| Business number | 02XY |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H3N3O3 |
| Molecular weight | 129.07 |
| label |
cyanuric acid, cyanuric acid, 1,3,5-Triazine-2,4,6-(1H,3H,5H)trione, 2,4,6-Tris(2′-hydroxy-4′-n-butoxyphenyl)-1,3,5-triazine, S-triazine-2,4,6-triol, Symmetric trihydroxytriazabenzene, Triazine-5, isocyanuric acid, Tricarbamide, Tricyanic acid, Trihydroxy-1,3,5-triazine, Trihydroxycyanidine, ,4,6-Trihydroxy-S-triazine, ,4,6-Trioxohexahydro-1,3,5-triazine, [1,3,5]Triazinane-2,4,6-trione, Heterocyclic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:108-80-5
MDL number:MFCD00082990
EINECS number:211-620-8
RTECS number:XZ1800000
BRN number:126982
PubChem number:24851182
Physical property data
1. Properties: odorless white crystals
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.768
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1 ): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): >360
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point ( ºC, mm Hg): Not determined
7. Refractive index (D20): Not determined
8. Flash Point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (ºC): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturation vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol ): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (polymer) Log value of the partition coefficient (alcohol/water): Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V ): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid and hot inorganic acid.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 7700 mg/kg
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.17
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 64.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 234.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 176.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.37
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -1.2
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 5
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 87.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 136
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with strong oxidizing agents.
In animal experiments, it was proved that the acute toxicity was not obvious. Rats were given 30mg/kg by gavage, six times a week for 6 consecutive months to reduce the body weight. Growth is slowing. However, local injections can cause sarcomas. It is irritating to human skin and mucous membranes and decomposes to produce hydrocyanic acid above 330°C. Local overheating should be avoided during the production process. Operators should wear protective equipment.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Packed in plastic drums or iron drums lined with plastic bags to prevent heat, sun and moisture. Store and transport according to regulations on highly toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the polymerization of urea. Mix urea and ammonium chloride, heat to melt, stir and heat to 210°C, the solution will thicken, heat to above 230°C and the melt will gradually solidify, stir-fry evenly, continue to heat to 250°C, and keep warm for 15 minutes. Cool to 100°C, add a small amount of water to soak, bring it down to room temperature, soak in water and then crush it to filter out the solid matter. Add water and hydrochloric acid to the solid matter, stir and heat to 110°C, keep warm for 3 hours, add hydrochloric acid and water in batches, cool to 30°C, wash with water until neutral, filter, wash the filter cake with water, and dry to obtain the finished product. The purity of industrial products is ≥95%, and each ton of product consumes 1,200kg of urea.
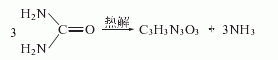
2.Urea high-temperature pyrolysis method uses urea as raw material, and produces crude cyanuric acid through high-temperature pyrolysis, which is then acidified with sulfuric acid, filtered, washed, and dried to obtain finished cyanuric acid. The reaction formula is as follows:
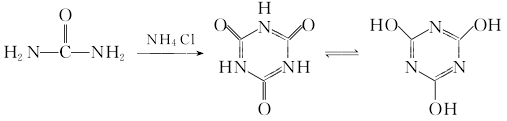
In the pyrolysis process, urea and ammonium chloride are put into iron-free containers in a ratio of 1:0.04, placed on the trolley one by one, and a hydraulic press is used to lift the trolley full of materials. The car roof enters the tunnel kiln with a temperature gradient (the car enters the kiln at intervals of 15 to 20 minutes). After four different zones of preheating, heating, constant temperature, and cooling, urea is melted, deaminated, and polymerized to generate 65% to 85% of urea. Crude cyanuric acid. The control temperatures of the four different temperature zones are 260°C at 1 point, 290°C at 2 points, 270°C at 3 points, and 150°C at 4 points. The time for the materials to be in the kiln is 6 to 7 hours.
In the refining process, the crushed crude cyanuric acid is added to a reaction kettle containing 23% to 25% sulfuric acid solution. (Jacketed enamel reactor), use steam to heat to 170°C for boiling reaction, so that the by-products cyanuric acid monoamide and cyanuric acid diamide are converted into cyanuric acid again. After 7 to 8 hours of reaction, flow cooling water into the jacket to cool the material to below 90°C, then put it into a washing tank, wash it with water until pH>4, and filter it to obtain a wet product with a moisture content of <25%. Cyanic acid.
Drying process: Use box dryer for drying. The initial moisture content of the material is <25%, and the final moisture content after drying is ≤0.5%.
Purpose
Mainly used for the preparation of new bleaching agents, disinfectants, water treatment agents, resins, coatings and metal cyanide corrosion inhibitors.
Used in the manufacture of cyanuric acid-formaldehyde resin, epoxy resin, melamine resin, etc. As a raw material for organic synthesis, it is used to prepare chlorinated derivatives such as cyanic acid, trichloroisocyanuric acid, sodium (or potassium) dichloroisocyanurate, etc.; it is also used to make pesticides, insecticides, herbicides, adhesives, and polymers. Ester and foam plastic flame retardants, paints and coatings, oil-resistant insulation plasticizers, high-temperature fiberglass, laminated plastics and rubber heat stabilizers, etc. In addition, it can also be used as fabric and paper bleach, agricultural sterilant, hospital and swimming pool water disinfectant, etc.
It is used to synthesize chlorinated derivatives and can also be used as a stabilizer for swimming pool chlorine treatment agents. Flame retardant for nylon, polyester and polyurethane foam, heat stabilizer for butadiene rubber, etc.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

