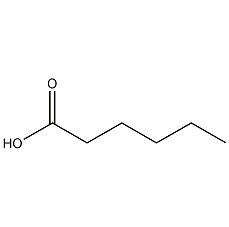
Structural formula
| Business number | 03V6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H12O2 |
| Molecular weight | 116.16 |
| label |
Just sour, Caprylic acid, hypocaprylic acid, Butylacetic acid, butyl acetic acid, Pentane-1-carboxylic acid, n-Hexanoic acid, caproic acid, Butylacetic acid, Hexylic acid, Pentiformic acid, acid solvents, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:142-62-1
MDL number:MFCD00004421
EINECS number:205-550-7
RTECS number:MO5250000
BRN number:773837
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or light yellow oily liquid with unpleasant coconut oil smell and spicy taste.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 202~203
3. Melting point (ºC): -3
4. Relative density (g/ mL, 20/4ºC): 0.9212
5. Relative density (g/mL, 25/4ºC): 0.9230
6. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1 ): 4.0
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4168
8. Viscosity (mPa·s,15ºC): 3.525
9. Viscosity (mPa ·s,30ºC): 2.511
10. Flash point (ºC): 102
11. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 94ºC): 64.69
12. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 190ºC): 54.85
13. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 15.07
14. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid ): 3490.11
15. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 0~23ºC, constant pressure): 2.14
16. Vapor pressure (kPa, 61.7ºC): 0.13
17. Dissociation constant (25ºC, water): 1.32×10-5
18. Solubility: Insoluble in water. Miscible with organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, acetone, chloroform, and benzene.
19. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4148
20. Critical temperature (ºC): 381.85
21. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.38
22. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.281
23. Critical volume (cm 3·mol-1): 313
24. Critical compression factor: 0.256
25. �Alcohol can be washed, dried and distilled. Caproic acid occurs naturally in coconut oil, strawberries, goat’s milk, geranium leaves, camphor, etc., and can be obtained from coconut oil.
Purification method: Under a pressure of 6.67KPa, use a packed tower with 30 theoretical plates for rectification. It can also be refined by fractional crystallization.
8.Carry out alkaline hydrolysis of diethyl n-butylmalonate, and then decarboxylate it in acidic medium to obtain hexanoic acid. The obtained hexanoic acid is extracted with diethyl ether, the diethyl ether is evaporated, then benzene is added to azeotropically evaporate water and benzene, and finally the hexanoic acid is evaporated.
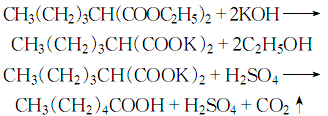
9. Tobacco : OR, 49; BU, 56; OR, 26; FC, 9, 18; OR, 18; BU, 9, 18; FC, BU, OR, 40; Obtained from the fractionation of coconut oil volatile fatty acids.
10. Preparation method:
Add 50g of 2-octanol (2) and 150g of 70% nitric acid into the reaction bottle, stir and heat to start the reaction, and the reaction will be violently exothermic. , and generate nitric oxide. While maintaining the reaction temperature at 90-100°C, add another 210g of 2-octanol and 70% nitric acid in batches alternately. After the addition, continue the reaction at 90-100°C for 2 hours. After cooling, separate the oil layer and wash with water. Use 10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to make it strongly alkaline and separate out the nitrite. Adjust the water layer to acidity with sulfuric acid, dry and fractionate under reduced pressure over anhydrous sodium sulfate, collect the fractions at 198-208°C, re-fractionate, and collect the fractions at 202-206°C to obtain about 115g of n-hexanoic acid (1), with a yield of 50%. [1]
11.. Preparation method:
Diethyl n-butyl malonate (4): In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser (installed with a calcium chloride drying tube), and dropping funnel, add 2500 mL of absolute ethanol, add 115 g (5 mol) of metallic sodium in batches, and stir at about 60°C. Reaction, after all the sodium has reacted, add 825g (5mol) of diethyl malonate (2) dropwise. After the addition is completed, stir the reaction for 30 minutes. Add 685g (5mol) of n-bromobutane (3) dropwise. The reaction heat is about The addition was completed in 3 hours, and then the reflux reaction was continued for 2 hours. Change to a distillation device and evaporate the ethanol under reduced pressure. After cooling, add 2L of crushed, stir thoroughly to dissolve the generated sodium bromide, separate the water layer, and distill the oil layer under reduced pressure. Collect the fractions at 140~145℃/5.33kPa to obtain diethyl n-butylmalonate (4) d4 250.983, nD251.4250. Easily soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone, ethyl acetate, insoluble in water. Caproic acid (1): In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, reflux condenser, and dropping funnel, add 200 g of potassium hydroxide and 200 mL of water. Slowly add 200g (0.925mol) of diethyl n-butylmalonate (4) while stirring, and the reaction proceeds vigorously and refluxes. When all the ester was added, the reaction was refluxed for 3 hours. After cooling, the upper organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with diethyl ether. Combine the organic layers and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate. After evaporating the ether, continue distillation and collect the fractions at 200-206°C to obtain 80g of hexanoic acid (1) with a yield of 75%. [2]
Purpose
1. Caproic acid is a food flavoring allowed by my country’s regulations and is mainly used in cheese, cream and fruit flavors. The dosage is based on normal production needs, generally 450 mg/kg in seasonings; 28 mg/kg in candies; 22 mg/kg in baked goods; and 4.3 mg/kg in cold drinks. A basic organic raw material that can be used to produce a variety of caproate products. It is used in medicine to prepare hexamethasone. It can also be used as spices, thickeners for lubricating oils, rubber processing aids, varnish drier, etc.
2.Caproic acid is a food spice in my country and is used to prepare various flavors and as a raw material to synthesize other food spices. Mainly used in cheese, cream and fruit flavors. The dosage is based on normal production needs, generally 450 mg/kg in seasonings and 28 mg/kg in candies. kg; 22mg/kg in baked goods; 4.3mg/ in cold drinks kg.
3.Manufacture of spices, synthetic resins and rubber. Also used in the pharmaceutical industry.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

