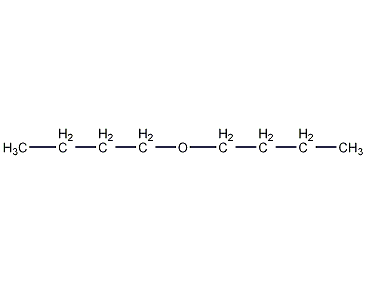
Structural formula
| Business number | 03VN |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H18O |
| Molecular weight | 130.23 |
| label |
n-butyl ether, dibutyl ether, butyl ether, dibutane oxide, n-Butyl ether, Butyl exide, Oxide butane, 1,1-Exybis-,butane, 1-Butoxybutane, Ether solvents, thinner, Extracting agent, refined preparations, electronic grade cleaning agent, Reagents for measuring bismuth |
Numbering system
CAS number:142-96-1
MDL number:MFCD00009461
EINECS number:205-575-3
RTECS number:EK5425000
BRN number:1732752
PubChem number:24856439
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with slight ether smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -95.4[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 142[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.77[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 4.48[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.64 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -5353.7[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 2.46[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 3.08~3.21[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 25[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 194.4[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%) : 7.6[12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.5[13]
14. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in acetone, dichloropropane and gasoline, miscible in ethanol and ether. [14]
15. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.3992
16. Refractive index (n25ºC): 1.3968
17 . Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 0.741
18. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.602
19. Flash point (ºC, opening): 37.8
p>
20. Flash point (ºC, closed): 25
21. Fire point (ºC): 194.4
22. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg): 375.1
23. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 34.45
24. Vapor pressure (kPa, 127.7ºC): 76.06
25. Vapor pressure (kPa, 29.7ºC): 1.93
26. Vapor pressure (kPa, 11.3ºC): 1.00
27. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.00087
28. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.7641
29. Eccentricity factor: 0.467
30. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 15.969
31. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.288×1010
32. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1 ): 91.920
33. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ�Wash twice with saturated CaCl2, dry with anhydrous CaCl2 overnight, and distill under reduced pressure (water pump) to collect the 107-110°C fraction, which is the colorless transparent liquid n-butyl ether.
4. Preparation method:
![]()
In a reaction bottle equipped with a thermometer (the end of the thermometer is immersed below the liquid level, 0.5-1cm from the bottom of the bottle) and a water separator (a condenser is installed on the water separator), add n-butanol (2) 50g (62mL, 0.64mol), 9mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, and a few grains of zeolite. Use an electric heating mantle to heat to reflux. At this time, the temperature of the reaction solution is around 110°C ①, and the generated water is collected in the water vapor. Continue to heat and reflux until no water evaporates. Cool the reaction flask, add 70 mL of water, use a separatory funnel to separate the organic layer and wash it twice with 50% sulfuric acid to remove unreacted butanol. Wash twice more with water and dry with anhydrous calcium chloride. Distill and collect the fractions at 140-144°C to obtain 15g of n-butyl ether with a yield of 32%. Note: ① The appropriate reaction temperature should be 130~140℃, but due to the formation of azeotrope, the temperature is often not reached at the beginning. When the reaction is near the end, the temperature can be raised to 135℃. n-butanol (bp117.5℃), n-butyl ether (bp141℃) and water can form ternary azeotrope and binary azeotrope. A certain amount of water can be added to the water separator during the experiment. The relevant data are as follows (Table I-6-1). [26]
5. Preparation method:
Add 4.45kg (60mol) of n-butanol (2) into a 10L three-neck reaction flask, slowly add 0.8kg of concentrated sulfuric acid, add zeolite, and load Fractionation device. Slowly heat to boiling, control the temperature at the top of the fractionation column to not be higher than 95°C, and carry out fractional dehydration at a distillation rate of 2 to 3 drops/second until dehydration is complete, which takes about 20 hours. A total of about 600~660mL was evaporated. The reaction solution gradually increased from the initial 110°C to 145°C, and the color also became darker. After cooling, add 1L of water. After shaking thoroughly, let the organic layer stand and wash three times with 50% sulfuric acid and two times with 5% ferrous sulfate (to remove peroxide), then wash with water, and dry over anhydrous sodium carbonate. Fractionate under reduced pressure and then under normal pressure to collect fractions at 140-142.5°C to obtain 2.0kg of product (1) with a yield of 50%. [27]
Purpose
1. Used as an electronic grade cleaning agent, and also used as an extraction agent and refining agent for organic acids, waxes, resins, etc.
2. Among ethers, n-butyl ether has strong solubility for many natural and synthetic oils, resins, rubbers, organic acid esters, alkaloids, etc. The solubility of butyl ether in water (20°C) is 0.03% (weight), and the solubility of water in butyl ether (20°C) is 0.19% (weight). It has good separability with water. It generates less peroxide during storage, has low toxicity and danger, and is a very safe solvent. It is used as a solvent for extraction and purification of resins, greases, organic acids, esters, waxes, alkaloids, hormones, etc.; a mixed solution with butyl phosphate can be used as a solvent for the separation of rare earth elements. Since butyl ether is an inert solvent, it can also be used as a solvent for organic synthesis reactions of Grignard reagents, rubber, pesticides, etc.
3. Since butyl ether is an inert solvent, it can also be used as a solvent for organic synthesis reactions of Grignard reagents, rubber, pesticides, etc. and as a diluent for adhesives. It has good separation properties from water, generates less peroxide during storage, has low toxicity and danger, and is a very safe solvent. Used as extraction agent and refining solvent for resins, oils, organic acids, esters, waxes, alkaloids, hormones, etc. The mixed solution with butyl phosphate can be used as a solvent for separating rare earth elements.
4. Used as solvent for organic synthesis. [25]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

